Abstract
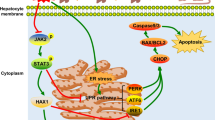
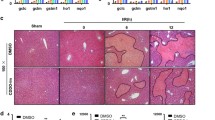
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is the main cause of primary graft dysfunction of liver allografts. Cobalt-protoporphyrin (CoPP)–dependent induction of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 has been shown to protect the liver from I/R injury. This study analyzes the apoptotic mechanisms of HO-1-mediated cytoprotection in mouse liver exposed to I/R injury. HO-1 induction was achieved by the administration of CoPP (1.5 mg/kg body weight i.p.). Mice were studied in in vivo model of hepatic segmental (70 %) ischemia for 60 min and reperfusion injury. Mice were randomly allocated to four main experimental groups (n = 10 each): (1) A control group undergoing sham operation. (2) Similar to group 1 but with the administration of CoPP 72 h before the operation. (3) Mice undergoing in vivo hepatic I/R. (4) Similar to group 3 but with the administration of CoPP 72 h before ischemia induction. When compared with the I/R mice group, in the I/R+CoPP mice group, the increased hepatic expression of HO-1 was associated with a significant reduction in liver enzyme levels, fewer apoptotic hepatocytes cells were identified by morphological criteria and by immunohistochemistry for caspase-3, there was a decreased mean number of proliferating cells (positively stained for Ki67), and a reduced hepatic expression of: C/EBP homologous protein (an index of endoplasmic reticulum stress), the NF-κB’s regulated genes (CIAP2, MCP-1 and IL-6), and increased hepatic expression of IκBa (the inhibitory protein of NF-κB). HO-1 over-expression plays a pivotal role in reducing the hepatic apoptotic IR injury. HO-1 may serve as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in hepatic I/R injury during liver transplantation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clavien PA, Harvey PR, Strasberg SM (1992) Preservation and reperfusion injuries in liver allografts. An overview and synthesis of current studies. Transplantation 53:957–978
Jaeschke H (1996) Preservation injury: mechanisms, prevention and consequences. J Hepatol 25:774–780
Kojima Y, Suzuki S, Tsuchiya Y, Konno H, Baba S, Nakamura S (2003) Regulation of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine responses by kupffer cells in endotoxin-enhanced reperfusion injury after total hepatic ischemia. Transpl Int 16:231–240
Nathan C (2002) Points of control in inflammation. Nature 420:846–852
Geuken E, Buis CI, Visser DS et al (2005) Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human livers before transplantation correlates with graft injury and function after transplantation. Am J Transpl 5:1875
Katori M, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2002) Heme oxygenase-1 system in organ transplantation. Transplantation 74:905
Shi W, Haberland ME, Jien ML, Lusis AJ (2000) Endothelial responses to oxidized lipoproteins determine genetic susceptibility to atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation 102:75
Sass G, Barikbin R, Tiegs G (2012) The multiple functions of heme oxygenase-1 in the liver. Z Gastroenterol 50(1):34–40
Amersi F, Buelow R, Kato H, Ke B, Coito AJ, Shen XD et al (1999) Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 protects genetically fat Zucker rat livers from ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 104:1631
Coito AJ, Buelow R, Shen XD, Amersi F, Moore C, Volk HD et al (2002) Heme oxygenase-1 gene transfer inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and protects genetically fat Zucker rat livers from ischemia–reperfusion injury. Transplantation 74:96
Kato H, Amersi F, Buelow R, Melinek J, Coito AJ, Ke B et al (2001) Heme oxygenase-1 overexpression protects rat livers from ischemia/reperfusion injury with extended cold preservation. Am J Transpl 1:121
Suttner DM, Dennery PA (1999) Reversal of HO-1 related cytoprotection with increased expression is due to reactive iron. FASEB J 13:1800–1809
Suttner DM, Sridhar K, Lee CS, Tomura T, Hansen TN, Dennery PA (1999) Protective effects of transient HO-1 overexpression on susceptibility to oxygen toxicity in lung cells. Am J Physiol 276:L443–L451
Selzner N, Selzner M, Jochum W, Clavien PA (2003) Ischemic preconditioning protects the steatotic mouse liver against reperfusion injury: an ATP dependent mechanism. J Hepatol 39:55–61
Nakao A, Kimizuka K, Stolz DB, Neto JS, Kaizu T, Choi AM, Uchiyama T et al (2003) Carbon monoxide inhalation protects rat intestinal grafts from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 163:1587–1598
Fondevila C, Shen XD, Tsuchiyashi S, Yamashita K, Csizmadia E, Lassman C et al (2004) Biliverdin therapy protects rat livers from ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology 40:1333–1341
Wang CF, Wang ZY, Tao SF, Ding J, Sun LJ, Li JY, Quan ZW (2012) Preconditioning donor liver with Nodosin perfusion lessens rat ischemia reperfusion injury via heme oxygenase-1 upregulation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(4):832–840
Zhang SC, Shi Q, Feng YN, Fang J (2012) Tissue-protective effect of glutamine on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via induction of heme oxygenase-1. Pharmacology 91(1–2):59–68
Fang J, Qin H, Seki T, Nakamura H, Tsukigawa K, Shin T, Maeda H (2011) Therapeutic potential of pegylated hemin for reactive oxygen species-related diseases via induction of heme oxygenase-1: results from a rat hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339(3):779–789
Tsuchihashi S, Zhai Y, Bo Q, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2007) Heme oxygenase-1 mediated cytoprotection against liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: inhibition of type-1 interferon signaling. Transplantation 83(12):1628–1634
Schmidt R (2007) Cobalt protoporphyrin as a potential therapeutic agent? FASEB J 21(11):2639–2640
Froh M, Conzelmann L, Walbrun P, Netter S, Wiest R, Wheeler MD, Lehnert M, Uesugi T, Scholmerich J, Thurman RG (2007) Heme oxygenase-1 overexpression increases liver injury after bile duct ligation in rats. World J Gastroenterol 13:3478–3486
Liu J, Ren F, Cheng Q, Bai L, Shen X, Gao F et al (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates liver inflammatory immune response in the pathogenesis of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplantation 94(3):211–217
Ben-Ari Z, Pappo O, Yitzhaki S, Cheporko Y, Shainberg A, Zinman T et al (2009) Uridine-5´-triphosphate protects against hepatic-ischemic/reperfusion injury in mice. Transplantation 87(8):1155–1162
Wang XZ, Lawson B, Brewer JW, Zinszner H, Sanjay A, Mi LJ et al (1996) Signals from the stressed endoplasmic reticulum induce C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP/GADD153). Mol Cell Biol 16:4273–4280
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Bailly-Maitre B, Fondevila C, Kaldas F, Droin N, Luciano F, Ricci JE et al (2006) Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2809–2814
Hochhauser E, Pappo O, Ribakovsky E, Ravid A, Kurtzwald E, Cheporko Y et al (2008) Recombinant human erythropoietin attenuates hepatic injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion in an isolated mouse liver model. Apoptosis 13(1):77–86
Ben-Ari Z, Avlas O, Fallach R, Schmilovitz-Weiss H, Chepurko Y, Pappo O, Hochhauser E (2012) Ischemia and reperfusion liver injury is reduced in the absence of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell Physiol Biochem 30(2):489–498
Arii S, Teramoto K, Kawamura T (2003) Current progress in the understanding of and therapeutic strategies for ischemia and reperfusion injury of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 10(3):189–194
Kaplowitz N, Tsukamoto H (1996) Oxidative stress and liver damage. Prog Liver Dis 14:131–159
Teoh NC, Farrell GC (2003) Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:891–902
Muraoka K, Shimizu K, Sun X (1997) Hypoxia, but not reoxygenation, induces IL-6 gene expression through NF-κB activation. Transplantation 63:466–470
Xu MQ, Shuai XR, Yan ML, Zhang MM, Yan LN (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver graft. World J Gastroenterol 11(44):6960–6967
Giakoustidis DE, Giakoustidis AE, Iliadis S, Koliakou K, Antoniadis N, Kontos N et al (2010) Attenuation of liver ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis by epigallocatechin-3-gallate via down-regulation of NF-kappaB and c-Jun expression. J Surg Res 159(2):720–728
Devey L, Mohr E, Bellamy C, Simpson K, Henderson N, Harrison EM et al (2009) c-Jun terminal kinase-2 gene deleted mice overexpress hemeoxygenase-1 and are protected from hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. Transplantation 88(3):308–316
Kushida T, Li Volti G, Quan S, Goodman A, Abraham NG (2002) Role of human heme oxygenase-1 in attenuating TNF-alpha-mediated inflammation injury in endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem 87:377–385
Petrache I, Otterbein LE, Alam J, Wiegand GW, Choi AM (2000) Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in cultured fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 278:L312–L319
Abraham NG, Kappas A (2005) Heme oxygenase and the cardiovascular-renal system. Free Radic Biol Med 39(1):1–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
O. Pappo and E. Hochhauser are two last co authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Ari, Z., Issan, Y., Katz, Y. et al. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 protects mouse liver from apoptotic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Apoptosis 18, 547–555 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0814-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0814-x