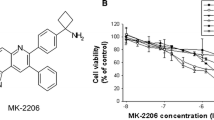
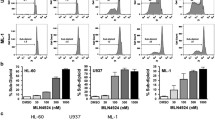
Abstract
The mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase (MEK)/ERK pathway was shown to be constitutively activated in a large number of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cells, suggesting the important roles of this pro-survival signaling in leukemogenesis and proliferation of AML cells. This study explored the impact of the MEK inhibitor AZD6244 on the effect of cytarabien (AraC), one of the most commonly used anti-leukemia agents, to induce growth arrest and apoptosis of AML cells. AZD6244 effectively blocked AraC-induced MEK/ERK activation and enhanced its ability to induce growth arrest and apoptosis of NB4 and HL60 cells in parallel with induction of DNA damage as measured by detection of γ-H2AX by Western Blot analysis, resulting in enhanced expression of p21waf1 and downregulation of c-Myc and Bcl-xl in these cells. Enhanced induction of apoptosis mediated by combination of AZD6244 and AraC was also shown in freshly isolated AML cells (n = 3). Taken together, concomitant administration of AraC and the inhibitor of MEK/ERK signaling may be useful for treatment of individuals with AML.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
Acute myelogeneous leukemia
- APL:
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia
- HDACI:
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- MEK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase
- AraC:
-
Cytarabine
References
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG (1998) Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res 74:49–139
Rubinfeld H, Seger R (2005) The ERK cascade: a prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol 31:151–174
Deng X, Kornblau SM, Ruvolo PP, May WS Jr (2001) Regulation of Bcl2 phosphorylation and potential significance for leukemic cell chemoresistance. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 28:30–37
Carter BZ, Milella M, Tsao T, McQueen T, Schober WD, Hu W, Dean NM, Steelman L, McCubrey JA, Andreeff M (2003) Regulation and targeting of antiapoptotic XIAP in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 17:2081–2089
Jia W, Yu C, Rahmani M, Krystal G, Sausville EA, Dent P, Grant S (2003) Synergistic antileukemic interactions between 17-AAG and UCN-01 involve interruption of RAF/MEK- and AKT-related pathways. Blood 102:1824–1832
Troppmair J, Rapp UR (2003) Raf and the road to cell survival: a tale of bad spells, ring bearers and detours. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1341–1345
Harada H, Quearry B, Ruiz-Vela A, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Survival factor-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylates BIM, inhibiting its association with BAX and proapoptotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15313–15317
Marani M, Hancock D, Lopes R, Tenev T, Downward J, Lemoine NR (2004) Role of Bim in the survival pathway induced by Raf in epithelial cells. Oncogene 23:2431–2441
Ley R, Balmanno K, Hadfield K, Weston C, Cook SJ (2003) Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein, Bim. J Biol Chem 278:18811–18816
Weston CR, Balmanno K, Chalmers C, Hadfield K, Molton SA, Ley R, Wagner EF, Cook SJ (2003) Activation of ERK1/2 by deltaRaf-1: ER* represses Bim expression independently of the JNK or PI3 K pathways. Oncogene 22:1281–1293
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW (2004) MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 23:5301–5315
Gélinas C, White E (2005) BH3-only proteins in control: specificity regulates MCL-1 and BAK-mediated apoptosis. Genes Dev 19:1263–1268
Minami Y, Yamamoto K, Kiyoi H, Ueda R, Saito H, Naoe T (2003) Different antiapoptotic pathways between wild-type and mutated FLT3: insights into therapeutic targets in leukemia. Blood 102:2969–2975
Chang F, Steelman LS, Lee JT, Shelton JG, Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, Franklin RA, McCubrey JA (2003) Signal transduction mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway from cytokine receptors to transcription factors: potential targeting for therapeutic intervention. Leukemia 17:1263–1293
Keating MJ, McCredie KB, Bodey GP, Smith TL, Gehan E, Freireich EJ (1982) Improved prospects for long-term survival in adults with acute myelogenous leukemia. JAMA 248:2481–2486
Rustum YM, Preisler HD (1979) Correlation between leukemic cell retention of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate and response to therapy. Cancer Res 39:42–49
Kim SC, Hahn JS, Min YH, Yoo NC, Ko YW, Lee WJ (1999) Constitutive activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in human acute leukemias: combined role of activation of MEK, hyperexpression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and downregulation of a phosphatase, PAC1. Blood 93:3893–3899
Tedeschi A, Montillo M, Strocchi E, Cafro AM, Tresoldi E, Intropido L, Nichelatti M, Marbello L, Baratè C, Camaggi CM, Morra E (2007) High-dose idarubicin in combination with Ara-C in patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a pharmacokinetic and clinical study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59:771–779
Candoni A, Michelutti A, Simeone E, Damiani D, Baccarani M, Fanin R (2006) Efficacy of liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine as reinduction chemotherapy in relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia despite expression of multidrug resistance–related proteins. Eur J Haematol 77:293–299
Giebel S, Krawczyk-Kulis M, Adamczyk-Cioch M, Jakubas B, Palynyczko G, Lewandowski K, Dmoszynska A, Skotnicki A, Nowak K, Holowiecki J, Polish Adult Leukemia Group (2006) Fludarabine, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone (FLAM) for the treatment of relapsed and refractory adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A phase study by the Polish Adult Leukemia Group (PALG). Ann Hematol 85:717–722
Cadman E, Farber L, Berd D, Bertino J (1977) Combination therapy for diffuse histiocytic lymphoma that includes antimetabolites. Cancer Treat Rep 61:1109–1116
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Meijerink JP, Ebus ME, Peters GJ, Noordhuis P, Janka-Schaub GE, Armstrong SA, Korsmeyer SJ, Pieters R (2003) Differential mRNA expression of Ara-C-metabolizing enzymes explains Ara-C sensitivity in MLL gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 101:1270–1276
Bhuyan BK, Fraser TJ, Gray LG, Kuentzel SL, Neil GL (1973) Cell-kill kinetics of several S-phase-specific drugs. Cancer Res 33:888–894
Kaspers GJ, Zwaan CM, Veerman AJ, Rots MG, Pieters R, Bucsky P, Domula M, Göbel U, Graf N, Havers W, Jorch N, Kabisch K, Spaar HJ, Ritter J, Creutzig U (1999) Cellular drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia: literature review and preliminary analysis of an ongoing collaborative study. Klin Padiatr 211:239–244
Yamada S, Hongo T, Okada S, Watanabe C, Fujii Y, Ohzeki T (2001) Clinical relevance of in vitro chemoresistance in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 15:1892–1897
Sarkar M, Han T, Damaraju V, Carpenter P, Cass CE, Agarwal RP (2005) Cytosine arabinoside affects multiple cellular factors and induces drug resistance in human lymphoid cells. Biochem Pharmacol 70:426–432
Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, Ballard J, Colwell H, Evans RJ, Parry J, Smith D, Brandhuber BJ, Gross S, Marlow A, Hurley B, Lyssikatos J, Lee PA, Winkler JD, Koch K, Wallace E (2007) Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 13:1576–1583
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Takeuchi S, Phillip Koeffler H, Yokoyama A (2008) MS-275, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with selectivity against HDAC1, induces degradation of FLT3 via inhibition of chaperone function of heat shock protein 90 in AML cells. Leuk Res 32:1382–1392
Early AP, Preisler HD, Slocum H, Rustum YM (1982) A pilot study of high-dose 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine for acute leukemia and refractory lymphoma: clinical response and pharmacology. Cancer Res 42:1587–1594
Mross K, Maessen P, van der Vijgh WJ, Gall H, Boven E, Pinedo HM (1988) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of epidoxorubicin and doxorubicin in humans. J Clin Oncol 6:517–526
Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin W, Morris C, Wilson D, Molina JR, Hanson LJ, Gore L, Chow L, Leong S, Maloney L, Gordon G, Simmons H, Marlow A, Litwiler K, Brown S, Poch G, Kane K, Haney J, Eckhardt SG (2008) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol 26:2139–2146
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Ruvolo VR, McQueen T, Evans RL, Bornmann WG, McCubrey J, Cortes J, Andreeff M (2008) Sorafenib induces apoptosis of AML cells via Bim-mediated activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leukemia 22:808–818
Yee KW, Schittenhelm M, O’Farrell AM, Town AR, McGreevey L, Bainbridge T, Cherrington JM, Heinrich MC (2004) Synergistic effect of SU11248 with cytarabine or daunorubicin on FLT3 ITD-positive leukemic cells. Blood 104:4202–4209
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Takeshita A, Taniguchi A, Komatsu N, Togitani K, Koeffler HP, Yokoyama A (2008) Blockade of MEK/ERK signaling enhances sunitinib-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of leukemia cells possessing activating mutations of the FLT3 gene. Leuk Res 32:865–872
Möllgård L, Deneberg S, Nahi H, Bengtzen S, Jonsson-Videsäter K, Fioretos T, Andersson A, Paul C, Lehmann S (2008) The FLT3 inhibitor PKC412 in combination with cytostatic drugs in vitro in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62:439–448
Miranda MB, McGuire TF, Johnson DE (2002) Importance of MEK-1/-2 signaling in monocytic and granulocytic differentiation of myeloid cell lines. Leukemia 16:683–692
Wang X, Studzinski GP (2001) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) defines the first phase of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation of HL60 cells. J Cell Biochem 80:471–482
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Koeffler HP, Yokoyama A (2008) Inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced growth arrest, apoptosis and acetylation of histone H3 on p21(waf1) promoter in acute myelogenous leukemia cell. Leukemia 22:1449–1452
Friday BB, Yu C, Dy GK, Smith PD, Wang L, Thibodeau SN, Adjei AA (2008) BRAF V600E disrupts AZD6244-induced abrogation of negative feedback pathways between extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Raf proteins. Cancer Res 68:6145–6153
Vigneron A, Cherier J, Barré B, Gamelin E, Coqueret O (2006) The cell cycle inhibitor p21waf1 binds to the myc and cdc25a promoters upon DNA damage and induces transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem 281:34742–34750
Miranda MB, Dyer KF, Grandis JR, Johnson DE (2003) Differential activation of apoptosis regulatory pathways during monocytic vs granulocytic differentiation: a requirement for Bcl-X(L)and XIAP in the prolonged survival of monocytic cells. Leukemia 17:390–400
Sanz C, Benito A, Silva M, Albella B, Richard C, Segovia JC, Insunza A, Bueren JA, Fernández-Luna JL (1997) The expression of Bcl-x is downregulated during differentiation of human hematopoietic progenitor cells along the granulocyte but not the monocyte/macrophage lineage. Blood 89:3199–3204
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (to Takayuki Ikezoe), The Kochi University President’s Discretionary Grant (to Takayuki Ikezoe), Takeda Science Foundation (to Takayuki Ikezoe), AstraZeneca Research Grant 2008 (to Takayuki Ikezoe) and Sagawa Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research (to Takayuki Ikezoe). Chie Nishioka is grateful for a JSPS Research Fellowship for Young Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishioka, C., Ikezoe, T., Yang, J. et al. Inhibition of MEK signaling enhances the ability of cytarabine to induce growth arrest and apoptosis of acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Apoptosis 14, 1108–1120 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0372-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0372-4