Abstract
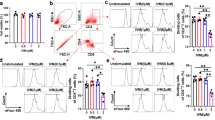
Recent data show that anti-CD20 therapy is effective for some autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS). However, the efficacy of anti-CD20 therapy for MS is largely limited because anti-CD20 antibodies target only B cells. In previous studies, we have investigated the function of MS4a4B, a novel CD20 homologue, in T cell proliferation. Here, we found that MS4a4B regulates not only T cell proliferation but also T cell apoptosis. Knockdown of MS4a4B by MS4a4B-siRNA or MS4a4B-shRNA-expressing vector promoted apoptosis in primary T cells and T32 cell line. In contrast, vector-driven over-expression of MS4a4B reduced apoptosis in EL-4 cells. Machinery analysis showed that MS4a4B-mediated T cell survival was associated with decreased activity of caspases 3, 8 and 9. Interestingly, binding of anti-MS4a4B antibodies to T cells induced activated T cells to undergo apoptosis. To test whether anti-MS4a4B antibody interferes with MS4a4B-mediated protection of T cells, we injected anti-MS4a4B antibodies into mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). The results show that anti-MS4a4B treatment ameliorated the severity of EAE, accompanied by decreased Th1 and Th17 cell responses and reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the central nervous system, suggesting that MS4a4B may serve as a target of antibody-based therapy for T cell-mediated diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reichert JM, Rosensweig CJ, Faden LB, Dewitz MC (2005) Monoclonal antibody successes in the clinic. Nat Biotechnol 23:1073–1078
Taylor RP, Lindorfer MA (2008) Immunotherapeutic mechanisms of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Curr Opin Immunol 20:444–449
Tedder TF, Engel P (1994) CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today 15:450–454
Buttmann M (2010) Treating multiple sclerosis with monoclonal antibodies: a 2010 update. Expert Rev Neurother 10:791–809
Axtell RC, de Jong BA, Boniface K, van der Voort LF, Bhat R, De Sarno P, Naves R, Han M, Zhong F, Castellanos JG et al (2010) T helper type 1 and 17 cells determine efficacy of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis and experimental encephalomyelitis. Nat Med 16:406–412
Matsushita T, Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF (2008) Regulatory B cells inhibit EAE initiation in mice while other B cells promote disease progression. J Clin Investig 118:3420–3430
Chatenoud L, Bluestone JA (2007) CD3-specific antibodies: a portal to the treatment of autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 7:622–632
Perruche S, Zhang P, Liu Y, Saas P, Bluestone JA, Chen W (2008) CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance involves transforming growth factor-beta from phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells. Nat Med 14:528–535
Chatenoud L (2003) CD3-specific antibody-induced active tolerance: from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Immunol 3:123–132
Xu H, Williams MS, Spain LM (2006) Patterns of expression, membrane localization, and effects of ectopic expression suggest a function for MS4a4B, a CD20 homolog in Th1 T cells. Blood 107:2400–2408
Ishibashi K, Suzuki M, Sasaki S, Imai M (2001) Identification of a new multigene four-transmembrane family (MS4A) related to CD20, HTm4 and beta subunit of the high-affinity IgE receptor. Gene 264:87–93
Liang Y, Tedder TF (2001) Identification of a CD20-, FcepsilonRIbeta-, and HTm4-related gene family: sixteen new MS4A family members expressed in human and mouse. Genomics 72:119–127
Howie D, Nolan KF, Daley S, Butterfield E, Adams E, Garcia-Rueda H, Thompson C, Saunders NJ, Cobbold SP, Tone Y et al (2009) MS4A4B is a GITR-associated membrane adapter, expressed by regulatory T cells, which modulates T cell activation. J Immunol 183:4197–4204
Venkataraman C, Schaefer G, Schindler U (2000) Cutting edge: Chandra, a novel four-transmembrane domain protein differentially expressed in helper type 1 lymphocytes. J Immunol 165:632–636
Xu H, Yan Y, Williams MS, Carey GB, Yang J, Li H, Zhang GX, Rostami AM (2010) MS4a4B, a CD20 homologue in T cells, inhibits T cell propagation by modulation of cell cycle. PLoS ONE 5:e13780
Yan Y, Zhang GX, Williams MS, Carey GB, Li H, Yang J, Rostami A, Xu H (2012) TCR stimulation upregulates MS4a4B expression through induction of AP-1 transcription factor during T cell activation. Mol Immunol 52:71–78
Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) How to successfully apply animal studies in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to research on multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 60:12–21
Yan Y, Zhang GX, Gran B, Fallarino F, Yu S, Li H, Cullimore ML, Rostami A, Xu H (2010) IDO upregulates regulatory T cells via tryptophan catabolite and suppresses encephalitogenic T cell responses in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 185:5953–5961
Deans JP, Li H, Polyak MJ (2002) CD20-mediated apoptosis: signalling through lipid rafts. Immunology 107:176–182
Hofmeister JK, Cooney D, Coggeshall KM (2000) Clustered CD20 induced apoptosis: src-family kinase, the proximal regulator of tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium influx, and caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 26:133–143
Arens R, Schepers K, Nolte MA, van Oosterwijk MF, van Lier RA, Schumacher TN, van Oers MH (2004) Tumor rejection induced by CD70-mediated quantitative and qualitative effects on effector CD8+ T cell formation. J Exp Med 199:1595–1605
Dayde D, Ternant D, Ohresser M, Lerondel S, Pesnel S, Watier H, Le Pape A, Bardos P, Paintaud G, Cartron G (2009) Tumor burden influences exposure and response to rituximab: pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling using a syngeneic bioluminescent murine model expressing human CD20. Blood 113:3765–3772
Halfteck GG, Elboim M, Gur C, Achdout H, Ghadially H, Mandelboim O (2009) Enhanced in vivo growth of lymphoma tumors in the absence of the NK-activating receptor NKp46/NCR1. J Immunol 182:2221–2230
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY, Ravagnan L et al (2001) Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 410:549–554
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS, Liang J (2005) Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 37:719–727
Krammer PH, Arnold R, Lavrik IN (2007) Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 7:532–542
Xu H, Zhang GX, Wysocka M, Wu CY, Trinchieri G, Rostami A (2000) The suppressive effect of TGF-beta on IL-12-mediated immune modulation specific to a peptide Ac1-11 of myelin basic protein (MBP): a mechanism involved in inhibition of both IL-12 receptor beta1 and beta2. J Neuroimmunol 108:53–63
Zhang GX, Xu H, Kishi M, Calida D, Rostami A (2002) The role of IL-12 in the induction of intravenous tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 168:2501–2507
Donato JL, Ko J, Kutok JL, Cheng T, Shirakawa T, Mao XQ, Beach D, Scadden DT, Sayegh MH, Adra CN (2002) Human HTm4 is a hematopoietic cell cycle regulator. J Clin Investig 109:51–58
Tedder TF, Forsgren A, Boyd AW, Nadler LM, Schlossman SF (1986) Antibodies reactive with the B1 molecule inhibit cell cycle progression but not activation of human B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 16:881–887
Janas E, Priest R, Wilde JI, White JH, Malhotra R (2005) Rituxan (anti-CD20 antibody)-induced translocation of CD20 into lipid rafts is crucial for calcium influx and apoptosis. Clin Exp Immunol 139:439–446
Zhan Y, Funda DP, Every AL, Fundova P, Purton JF, Liddicoat DR, Cole TJ, Godfrey DI, Brady JL, Mannering SI et al (2004) TCR-mediated activation promotes GITR upregulation in T cells and resistance to glucocorticoid-induced death. Int Immunol 16:1315–1321
Nocentini G, Giunchi L, Ronchetti S, Krausz LT, Bartoli A, Moraca R, Migliorati G, Riccardi C (1997) A new member of the tumor necrosis factor/nerve growth factor receptor family inhibits T cell receptor-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6216–6221
Spinicelli S, Nocentini G, Ronchetti S, Krausz LT, Bianchini R, Riccardi C (2002) (GITR) interacts with the pro-apoptotic protein Siva and induces apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9:1382–1384
Nishio J, Feuerer M, Wong J, Mathis D, Benoist C (2010) Anti-CD3 therapy permits regulatory T cells to surmount T cell receptor-specified peripheral niche constraints. J Exp Med 207:1879–1889
Penaranda C, Tang Q, Bluestone JA (2011) Anti-CD3 therapy promotes tolerance by selectively depleting pathogenic cells while preserving regulatory T cells. J Immunol 187:2015–2022
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Katherine Regan for editorial assistance. We thank Hong Dai and Ke Li for helpful technical assistance. This work was supported by Grants from the American Heart Association (H.X.) and from the National Institutes of Health (A.M.R.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yaping Yan and Zichen Li have contributed equally to this study.
H. Xu is the primary corresponding author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, GX. et al. Anti-MS4a4B treatment abrogates MS4a4B-mediated protection in T cells and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Apoptosis 18, 1106–1119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0870-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0870-2