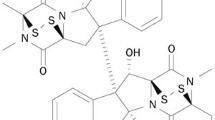
Abstract
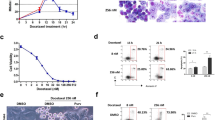
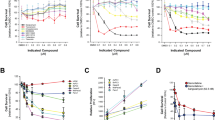
F14512, an epipodophyllotoxin derivative equipped with a spermine moiety, is selectively taken up by the polyamine transport system over-active in tumor cells. F14512 was identified as a selective anticancer agent with a broad spectrum of antitumor activities and is currently undergoing phase I clinical trial in onco-hematology. However, the mechanism by which F14512 exerts its selective effects on neoplastic cells remains poorly understood. In this study, using mainly P388 leukemia cells, we showed that activation of the DNA damage response by F14512 did not induce immediate apoptosis but resulted in an early growth arrest. F14512-induced G2 arrest was accompanied by the appearance of a senescence-like phenotype (characterized by an increased β-galactosidase staining) with up-regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16, and cyclin D1. The early senescence-based cell cycle block was characterized by a marked increase of the level of the IAP protein survivin, but not cIAP2, in P388 cells as well as in three other leukemia and melanoma cell types. The Thr(34)-phosphorylated form of survivin was observed within 4 h after F14512 exposure. Inhibition of survivin by siRNA resulted in a switch from senescence-like growth arrest to apoptosis. Compared with the parental drug etoposide, F14512-induced DNA damage signaling pathway resulted in greater senescence like-growth arrest and delayed apoptosis. Collectively, our data show that senescence arrest and subsequent apoptosis are powerful mechanisms mediating the chemotherapeutic effects of F14512 and identify survivin as the molecular determinant responsible for a qualitative shift in cell fate from senescence to apoptosis upon treatment with F14512.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IAP:
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis
- DSBs:
-
Double-strand breaks
- RT:
-
Room temperature
- z.VAD.fmk:
-
Benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-DL-Asp-fluoromethylketone
- PTS:
-
Polyamine transport system
- NSCLC:
-
Non small cell lung carcinoma
Reference list
Xie S, Wang J, Zhang Y, Wang C (2010) Antitumor conjugates with polyamine vectors and their molecular mechanisms. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:1049–1061
Barret J-M, Kruczynski A, Vispé S, Annereau J-P, Brel V, Guminski Y, Delcros J-G, Lansiaux A, Guilbaud N, Imbert T, Bailly C (2008) F14512, a potent antitumor agent targeting topoisomerase II vectored into cancer cells via the polyamine transport system. Cancer Res 68:9845–9853
Annereau J-P, Brel V, Dumontet C, Guminski Y, Imbert T, Broussas M, Vispé S, Bréand S, Guilbaud N, Barret JM, Bailly C (2010) A fluorescent biomarker of the polyamine transport system to select patients with AML for F14512 treatment. Leuk Res 34:1383–1389
Kruczynski A, Vandenberghe I, Pillon A, Pesnel S, Goetsch L, Barret J-M, Guminski Y, Le Pape A, Imbert T, Bailly C, Guilbaud N (2011) Preclinical activity of F14512, designed to target tumors expressing an active polyamine transport system. Investig New Drugs 29:9–21
Gentry AC, Pitts SL, Jablonsky MJ, Bailly C, Graves DE, Osheroff N (2011) Interactions between the etoposide derivative F14512 and human type II topoisomerases: implications for the C4 spermine moiety in promoting enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage. Biochemistry 50:3240–3249
Chelouah S, Monod-Wissler C, Bailly C, Barret J-M, Guilbaud N, Vispé S, Käs E (2011) An integrated drosophila model system reveals unique properties for F14512, a novel polyamine-containing anticancer drug that targets topoisomerase II. PLoS One 6:e23597
Nitiss JL (2009) Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 9:338–350
Chang BD, Broude EV, Dokmanovic M, Zhu H, Ruth A, Xuan Y, Kandel ES, Lausch E, Christov K, Roninson IB (1999) A senescence-like phenotype distinguishes tumor cells that undergo terminal proliferation arrest after exposure to anticancer agents. Cancer Res 59:3761–3767
Sordet O, Khan QA, Kohn KW, Pommier Y (2003) Apoptosis induced by topoisomerase inhibitors. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 3:271–290
Montecucco A, Biamonti G (2007) Cellular response to etoposide treatment. Cancer Lett 252:9–18
Chiu CC, Li CH, Ung MW, Fuh TS, Chen WL, Fang K (2005) Etoposide (VP-16) elicits apoptosis following prolonged G2-M cell arrest in p53-mutated human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett 223:249–258
Ishiguro K, Shyam K, Penketh PG, Sartorelli AC (2005) Role of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase in the cytotoxic activity of cloretazine. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1755–1763
Ballot C, Kluza J, Lancel S, Martoriati A, Hassoun SM, Mortier L, Vienne JC, Briand G, Formstecher P, Bailly C, Neviere R, Marchetti P (2010) Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration mediates apoptosis induced by the anti-tumoral alkaloid lamellarin D. Apoptosis 15:769–781
Debacq-Chainiaux F, Erusalimsky JD, Campisi J, Toussaint O (2009) Protocols to detect senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-betagal) activity, a biomarker of senescent cells in culture and in vivo. Nat Protoc 4:1798–1806
Ballot C, Kluza J, Martoriati A, Nyman U, Formstecher P, Joseph B, Bailly C, Marchetti P (2009) Essential role of mitochondria in apoptosis of cancer cells induced by the marine alkaloid Lamellarin D. Mol Cancer Ther 8:3307–3317
Kawabe Y, Ochi A (1991) Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8 + CD4 + T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature 349:245–248
Gallego M-A, Ballot C, Kluza J, Hajji N, Martoriati A, Castéra L, Cuevas C, Formstecher P, Joseph B, Kroemer G, Bailly C, Marchetti P (2008) Overcoming chemoresistance of non-small cell lung carcinoma through restoration of an AIF-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 27:1981–1992
Gallego M-A, Joseph B, Hemström TH, Tamiji S, Mortier L, Kroemer G, Formstecher P, Zhivotovsky B, Marchetti P (2004) Apoptosis-inducing factor determines the chemoresistance of non-small-cell lung carcinomas. Oncogene 23:6282–6291
Castera L, Hatzfeld-Charbonnier AS, Ballot C, Charbonnel F, Dhuiege E, Velu T, Formstecher P, Mortier L, Marchetti P (2009) Apoptosis-related mitochondrial dysfunction defines human monocyte-derived dendritic cells with impaired immuno-stimulatory capacities. J Cell Mol Med 13:1321–1335
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O (1995) A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9363–9367
Chang BD, Swift ME, Shen M, Fang J, Broude EV, Roninson IB (2002) Molecular determinants of terminal growth arrest induced in tumor cells by a chemotherapeutic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:389–394
O’Connor DS, Grossman D, Plescia J, Li F, Zhang H, Villa A, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC (2000) Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13103–13107
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8:61–70
Provenzano M, Bracci L, Wyler S, Hudolin T, Sais G, Gosert R, Zajac P, Palu G, Heberer M, Hirsch HH, Spagnoli GC (2006) Characterization of highly frequent epitope-specific CD45RA+/CCR7+/− T lymphocyte responses against p53-binding domains of the human polyomavirus BK large tumor antigen in HLA-A*0201 + BKV-seropositive donors. J Transl Med 4:47
Kurz DJ, Decary S, Hong Y, Erusalimsky JD (2000) Senescence-associated (beta)-galactosidase reflects an increase in lysosomal mass during replicative ageing of human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 20):3613–3622
Elmore LW, Rehder CW, Di X, McChesney PA, Jackson-Cook CK, Gewirtz DA, Holt SE (2002) Adriamycin-induced senescence in breast tumor cells involves functional p53 and telomere dysfunction. J Biol Chem 277:35509–35515
Rebbaa A, Zheng X, Chou PM, Mirkin BL (2003) Caspase inhibition switches doxorubicin-induced apoptosis to senescence. Oncogene 22:2805–2811
Mansilla S, Piña B, Portugal J (2003) Daunorubicin-induced variations in gene transcription: commitment to proliferation arrest, senescence and apoptosis. Biochem J 372:703–711
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G, Jarrard DF (2010) Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 102:1536–1546
O’Connor DS, Wall NR, Porter ACG, Altieri DC (2002) A p34(cdc2) survival checkpoint in cancer. Cancer Cell 2:43–54
Wang Q, Wu PC, Roberson RS, Luk BV, Ivanova I, Chu E, Wu DY (2011) Survivin and escaping in therapy-induced cellular senescence. Int J Cancer 128:1546–1558
Kanwar RK, Cheung CHA, Chang J-Y, Kanwar JR (2010) Recent advances in anti-survivin treatments for cancer. Curr Med Chem 17:1509–1515
Acknowledgments
This work received a financial support from INSERM, UNIVERSITE DE LILLE II, the Ligue Contre le Cancer (Comité de l’Aisne) and the Institut de Recherche Pierre Fabre (to PM). JK received a fellowship from the ARC. The authors acknowledge the Institut de Recherche Pierre Fabre (IRPF) for providing F96982 and F14512 and for useful discussions with the CROE research group.
Conflict of interest
Christian Bailly is employed by Pierre Fabre Médicament which provided a support to this work. The products F96982 and F14512 were synthesized by Pierre Fabre Médicament.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballot, C., Jendoubi, M., Kluza, J. et al. Regulation by survivin of cancer cell death induced by F14512, a polyamine-containing inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II. Apoptosis 17, 364–376 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0681-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0681-2