Abstract
Apoptosis is essential for normal development and the maintenance of homeostasis. It plays a necessary role to protect against carcinogenesis by eliminating damaged cells. Many studies have demonstrated that the dysregulation of apoptosis results in cancer and this provides an approach to develop therapeutic agents via inducing apoptosis. In our previous studies 4β-cinnamido linked podophyllotoxin conjugates were synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxic activity in a panel of five human cancer cell lines and the new molecules like 17a and 17f were considered as potential leads. The cytotoxic activity was comparable to etoposide. These observations prompted us to investigate the mechanism underplaying the cytotoxic activity and apoptotic pathway induced by these compounds in human lung cancer cells A459. The results of the present study revealed that these compounds exhibited DNA topoisomerase IIα inhibition and induced mitochondrial mediated apoptosis. It was further confirmed by Mitochondrial membrane potential, Cytochrome c release, cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, regulation of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and pro apoptotic protein Bax studied by Western blot analysis. Annexin V-FITC assay also suggested that these compounds induced cell death by apoptosis. Pretreatment with N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) prevented the generation of ROS. Further, pretreatment with NAC significantly inhibited 17a and 17f induced apoptosis, suggesting that ROS are the key mediators for 17a and 17f induced apoptosis. These data indicate that these compounds might induce apoptosis in A549 cells through a ROS mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway. Moreover, these compounds did not significantly inhibit the noncancerous human embryonic kidney cells, HEK-293. Docking studies also elucidate the potential of these molecules to bind to the DNA topoisomerase II.
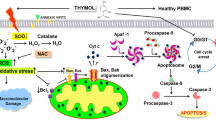
Graphical Abstract
Podophyllotoxin analogs were investigated for their mechanism and apoptotic pathway against lung cancer cell line, A549. These podophyllotoxin analogs inhibited DNA topoisomerase IIα and induced mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in lung cancer cell line, A549. Western blot analysis suggested that these compounds inhibited the DNA topoisomerase IIα. Studies like, Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm), Generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Annexin V-FITC assay suggested that these compounds induced mitochondrial mediated apoptosis. Pretreatment with N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) suggested that ROS plays a role in 17a and 17f induced apoptosis. Further the apoptotic effect of these compounds was confirmed by western blot analysis of pro apoptotic protein Bax and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2, Cytochrome c release and cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Moreover, these compounds did not significantly inhibit the noncancerous human embryonic kidney cells, HEK-293.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woessner RD, Mattern MR, Mirabelli CK, Johnson RK, Drake FH (1991) Proliferation and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ 2:209–214
Isaacs RJ, Davies SL, Sandri MI, Redwood C, Wells NJ, Hickson ID (1998) Physiological regulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1400:121–137. doi:10.1016/S01674781(98)00131-6
Bromberg KD, Burgin AB, Osheroff N (2003) A two-drug model for etoposide action against human topoisomerase IIalpha. J Biol Chem 278:7406–7412. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212056200
Abdel-Aziz Mohamed, Park So-Eun, Gamal El-Din AA, Abuo-Rahma Mohamed A, Sayed Youngjoo Kwon (2013) Novel N-4-piperazinyl-ciprofloxacin-chalcone hybrids: synthesis, physicochemical properties, anticancer and topoisomerase I and II inhibitory activity. Eur J Med Chem 69:427–438. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.08.040
Nitiss JL (2009) Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 9(5):338–350. doi:10.1038/nrc2607
Nitiss JL (2009) Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 9:338–350. doi:10.1038/nrc2607
Wang HK, Morris-Natschke SL, Lee KH (1997) Recent advances in the discovery and development of topoisomerase inhibitors as antitumor agents. Med Res Rev 17:367–425. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1128(199707)
Bailly Christian (2012) Contemporary challenges in the design of topoisomerase II inhibitors for cancer chemotherapy. Chem Rev 112:3611–3640. doi:10.1021/cr200325f
Kamal A, Kumar BA, Arifuddinc M (2003) A one-pot, efficient and facile synthesis of 4β-arylaminopodophyllotoxins: synthesis of NPF and GL-331 as DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors. Tetrahedron Lett 44:8457–8459. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2003.09.110
Kamal A, Laxman N, Ramesh G (2000) Facile and efficient one-pot synthesis of 4beta-arylaminopodophyllotoxins: synthesis of DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors (NPF and W-68). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:2059–2062. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(00)00407-8
Kamal A, Mallareddy A, Suresh P, Nayak VL, Shetti RV, Rao NS, Tamboli JR, Shaik TB, Vishnuvardhan MVPS, Ramakrishna S (2012) Synthesis and anticancer activity of 4β-alkylamidochalcone and 4β cinnamido linked podophyllotoxins as apoptotic inducing agents. Eur J Med Chem 47:530–545. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.11.024
Shafi Gowhar, Munshi Anjana, Hasan Tarique N, Alshatwi Ali A, Jyothy A, Lei David KY (2009) Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by chloroform fraction of seed extracts of Nigella sativa. Cancer Cell Int 9:1–8. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-9-29
Chakravarti Bandana, Maurya Ranjani, Siddiqui Jawed Akhtar, Bid Hemant Kumar, Rajendran SM, Yadav Prem P, Konwar Rituraj (2012) In vitro anti-breast cancer activity of ethanolic extract of Wrightia tomentosa: role of pro-apoptotic effects of oleanolic acid and urosolic acid. J Ethnopharmacol 142:72–79. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.04.015
Ding Guoyu, Liu Feng, Yang Ting, Jiang Yuyang, Hua Fu, Zhao Yufen (2006) A novel kind of nitrogen heterocycle compound induces apoptosis of human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells. Bioorg Med Chem 14:3766–3774. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.01.050
Keerthy HK, Garg M, Mohan CD, Madan V, Kanojia D, Shobith R, Nanjundaswamy S, Mason DJ, Bender A, Basappa, Rangappa KS, Koeffler HP (2014) Synthesis and characterization of novel 2-amino-chromene-nitriles that target Bcl-2 in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. PLoS One 9:e107118. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107118
Hayano Takahide, Garg Manoj, Yin Dong, Sudo Makoto, Kawamata Norihiko, Shi Shuo, Chien Wenwen, Ding Ling-wen, Leong Geraldine, Mori Seiichi, Xie Dong, Tan Patrick, Phillip Koeffler H (2013) SOX7 is down-regulated in lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 32:17. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-32-17
Botta Maurizio, Armaroli Silvia, Castagnolo Daniele, Fontana Gabriele, Pera Paula, Bombardelli Ezio (2007) Synthesis and biological evaluation of new taxoids derived from 2 deacetoxytaxinine. J Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:1579–1583. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.12.101
Wells NJ, Hickson ID (1995) Human topoisomerase II alpha is phosphorylated in a cell Cycle phase-dependent manner by a proline-directed kinase. Eur J Biochem 231:491–497. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.0491e.x
Zhang A, Lyu YL, Lin CP, Zhou N, Azarova AM, Wood LM, Liu LF (2006) A protease pathway for the repair of topoisomerase II-DNA covalent complexes. J Biol Chem 281:35997–36003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604149200
Jiang Xuejun, Wang Xiaodong (2004) Cytochrome c-mediated Apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 73:87–106. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073706
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (1997) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 275:1132–1136. doi:10.1126/science.275.5303.1132
Gonda K, Tsuchiya H, Sakabe T, Akechi Y, Ikeda R, Nishio R, Terabayashi K, Ishii K, Matsumi Y, Ashla AA, Okamoto H, Takubo K, Matsuoka S, Watanabe Y, Hoshikawa Y, Kurimasa A, Shiota G (2008) Synthetic retinoid CD437 induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 370:629–633. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.008
Sánchez Y, Simón GP, Calviño E, de Blas E, Aller P (2010) Curcumin stimulates reactive oxygen species production and potentiates apoptosis induction by the antitumor drugs arsenic trioxide and lonidamine in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335:114–123. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.168344
Liu K, Zhang D, Chojnacki J, Du Y, Fu H, Grant S, Zhang S (2013) Design and biological characterization of hybrid compounds of curcumin and thalidomide for multiple myeloma. Org Biomol Chem 11:4757–4763. doi:10.1039/C3OB40595H
Kamal A, Srikanth YV, Naseer Ahmed Khan M, Ashraf M, Kashi Reddy M, Sultana F, Kaur T, Chashoo G, Suri N, Sehar I, Wani ZA, Saxena A, Sharma PR, Bhushan S, Mondhe DM, Saxena AK (2011) 2-Anilinonicotinyl linked 2-aminobenzothiazoles and [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5b] [1,2,4] benzothiadiazine conjugates as potential mitochondrial apoptotic inducers. Bioorg Med Chem 19:7136–7150. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2011.09.060
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH (1999) Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 68:383–424. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.383
Denault JB, Salvesen GS (2002) Caspases: keys in the ignition of cell death. Chem Rev 102:4489–4500. doi:10.1021/cr010183n
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 7:321–328. doi:10.1023/A:1016119328968
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776. doi:10.1038/35037710
Ravelli RB, Gigant B, Curmi PA, Jourdain I, Lachkar S, Sobel A, Knossow M (2004) Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain. Nature 428:198–202. doi:10.1038/nature02393
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, et al (2009) PM3 Semi-empirical calculations done using Gaussian 09. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford. http://www.gaussian.com/
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791. doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Ferreira Carlos G, Epping Mirjam, Kruyt Frank A E, Giaccone Giuseppe (2002) Apoptosis: target of Cancer Therapy. Clin Cancer Res 8:2024–2034
Debatin Klaus-Michael, Poncet Delphine, Kroemer Guido (2002) Chemotherapy: targeting the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Oncogene 21:8786–8803. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206039
Norbury Chris J, Zhivotovsky Boris (2004) DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23:2797–2808. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207532
Barbora B, Holoubek A (2011) Generation of reactive oxygen species during apoptosis induced by DNA-damaging agents and/or histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. doi:10.1155/2011/253529
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi (India) for financial support under the 12th Five Year Plan project “Affordable Cancer Therapeutics (ACT)” (CSC0301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, A., Nayak, V.L., Bagul, C. et al. Investigation of the mechanism and apoptotic pathway induced by 4β cinnamido linked podophyllotoxins against human lung cancer cells A549. Apoptosis 20, 1518–1529 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1173-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1173-6