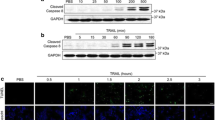
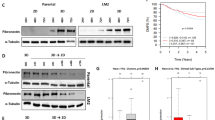
Abstract
Although multiple mechanisms have been implicated in chemoresistance, recent evidence has suggested that the attachment of cells to extracellular matrix proteins such as fibronectin (FN) may mediate the signals that participate in cell survival and resistance to apoptosis. We established previously that human ovarian cancer cells and breast cancer cells adhering to FN acquire a survival advantage through activation of the PI3-kinase/Akt2 pathway. However, the mechanism by which Akt2 regulates chemoresistance in adherent cells is unknown. In the present study, we have investigated the role of the interaction between the Akt2/survivin survivial pathway and the ASK1/p38 apoptotic pathway in the phenomenon of resistance to docetaxel. We show here that the resistance of FN-adhered A2780 or MDA-MB-231 cells to docetaxel requires survivin, and we present evidence that attenuation of the antiapoptotic activity of survivin is p38-dependent. The activation of p38 kinase in response to docetaxel, on the other hand, is abolished by FN adhesion. We further demonstrate that FN adhesion-mediated inhibition of p38 activation was governed by Akt2 via the promotion of direct protein association of ASK1 with p38. Our results indicate for the first time that p38 plays a critical role in FN adhesion-mediated resistance to docetaxel. The present findings may help us to understand the formation of FN adhesion-mediated chemoresistance and facilitate development of novel antineoplastic strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- CAM-DR:
-
Adhesion-mediated drug resistance
- FN:
-
Fibronectin
- PLL:
-
Polylysine
- PI 3K:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol 3′-kinase
- IAP:
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis
- ASK1:
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
References
Sarosy G, Reed E (1993) Taxol dose intensification and its clinical implications. J Natl Med Assoc 85(6):427–431
Rowinsky EK (1994) Update on the antitumor activity of Taxel in clinical trials. Ann Pharmacother 28:S18–S22
Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Kimura A, Hisamoto K, Hayakawa J, Nishio Y, Adachi K, Takahashi K, Arimoto-Ishida E, Nakatsuji Y, Tasaka K, Murata Y (2002) Inhibition of phosphorylation of BAD and Raf-1 by Akt sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel. J Biol Chem 277(36):33490–33500
Schiff PB, Horwitz SB (1981) Taxol assembles tubulin in the absence of exogenous guanosine 5′-triphosphate or microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry 20:3247–3252
Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB (1979) Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 277:665–667
Horwitz SB (1992) Mechanism of action of taxol. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:134–136
Cannistra SA (1993) Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med 329:1550–1559
Fisher DE (1994) Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell 78:539–542
Lowe SW, Bodis S, McClatchey A, Remington L, Ruley HE, Fisher DE, Housman DE, Jacks T (1994) p53 status and the efficacy of cancer therapy in vivo. Science 266:807–810
Dole MG, Clarke MF, Holman P, Benedict M, Lu J, Jasty R, Eipers P, Thompson CB, Rode C, Bloch C, Nunez G, Castle VP (1996) Bcl-xS enhances adenoviral vector-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 56:5734–5740
Chao DT, Linette GP, Boise LH, White LS, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 repress a common pathway of cell death. J Exp Med 182:821–828
Datta R, Manome Y, Taneja N, Boise LH, Weichselbaum R, Thompson CB, Slapak CA, Kufe D (1995) Overexpression of Bcl-XL by cytotoxic drug exposure confers resistance to ionizing radiation-induced internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Cell Growth Differ 6:363–370
Dole MG, Jasty R, Cooper MJ, Thompson CB, Nunez G, Castle VP (1995) Bcl-xL is expressed in neuroblastoma cells and modulates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 55:2576–2582
MacKeigan JP, Taxman DJ, Hunter D, Earp HS III, Graves LM, Ting JP (2002) Inactivation of the antiapoptotic phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway by the combined treatment of taxol and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 8(7):2091–2099
Olson JM, Hallahan AR (2004) p38 MAP kinase: a convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 10(3):125–129
Losa JH, Parada Cobo C, Viniegra JG, Sanchez-Arevalo Lobo VJ, Ramon y Cajal S, Sanchez-Prieto R (2003) Role of the p38 MAPK pathway in cisplatin-based therapy. Oncogene 22(26):3998–4006
Deacon K, Mistry P, Chernoff J, Blank JL, Patel R (2003) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest. Mol Biol Cell 14(5):2071–2087
Chao J-I, Kuo P-C, Hsu T-S (2004) Down-regulation of survivin in nitric oxide-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis of the human lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 279(19):20267–20276
Bu SZ, Huang Q, Jiang YM, Min HB, Hou Y, Guo ZY, Wei JF, Wang JW, Ni X, Zheng SS (2006) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinases is required for counteraction of 2-methoxyestradiol to estradiol-stimulated cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cells via phosphorylation Bcl-2. Apoptosis 11(3):413–425
Matsuzawa A, Nishitoh H, Tobiume K, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2002) Physiological roles of ASK1-mediated signal transduction in oxidative stress- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: advanced findings from ASK1 knockout mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 4(3):415–425
Yuan Z-Q, Feldman RI, Sussman GE, Coppola D, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2003) AKT2 inhibition of cisplatin-induced JNK/p38 and Bax activation by phosphorylation of ASK1. J Biol Chem 278(26):23432–23440
Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Kimura A, Nishio Y, Arimoto-Ishida E, Yada-Hashimoto N, Tasaka K, Murata Y (2004) Estrogen inhibits paclitaxel-induced apoptosis via the phosphorylation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in human ovarian cancer cell lines. Endocrinology 145(1):49–58
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine–threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 275:661–665
Kauffmann-Zeh A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Ulrich E, Gilbert C, Coffer P, Downward J, Evan G (1997) Suppression of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by Ras signalling through PI(3)K and PKB. Nature 385:544–548
Kennedy SG, Wagner AJ, Conzen SD, Jordan J, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN, Hay N (1997) The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway delivers an anti-apoptotic signal. Genes Dev 11:701–713
Ahmed NN, Grimes HL, Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Tsichlis PN (1997) Transduction of interleukin-2 antiapoptotic and proliferative signals via Akt protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U. S. A. 94:3627–3632
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Kim D, Dan HC, Park S, Yang L, Liu Q, Kaneko S, Ning J, He L, Yang H, Sun M, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2005) AKT/PKB signaling mechanisms in cancer and chemoresistance. Front Biosci 10:975–987
Yuan ZQ, Sun M, Feldman RI, Wang G, Ma X, Jiang C, Coppola D, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2000) Frequent activation of AKT2 and induction of apoptosis by inhibition of hosphoinositid–3-OH kinase/AKT pathway in human ovarian cancer. Oncogene 19:2324–2330
Testa JR, Bellacosa A (2001) AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10983–10985
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Delpeso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G (1997) Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278:687–689
Hazlehurst LA, Landowski TH, Dolton WS (2003) Role of the tumor microenvironment in mediating de novo resistance to drugs and physiological mediators of cell death. Oncogene 22:7396–7402
Ahmed N, Riley C, Rice G, Quinn M (2005) Role of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen and laminin in the regulation of ovarian carcinoma functions in response to a matrix microenvironment. Clin Exp Metastasis 22(5):391–402
Cordes N, Beinke C, Plasswilm L, van Beuningen D (2004) Irradiation and various cytotoxic drugs enhance tyrosine phosphorylation and beta(1)-integrin clustering in human A549 lung cancer cells in a substratum-dependent manner in vitro. Strahlenther Onkol 180(3):157–164
Najmi S, Korah R, Chandra R, Abdellatif M, Wieder R (2005) Flavopiridol blocks integrin-mediated survival in dormant breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11:2038–2046
Xing H, Weng D, Chen G, Tao W, Zhu T, Yang X, Wu M, Song X, Meng L, Wang S, Zhou J, Xu G, Lu Y, Ma D. Activation of fibronectin/PI-3K/Akt2 leads to chemoresistance to docetaxel by regulating survivin protein expression in ovarian and breast cancer cells. (submitted)
Fornaro M, Plescia J, Chheang S, Tallini G, Zhu YM, King M, Altieri DC, Languino LR (2003) Fibronectin protects prostate cancer cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis via the AKT/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem 278:50402–50411
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C, Chilvers ER, Dransfield I, Donnelly SC, Strieter R, Haslett C (1999) Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med 5:662–668
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110:673–687
Clark EA, Brugge JS (1995) Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science 268:233–239
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1999) Integrin signaling. Science 285:1028–1032
Schwartz MA, Ginsberg MH (2002) Networks and crosstalk: integrin signalling spreads. Nat Cell Biol 4:E65–E68
Watt FM (2002) Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. EMBO J 21:19–26
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L et al (1996) Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new integrin-linkedprotein kinase. Nature 379:91–96
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X et al (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennström S et al (1997) Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and proteinkinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J 16:2783–2793
Hughes PE, Renshaw MW, Pfaff M et al (1997) Suppression of integrin activation: a novel function of a rRas/Raf-initiated MAP kinase pathway. Cell 88:521–530
Reshkin SJ, Bellizzi A, Cardone RA, Tommasino M, Casavola V, Paradiso A (2003) Paclitaxel induces apoptosis via protein kinase A- and p38 mitogen-activated protein-dependent inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) NHE isoform 1 in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 9(6):2366–2373
Cheng Y, Chang LW, Tsou TC (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinases mediate arsenic-induced down-regulation of survivin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Arch Toxicol 80(6):310–318
Sarker KP, Biswas KK, Yamakuchi M, Lee KY, Hahiguchi T, Kracht M, Kitajima I, Maruyama I (2003) ASK1-p38 MAPK/JNK signaling cascade mediates anandamide-induced PC12 cell death. J Neurochem 85(1):50–61
Arvidsson Y, Hamazaki TS, Ichijo H, Funa K (2001) ASK1 resistant neuroblastoma is deficient in activation of p38 kinase. Cell Death Differ 8(10):1029–1037
Chang HY, Nishitoh H, Yang X, Ichijo H, Baltimore D (1998) Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx. Science. 281(5384):1860–1863
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (No. 30571950, 30371657) and the “973” Program of China (No. 2002 CB513100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Note: Hui Xing and yang Chao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, H., Cao, Y., Weng, D. et al. Fibronectin-mediated activation of Akt2 protects human ovarian and breast cancer cells from docetaxel-induced apoptosis via inhibition of the p38 pathway. Apoptosis 13, 213–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0158-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0158-5