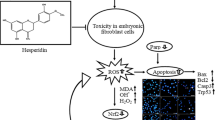
Abstract
T-2 toxin, a member of the trichothecene mycotoxin family produced by the Fusarium fungi, has been shown to exert a variety of toxic effects on multiple targets in vivo. However, the embryonic toxicity of T-2 toxin in vitro remains unclear. In the present study, two permanent cell lines, embryonic stem cells (ES cells D3) and fibroblast 3T3 cells, were used to evaluate T-2 toxin toxicity. Differentiated mouse ES cells were cultivated as embryoid bodies along with T-2 toxin at different concentrations (0.5, 1, and 2 ng/ml) for 24 h. The increases in cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid and DNA oxidative damage, and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential were observed at 1 and 2 ng/ml concentrations. Flow cytometry showed that T-2 toxin induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Furthermore, T-2 toxin opened the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, caused the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria and induced the upregulation of p53, caspase-9, caspase-3 expression and increased the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2. However, T-2 toxin-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in differentiated ES cells decreased significantly in the presence of the antioxidant Trolox. Taken together, these results demonstrate that T-2 toxin induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in differentiated murine ES cells, and ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway plays an important role in T-2 toxin induced apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH (1981) Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292(5819):154–156
Martin GR (1981) Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78(12):7634–7638
Rohwedel J, Sehlmeyer U, Shan J, Meister A, Wobus AM (1996) Primordial germ cell-derived mouse embryonic germ (EG) cells in vitro resemble undifferentiated stem cells with respect to differentiation capacity and cell cycle distribution. Cell Biol Int 20(8):579–587
Leahy A, Xiong JW, Kuhnert F, Stuhlmann H (1999) Use of developmental marker genes to define temporal and spatial patterns of differentiation during embryoid body formation. J Exp Zool 284(1):67–81
Sabapathy K, Klemm M, Jaenisch R, Wagner EF (1997) Regulation of ES cell differentiation by functional and conformational modulation of p53. EMBO J 16(20):6217–6230
Sarkar SA, Sharma RP (2002) All-trans-retinoic acid-mediated modulation of p53 during neural differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 18(4):243–257
Genschow E, Spielmann H, Scholz G, Seiler A, Brown N, Piersma A, Brady M, Clemann N, Huuskonen H, Paillard F, Bremer S, Becker K (2002) The ECVAM international validation study on in vitro embryotoxicity tests: results of the definitive phase and evaluation of prediction models. European centre for the validation of alternative methods. Altern Lab Anim 30(2):151–176
Riebeling C, Pirow R, Becker K, Buesen R, Eikel D, Kaltenhäuser J, Meyer F, Nau H, Slawik B, Visan A, Volland J, Spielmann H, Luch A, Seiler A (2011) The embryonic stem cell test as tool to assess structure-dependent teratogenicity: the case of valproic acid. Toxicol Sci 120(2):360–370
Guan K, Rohwedel J, Wobus AM (1999) Embryonic stem cell differentiation models: cardiogenesis, myogenesis, neurogenesis, epithelial and vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in vitro. Cytotechnology 30(1–3):211–226
Rohwedel J, Guan K, Hegert C, Wobus AM (2001) Embryonic stem cells as an in vitro model for mutagenicity, cytotoxicity and embryotoxicity studies: present state and future prospects. Toxicol In Vitro 15(6):741–753
Rolletschek A, Blyszczuk P, Wobus AM (2004) Embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac, neuronal and pancreatic cells as model systems to study toxicological effects. Toxicol Lett 149:361–369
Desjardins AE, Hohn TM, McCormick SP (1993) Trichothecene biosynthesis in Fusarium species: chemistry, genetics, and significance. Microbiol Rev 57(3):595–604
Rotter BA, Prelusky DB, Pestka JJ (1996) Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). Toxicol Environ Health 48(1):1–34
Chen F, Ma Y, Xue C, Ma J, Xie Q, Wang G, Bi Y, Cao Y (2008) The combination of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone at permitted feed concentrations causes serious physiological effects in young pigs. J Vet Sci 9(1):39–44
Lafarge-Frayssinet C, Chakor K, Lafont P, Frayssinet C (1990) Transplacental transfer of T2 toxin: pathological effect. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 10:64–68
Sehata S, Teranishi M, Atsumi F, Uetsuka K, Nakayama H, Doi K (2003) T-2 Toxin-induced morphological changes in pregnant rats. J Toxicol Pathol 16:59–65
Doi K, Ishigami N, Sehata S (2008) T-2 toxin-induced toxicity in pregnant mice and rats. Mol Sci 9(11):2146–2148
Sehata S, Kiyosawa N, Atsumi F, Ito K, Yamoto T, Teranishi M, Uetsuka K, Nakayama H, Doi K (2005) Microarray analysis of T-2 toxin-induced liver, placenta and fetal liver lesions in pregnant rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 57(1):15–28
Blakley BR, Hancock DS, Rousseaux CG (1987) Embryotoxic effects of prenatal T-2 toxin exposure in mice. Can J Vet Res 51(3):399–403
Thompson WL, Wannemacher RW Jr (1990) In vivo effects of T-2 mycotoxin on synthesis of proteins and DNA in rat tissues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105(3):483–491
Chang IM, Mar WC (1988) Effect of T-2 toxin on lipid peroxidation in rats: elevation of conjugated diene formation. Toxicol Lett 40(3):275–280
Schuster A, Hunder G, Fichtl B, Forth W (1987) Role of lipid peroxidation in the toxicity of T-2 toxin. Toxicon 25(12):1321–1328
Chen JH, Cao JL, Chu YL, Wang ZL, Yang ZT, Wang HL (2008) T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis involving Fas, p53, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in human chondrocytes. Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9(6):455–463
Chen JH, Chu YL, Cao JL et al (2006) T-2 toxin induces apoptosis, and selenium partly blocks, T-2 toxin induced apoptosis in chondrocytes through modulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Food Chem Toxicol 44:567–573
Sugamata M, Ihara T, Sekijima M, Kawai KI, Ueno I (1995) Induction of apoptosis by T-2 toxin and other natural toxins in HL-60 human promyelotic leukemia cells. Nat Toxins 3:129–137
Nagase M, Alam MM, Tsushima A, Yoshizawa T, Sakato N (2001) Apoptosis induction by T-2 toxin: activation of caspase-9, caspase-3, and DFF-40/CAD through cytosolic release of cytochrome c in HL-60 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65(8):1741–1747
Chaudhari M, Jayaraj R, Bhaskar AS, Lakshmana Rao PV (2009) Oxidative stress induction by T-2 toxin causes DNA damage and triggers apoptosis via caspase pathway in human cervical cancer cells. Toxicology 262(2):153–161
Wu J, Jing L, Yuan H, Peng SQ (2011) T-2 toxin induces apoptosis in ovarian granulosa cells of rats through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Toxicol Lett 202(3):168–177
Shinozuka J, Li G, Uetsuka K, Nakayama H, Doi K (1997) Process of the development of T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis in the lymphoid organs of mice. Exp Anim 46:117–126
Islam Z, Nagase M, Ota A, Ueda S, Yoshizawa T, Sakato N (1998) Structure-function relationship of T-2 toxin and its metabolites in inducing thymic apoptosis in vivo in mice. Biosci Biotech Biochem 62:1492–1497
Shinozuka J, Suzuki H, Tsutsui S, Nakayama H, Doi K (2001) T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis and C-Fos mRNA expression in ConA-stimulated mouse thymocyte primary culture. Toxicol Pathol 14:247–251
Desagher S, Martinou JC (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 10(9):369–377
Prigione A, Adjaye J (2010) Modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and bioenergetic metabolism upon in vitro and in vivo differentiation of human ES and iPS cells. Int J Dev Biol 54(11–12):1729–1741
St John JC, Amaral A, Bowles E, Oliveira JF, Lloyd R, Freitas M, Gray HL, Navara CS, Oliveira G, Schatten GP, Spikings E, Ramalho-Santos J (2006) The analysis of mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA in human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 331:347–374
Chung S, Dzeja PP, Faustino RS, Perez-Terzic C, Behfar A, Terzic A (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism is required for the cardiac differentiation of stem cells. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 4(suppl 1):S60–S67
Facucho-Oliveira JM, Alderson J, Spikings EC, Egginton S, St John JC (2007) Mitochondrial DNA replication during differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells. J Cell Sci 120(pt22):4025–4034
St John JC, Ramalho-Santos J, Gray HL, Petrosko P, Rawe VY, Navara CS, Simerly CR, Schatten GP (2005) The expression of mitochondrial DNA transcription factors during early cardiomyocyte in vitro differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. Cloning Stem Cells 7(3):141–153
Mandal S, Lindgren AG, Srivastava AS, Clark AT, Banerjee U (2011) Mitochondrial function controls proliferation and early differentiation potential of embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 29(3):486–495
Genschow E, Spielmann H, Scholz G, Pohl I, Seiler A, Clemann N, Bremer S, Becker K (2004) Validation of the embryonic stem cell test in the international ECVAM validation study on three in vitro embryotoxicity tests. Altern Lab Anim 32:209–244
Seiler A, Visan A, Buesen R, Genschow E, Spielmann H (2004) Improvement of an in vitro stem cell assay for developmental toxicity: the use of molecular endpoints in the embryonic stem cell test. Reprod Toxicol 18:231–240
Swift LM, Sarvazyan N (2000) Localization of dichlorofluorescin in cardiac myocytes: implication for assessment of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278(3):982–990
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74(1):214–226
Olive PL, Wlodek D, Durand RE, Banáth JP (1992) Factors influencing DNA migration from individual cells subjected to gel electrophoresis. Exp Cell Res 198(2):259–267
Scaduto RussellC, Lee W Jr, Grotyohann (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76:469–477
Laschinski G, Vogel R, Spielmann H (1991) Cytotoxicity test using blastocyst-derived euploid embryonal stem cells: a new approach to in vitro teratogenesis screening. Reprod Toxicol 5(1):57–64
Atroshi F, Rizzo A, Biese I, Veijalainen P, Antila E, Westermarck T (1997) T-2 toxin-induced DNA damage in mouse livers: the effect of pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 and α-tocopherol. Mol Aspects Med 18:S255–258
Ghibelli L, Fanelli C, Rotilio G, Lafavia E, Coppola S, Colussi C, Civitareale P, Ciriolo MR (1998) Rescue of cells from apoptosis by inhibition of active GSH extrusion. FASEB J 12(6):479–486
Frankic T, Pajk T, Rezar V, Levart A, Salobir J (2006) The role of dietary nucleotides in reduction of DNA damage induced by T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in chicken leukocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 44(11):1838–1844
Rich T, Allen RL, Wyllie AH (2000) Defying death after DNA damage. Nature 407(6805):777–783
Vousden KH (2000) p53: death star. Cell 103(5):691–694
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ (2000) Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408(6810):307–310
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Stark GR (1998) The p53 network. Biol Chem 273(1):1–4
Scherz-Shouval R, Elazar Z (2007) ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol 17(9):422–427
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192(1):1–15
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 5(5):415–418
Harris MH, Thompson CB (2000) The role of the Bcl-2 family in the regulation of outer mitochondrial membrane permeability. Cell Death Differ 7(12):1182–1191
Vilà B, Jaradat ZW, Marquardt RR, Frohlich AA (2002) Effect of T-2 toxin on in vivo lipid peroxidation and vitamin E status in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 40(4):479–486
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172699), National Key Project on Drug Development from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2009ZX09501-034) and International cooperation projects from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2008DFB300090 and 2011DFA32190).
Conflict of interest
The authors state no duality of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Wu, Y., Guo, J. et al. T-2 toxin induces apoptosis in differentiated murine embryonic stem cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Apoptosis 17, 895–907 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0724-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0724-3