Abstract
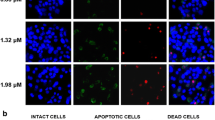
α-Mangostin is a dietary xanthone that has been shown to have anti-cancer and anti-proliferative properties in various types of human cancer cells. This study investigates the molecular mechanism of the apoptosis-inducing effects of α-mangostin on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. We observed that α-mangostin reduces the viability of HCC cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. α-Mangostin mediated apoptosis of SK-Hep-1 cells is accompanied by nuclear chromatin condensation and cell cycle arrest in the sub-G1 phases as well as phosphatidylserine exposure. Furthermore, α-mangostin triggered the mitochondrial caspase apoptotic pathway, as indicated by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, and the regulation of B cell lymphoma 2 family member expression. Moreover, α-mangostin inhibited a sustained activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation, and treatment with a p38 MAPK inhibitor enhanced α-mangostin-induced caspase activation and apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 cells. In vivo xenograft mice experiments revealed that α-mangostin significantly reduced tumor growth and weight in mice inoculated with SK-Hep-1 cells. These findings demonstrate that α-mangostin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis through inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and that α-mangostin inhibits the in vivo tumor growth of SK-Hep-1 xenograft mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Human hepatocellular carcinoma
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide
- JC-1:
-
5,5′,6,6′-Tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazol-carbocyanine iodide
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PARP:
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- Bcl-2:
-
B cell lymphoma 2
- Bax:
-
B cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein
References
Ng IO, Ng MM, Lai EC, Fan ST (1995) Better survival in female patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Possible causes from a pathologic approach. Cancer 75:18–22
Trevisani F, Cantarini MC, Wands JR, Bernardi M (2008) Recent advances in the natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 29:1299–1305
Sun SY (2005) Chemopreventive agent-induced modulation of death receptors. Apoptosis 10:1203–1210
Bishayee A, Ahmed S, Brankov N, Perloff M (2011) Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and therapy of breast cancer. Front Biosci 16:980–996
Gopalakrishnan G, Banumathi B, Suresh G (1997) Evaluation of the antifungal activity of natural xanthones from Garcinia mangostana and their synthetic derivatives. J Nat Prod 60:519–524
Sakagami Y, Iinuma M, Piyasena KG, Dharmaratne HR (2005) Antibacterial activity of alpha-mangostin against vancomycin resistant enterococci (VRE) and synergism with antibiotics. Phytomedicine 12:203–208
Shibata MA, Iinuma M, Morimoto J et al (2011) Alpha-mangostin extracted from the pericarp of the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn) reduces tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in an immunocompetent xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer carrying a p53 mutation. BMC Med 9:69
Kurose H, Shibata MA, Iinuma M, Otsuki Y (2012) Alterations in cell cycle and induction of apoptotic cell death in breast cancer cells treated with alpha-mangostin extracted from mangosteen pericarp. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:672428
Krajarng A, Nakamura Y, Suksamrarn S, Watanapokasin R (2011) Alpha-mangostin induces apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma cells through downregulation of ERK/JNK and AKT signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 59:5746–5754
Matsumoto K, Akao Y, Kobayashi E et al (2003) Induction of apoptosis by xanthones from mangosteen in human Leukemia cell lines. J Nat Prod 66:1124–1127
Watanapokasin R, Jarinthanan F, Nakamura Y et al (2011) Effects of alpha-mangostin on apoptosis induction of human colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 17:2086–2095
Johnson JJ, Petiwala SM, Syed DN et al (2012) Alpha-mangostin, a xanthone from mangosteen fruit, promotes cell cycle arrest in prostate cancer and decreases xenograft tumor growth. Carcinogenesis 33:413–419
Chao AC, Hsu YL, Liu CK et al (2011) Alpha-mangostin, a dietary xanthone, induces autophagic cell death by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in glioblastoma cells. J Agric Food Chem 59:2086–2096
Earnshaw WC (1999) Apoptosis. A cellular poison cupboard. Nature 397(6718):387–389
Saikumar P, Dong Z, Patel Y et al (1998) Role of hypoxia-induced Bax translocation and cytochrome c release in reoxygenation injury. Oncogene 17:3401–3415
Ho YT, Lu CC, Yang JS et al (2009) Berberine induced apoptosis via promoting the expression of caspase-8, -9 and -3, apoptosis-inducing factor and endonuclease g in SCC-4 human tongue squamous carcinoma cancer cells. Anticancer Res 29:4063–4070
Chen MJ, Yang PY, Ye YZ et al (2010) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in uveal melanoma cells through the mitochondrial pathway. Am J Chin Med 38:1131–1142
Goyal L (2001) Cell death inhibition: keeping caspases in check. Cell 104:805–808
Kagan VE, Borisenko GG, Tyurina YY et al (2004) Oxidative lipidomics of apoptosis: redox catalytic interactions of cytochrome c with cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1963–1985
Lee SK, Kim YC, Song SB et al (2010) Stabilization and translocation of p53 to mitochondria is linked to bax translocation to mitochondria in simvastatin-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1592–1597
Matsukawa J, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K et al (2004) The ASK1-MAP kinase cascades in mammalian stress response. J Biochem 136:261–265
Lub-de Hooge MN, de Jong S, Vermot-Desroches C et al (2004) Endotoxin increases plasma soluble tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand level mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Shock 22:186–188
Gonzalez-Guerrico AM, Kazanietz MG (2005) Phorbol ester-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells via autocrine activation of the extrinsic apoptotic cascade: a key role for Protein Kinase C delta. J Biol Chem 280:38982–38991
Abdollahi T, Robertson NM, Abdollahi A et al (2005) Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by IL-8 is mediated by the p38-MAPK pathway in OVAR3 cells. Apoptosis 10:1383–1393
Weldon CB, Parker AP, Patten D et al (2004) Sensitization of apoptotically-resistant breast carcinoma cells to TNF and TRAIL by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Int J Oncol 24:1473–1480
Jin CY, Park C, Kim GY et al (2009) Genistein enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. Chem Biol Interact 180:143–150
Liu B, Jian Z, Li Q et al (2012) Baicalein protects human melanocytes from H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis via inhibiting mitochondria-dependent caspase activation and the p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 53:183–193
Yu YL, Yu SL, Su KJ et al (2010) Extended O6-methylguanine methyltransferase promoter hypermethylation following n-butylidenephthalide combined with 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) on inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. J Agric Food Chem 58:1630–1638
Ying TH, Yang SF, Tsai SJ, Hsieh SC et al (2012) Fisetin induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer HeLa cells through ERK1/2-mediated activation of caspase-8-/caspase-3-dependent pathway. Arch Toxicol 86:263–273
Su CL, Wu CJ, Chen FN (2007) Supernatant of bacterial fermented soybean induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep 3B cells via activation of caspase 8 and mitochondria. Food Chem Toxicol 45:303–314
Yu YL, Chou RH, Wu CH et al (2012) Nuclear EGFR suppresses ribonuclease activity of polynucleotide phosphorylase through DNAPK-mediated phosphorylation at serine 776. J Biol Chem 287:31015–31026
Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD (2003) Bcl-2-family proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:691–699
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N (2003) Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:395–403
Dharmaratne HR, Piyasena KG, Tennakoon SB (2005) A geranylated biphenyl derivative from Garcinia malvgostana. Nat Prod Res 19:239–243
Menasria F, Azebaze AG, Billard C et al (2008) Apoptotic effects on B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells of heterocyclic compounds isolated from guttiferaes. Leuk Res 32:1914–1926
Sanchez-Perez Y, Morales-Barcenas R, Garcia-Cuellar CM et al (2010) The alpha-mangostin prevention on cisplatin-induced apoptotic death in LLC-PK1 cells is associated to an inhibition of ROS production and p53 induction. Chem Biol Interact 188:144–150
Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H (2011) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 351:41–58
Gambi N, Tramontano F, Quesada P (2008) Poly(ADPR)polymerase inhibition and apoptosis induction in CDDP-treated human carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol 75:2356–2363
Kroemer G, Reed JC. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6:513-519
Wang X (2001) The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15:2922–2933
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2000) Bcl-2 family: life-or-death switch. FEBS Lett 466:6–10
Kirkland RA, Franklin JL (2003) Bax, reactive oxygen, and cytochrome c release in neuronal apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 5:589–596
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J et al (1995) Opposing effects of ERK and JNK–p38 map kinases on apoptosis. Science 270:1326–1331
MacFarlane M, Cohen GM, Dickens M (2000) JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) and p38 activation in receptor-mediated and chemically-induced apoptosis of T-cells: differential requirements for caspase activation. Biochem J 348(Pt 1):93–101
Deschesnes RG, Huot J, Valerie K et al (2001) Involvement of p38 in apoptosis-associated membrane blebbing and nuclear condensation. Mol Biol Cell 12:1569–1582
Chang HL, Wu YC, Su JH (2008) Protoapigenone, a novel flavonoid, induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1/2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:841–849
Liu Q, Chen T, Chen H et al (2004) Triptolide (PG-490) induces apoptosis of dendritic cells through sequential p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation and caspase 3 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:980–986
Lee HJ, Wang CJ, Kuo HC et al (2005) Induction apoptosis of luteolin in human hepatoma HepG2 cells involving mitochondria translocation of Bax/Bak and activation of JNK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:124–131
Gopalakrishnan A, Xu CJ, Nair SS et al (2006) Modulation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and MAPK pathway by flavonoids in human prostate cancer PC3 cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 29:633–644
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC100-2313-B-040-001 and NSC101-2313-B-040-001) and Chung Shan Medical Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan (CSH-2011-C-026).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shun-Fa Yang and Yi-Hsien Hsieh contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, SC., Huang, MH., Cheng, CW. et al. α-Mangostin induces mitochondrial dependent apoptosis in human hepatoma SK-Hep-1 cells through inhibition of p38 MAPK pathway. Apoptosis 18, 1548–1560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0888-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0888-5