Abstract
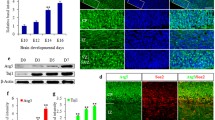
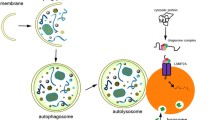
The deficiency of upstream regulators of the mitochondrial death pathway has been recently shown to trigger in vitro a cellular process of self-clearance with features of autophagy. We show here that, when Apaf1 (responsible for apoptosome formation) is downregulated in vivo in cortical precursors, cells express markers of neuronal differentiation, accumulate in ectopic cortical masses and show hallmarks of the beclin-1-dependent pathway of autophagy, probably activated by a depletion in growth factors in the cells' microenvironment. To visualize this process in a cell culture model system, we also used a neural precursor cell line to mimic growth factor starvation in the absence of the apoptosome and tracked autophagolysosome formation. Our findings demonstrate the existence of an interplay between the autophagy and apoptosis pathways in vivo in brain development, and possibly link the absence of apoptosis to the occurrence of pathological conditions associated with peculiar cellular morphotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de la Rosa EJ, de Pablo F (2000) Cell death in early neural development: beyond the neurotrophic theory. Trends Neurosci 23:454–458
Roth KA, D'Sa C (2001) Apoptosis and brain development. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 7:261–266
De Zio D, Giunta L, Corvaro M, Ferraro E, Cecconi F (2005) Expanding roles of programmed cell death in mammalian neurodevelopment. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:281–294
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, et al (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91:479–489
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):1–16
Salvesen GS, Renatus M (2002) Apoptosome: the seven-spoked death machine. Dev Cell 2:256–257
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H, et al (1998) Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 94:325–337
Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI, Roth KA, Gruss P (1998) Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development. Cell 94:727–737
Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, Elia AJ, Hakem A, Hakem R, et al (1998) Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell 94:739–750
Honarpour N, Du C, Richardson JA, Hammer RE, Wang X, Herz J (2000) Adult Apaf-1-deficient mice exhibit male infertility. Dev Biol 218:248–258
Baehrecke EH (2002) How death shapes life during development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:779–787
Levine B, Yuan J (2005) Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest 115:2679–2688
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C, Lindsten T, et al (2005) Growth factor regulation of autophagy and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell 120:237–248
Clarke PG (1990) Developmental cell death: morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol (Berl) 181:195–213
Kegel KB, Kim M, Sapp E, McIntyre C, Castano JG, Aronin N, et al (2000) Huntingtin expression stimulates endosomal-lysosomal activity, endosome tubulation, and autophagy. J Neurosci 20:7268–7278
Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, et al (2005) Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno-electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:113–122
Harris BS, Franz T, Ullrich S, Cook S, Bronson RT, Davisson MT (1997) Forebrain overgrowth (fog): a new mutation in the mouse affecting neural tube development. Teratology 55:231–240
Honarpour N, Gilbert SL, Lahn BT, Wang X, Herz J (2001) Apaf-1 deficiency and neural tube closure defects are found in fog mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9683–9687
Moreno S, Ferraro E, Eckert S, Cecconi F (2002) Apaf1 reduced expression levels generate a mutant phenotype in adult brain and skeleton. Cell Death Differ 9:340–342
Cozzolino M, Ferraro E, Ferri A, Rigamonti D, Quondamatteo F, Ding H, et al (2004) Apoptosome inactivation rescues proneural and neural cells from neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ 11:1179–1191
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K, Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H, et al (1999) Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 402:672–676
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, et al (2000) LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. Embo J 19:5720–5728
Kuan CY, Flavell RA, Rakic P (2000) Programmed cell death in mouse brain development. Results Probl Cell Differ 30:145–162
Levine B, Klionsky DJ (2004) Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 6:463–477
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S, et al (2004) Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 304:1500–1502
Boya P, Gonzalez-Polo RA, Casares N, Perfettini JL, Dessen P, Larochette N, et al (2005) Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 25:1025–1040
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB, et al (2004) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol 6:1221–1228
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N (2003) Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15077–15082
Hassoun J, Gambarelli D, Grisoli F, Pellet W, Salamon G, Pellissier JF, et al (1982) Central neurocytoma. An electron-microscopic study of two cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 56:151–156
Yuan J, Yankner BA (2000) Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature 407:802–809
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno, S., Imbroglini, V., Ferraro, E. et al. Apoptosome impairment during development results in activation of an autophagy program in cerebral cortex. Apoptosis 11, 1595–1602 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-9081-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-9081-4