Abstract
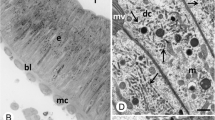
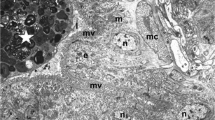
Detachment-induced apoptosis of enterocytes (anoikis) has not been investigated in vivo. Here we describe anoikis of fish enterocytes following detachment in a septicemia by Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, or following injection of its exotoxin. The in vivo study was complemented with an ex vivo time-lapse analysis using conditions duplicating the in vivo situation. Linings of enterocytes detached from intestine mucosa dissociate into isolated enterocytes which undergo caspase 3-mediated anoikis with cell rounding, loss of polarization, condensation of chromatin and fragmentation of the nuclear envelope, early swelling of mitochondria with rupture of the outer membrane, and brush border disappearance. One mechanism for brush border loss was shedding of apoptotic bodies incorporating the apical part of the enterocyte. Brush border disappearance was also associated with disassembly of the F-actin microvillar core and involved re-absorption into the cell, or expansion and vesiculation followed by shedding of microvillar fragments. The enterocyte anoikis terminates by secondary necrosis and lysis due to lack of elimination by phagocytosis of apoptosing enterocytes. The conditions prevailing in vivo in the gut lumen accelerate enterocyte secondary necrosis. Our results underscore the importance of analyzing anoikis under conditions similar to those occurring in vivo.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124:619–626
Meredith JE Jr, Fazeli B, Schwartz MA (1993) The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell 4:953–961
Radtke F, Clevers H (2005) Self-renewal and cancer of the gut: two sides of a coin. Science 307:1904–1909
Fouquet S, Lugo-Martinez VH, Faussat AM et al (2004) Early loss of E-cadherin from cell-cell contacts is involved in the onset of Anoikis in enterocytes. J Biol Chem 279:43061–43069
Grossmann J, Mohr S, Lapentina EG, Fiocchi C, Levine AD (1998) Sequential and rapid activation of select caspases during apoptosis of normal intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 274:G1117–G1124
Grossmann J, Walther K, Artinger M, Kiessling S, Scholmerich J (2001) Apoptotic signaling during initiation of detachment-induced apoptosis (“anoikis”) of primary human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ 12:147–155
Strater J, Wedding U, Barth TF et al (1996) Rapid onset of apoptosis in vitro follows disruption of beta 1-integrin/matrix interactions in human colonic crypt cells. Gastroenterology 110:1776–1784
Ikeda H, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M et al (1998) Apoptosis is a major mode of cell death caused by ischaemia and ischaemia/reperfusion injury to the rat intestinal epithelium. Gut 42:530–537
Miller TL, McGee DW (2002) Epithelial cells respond to proteolytic and non-proteolytic detachment by enhancing interleukin-6 responses. Immunology 105:101–110
Tarlton JF, Whiting CV, Tunmore D et al (2000) The role of up-regulated serine proteases and matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of a murine model of colitis. Am J Pathol 157:1927–1935
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD et al (1999) Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 27:1230–1251
Hotchkiss RS, Schmieg RE Jr, Swanson PE et al (2000) Rapid onset of intestinal epithelial and lymphocyte apoptotic cell death in patients with trauma and shock. Crit Care Med 28:3207–3217
Zhang C, Sheng ZY, Hu S et al (2002) The influence of apoptosis of mucosal epithelial cells on intestinal barrier integrity after scald in rats. Burns 28:731–737
Sousa S, Lecuit M, Cossart P (2005) Microbial strategies to target, cross or disrupt epithelia. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:489–498
Magariños B, Toranzo AE, Romalde JL (1996) Phenotypic and pathobiological characteristics of Pasteurella piscicida. Annu Rev Fish Dis 6:41–46
Thune RL, Stanley LA, Cooper RK (1993) Pathogenesis of Gram-negative bacterial infections in warmwater fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 3:37–68
do Vale A, Costa-Ramos C, Silva A et al (2006) Systemic macrophage and neutrophil destruction by secondary necrosis induced by a bacterial exotoxin in a Gram-negative septicemia. Cell Microbiol, In press
do Vale A, Marques F, Silva MT (2003) Apoptosis of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) neutrophils and macrophages induced by experimental infection with Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:129–144
do Vale A, Silva MT, dos Santos NMS et al (2005) AIP56, a novel plasmid-encoded virulence factor of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida with apoptogenic activity against sea bass macrophages and neutrophils. Mol Microbiol 58:1025–1038
Gilmore AP (2005) Anoikis. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1473–1477
Willingham MC (1999) Cytochemical methods for the detection of apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem 47:1101–1110
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–306
Reis MI, Nascimento DS, do Vale A, Silva MT, dos Santos NMS (2007) Molecular cloning and characterisation of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) caspase-3 gene. Mol Immunol 44:774–783
Silva MT, Appelberg R, Silva MN, Macedo PM (1987) In vivo killing and degradation of Mycobacterium aurum within mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun 55:2006–2016
Begg DA, Rodewald R, Rebhun LI (1978) The visualization of actin filament polarity in thin sections. Evidence for the uniform polarity of membrane-associated filaments. J Cell Biol 79:846–852
Murray HM, Wright GM, Goff GP (1996) A comparative histological and histochemical study of the post-gastric alimentary canal from three species of pleuronectid, the Atlantic halibut, the yellowtail flounder and the winter flounder. J Fish Biol 48:187–206
Mooseker MS (1985) Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Ann Rev Cell Biol 1:209–241
Secor SM (2005) Evolutionary and cellular mechanisms regulating intestinal performance of amphibians and reptiles. Integr Comp Biol 45:282–294
Saotome I, Curto M, McClatchey AI (2004) Ezrin is essential for epithelial organization and villus morphogenesis in the developing intestine. Dev Cell 6:855–864
Tyska MJ, Mackey AT, Huang JD et al (2005) Myosin-1a is critical for normal brush border structure and composition. Mol Biol Cell 16:2443–2457
Fujise T, Iwakiri R, Wu B et al (2006) Apoptotic pathway in the rat small intestinal mucosa is different between fasting and ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G110–G116
Haslett C (1999) Granulocyte apoptosis and its role in the resolution and control of lung inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:S5–S11
Hebert MJ, Takano T, Holthofer H, Brady HR (1996) Sequential morphologic events during apoptosis of human neutrophils. Modulation by lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. J Immunol 157:3105–3115
Gujral JS, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2003) Oncotic necrosis and caspase-dependent apoptosis during galactosamine-induced liver injury in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 190:37–46
Huhtala M, Heino J, Casciari D, de Luise A, Johnson MS (2005) Integrin evolution: insights from ascidian and teleost fish genomes. Matrix Biol 24:83–95
Babb SG, Marrs JA (2004) E-cadherin regulates cell movements and tissue formation in early zebrafish embryos. Dev Dyn 230:263–277
Bojarski C, Weiske J, Schoneberg T et al (2004) The specific fates of tight junction proteins in apoptotic epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 117:2097–2107
Weiske J, Schoneberg T, Schroder W et al (2001) The fate of desmosomal proteins in apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 276:41175–41181
Petit PX, Goubern M, Diolez P et al (1998) Disruption of the outer mitochondrial membrane as a result of large amplitude swelling: the impact of irreversible permeability transition. FEBS Lett 426:111–116
Vieira HL, Haouzi D, El Hamel C et al (2000) Permeabilization of the mitochondrial inner membrane during apoptosis: impact of the adenine nucleotide translocator. Cell Death Differ 7:1146–1154
Ludovico P, Sansonetty F, Silva MT, Corte-Real M (2003) Acetic acid induces a programmed cell death process in the food spoilage yeast Zygosaccharomyces bailii. FEMS Yeast Res 3:91–96
Silva RD, Sotoca R, Johansson B et al (2005) Hyperosmotic stress induces metacaspase- and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 58:824–34
Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Williamson EK, Schumacker PT, Thompson CB (1997) Bcl-xL regulates the membrane potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell 91:627–637
Levee MG, Dabrowska MI, Lelli JL Jr, Hinshaw DB (1996) Actin polymerization and depolymerization during apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Am J Physiol 271:C1981–C1992
Suarez-Huerta N, Mosselmans R, Dumont JE, Robaye B (2000) Actin depolymerization and polymerization are required during apoptosis in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 184:239–245
Hacker G (2000) The morphology of apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res 301:5–17
Kondo T, Takeuchi K, Doi Y et al (1997) ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin)-based molecular mechanism of microvillar breakdown at an early stage of apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139:749–758
Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M et al (1993) Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 364:806–809
Li MO, Sarkisian, MR, Mehal WZ, Rakic P, Flavell, RA (2003) Phosphatidylserine receptor is required for clearance of apoptotic cells. Science 302:1560–1563
Gregory CD, Devitt A (2004) The macrophage and the apoptotic cell: an innate immune interaction viewed simplistically? Immunology 113:1–14
Savill J, Fadok V (2000) Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature 407:784–788
Erjefalt J (2005) Transepithelial migration, necrosis and apoptosis as silent and pro-inflammatory fates of airway granulocytes. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:425–431
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Goreti Pinto, Alexandra Rema, Célia Lopes and Fátima Faria for assistance with histology. This work was supported by FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia) project POCI/MAR/56111/2004 funded by POCI 2010 and co-funded by FEDER, and grants SFRH/BPD/26816/2006 and SFRH/BPD/20881/2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
do Vale, A., Costa-Ramos, C., Silva, D.S.P. et al. Cytochemical and ultrastructural study of anoikis and secondary necrosis in enterocytes detached in vivo . Apoptosis 12, 1069–1083 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0040-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0040-x