Abstract
The structure of boundary layers (BLs) and wall heat flux is investigated as they evolve during the compression stroke in an optically accessible, single-cylinder research engine of passenger-car dimensions with a typical four-valve pent-roof design operated at motored and throttled conditions. Three-dimensional direct numerical simulations (DNS) of the compression stroke were carried out, which enable full resolution in space and time of all flow and temperature field structures in the entire domain, including the BLs. Since the high computational cost precludes calculation of the scavenging cycle, scale-resolving simulations were employed to provide initial fields for the DNS at intake valve closure. The analysis revealed that BLs deviate from ideal scaling laws commonly adopted in algebraic wall models, and that the non-zero streamwise pressure gradient correlates with changes in the near-wall profiles. Phenomenologically, such deviations are similar to those for developing BLs, and in particular for impinging flows. The momentum BL structure was found to be affected by the large-scale bulk flow motion, in contrast to the thermal BLs which exhibit a more structured behavior following the density increase due to compression. Inspection of the heat flux distribution confirmed the similarity between the flow and heat flux patterns and identified regions of intense heat flux, mainly in locations of strong directed flow towards the wall. The improved characterization of the boundary layer structure and its evolution during the compression stroke not only constitutes an important step towards improved understanding of near-wall phenomena in internal combustion engines, but the vast dataset also serves as a database for development of improved wall models.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
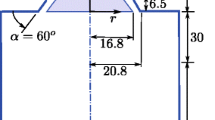
The z-axis is in the cylinder center and points to the piston, while the x-axis is directed from the intake to the exhaust side; the valve plane cuts through both intake and exhaust valves.
References
Alharbi, A.Y., Sick, V.: Investigation of boundary layers in internal combustion engines using a hybrid algorithm of high speed micro-PIV and PTV. Exp. Fluids 49, 949–959 (2010)
Angelberger, C., Poinsot, T., Delhay, B.: Improving Near-Wall Combustion and Wall Heat Transfer Modeling in SI Engine Computations. SAE Technical Paper 972881 (1997)
Arcoumanis, C., Whitelaw, J.H.: Fluid mechanics of internal combustion engines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 201, 57–74 (1987)
Bae, H.J., Lozano-Durán, A., Bose, S.T., Moin, P.: Dynamic slip wall model for large-eddy simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 859, 400–432 (2019)
Baum, E., Peterson, B., Böhm, B., Dreizler, A.: On the validation of LES applied to internal combustion engine flows: part 1—comprehensive experimental database. Flow Turbul. Combust. 92(2), 269–297 (2014)
Baumann, M., Mare, F.D., Janicka, J.: On the validation of large eddy simulation applied to internal combustion engine flows part II: numerical analysis. Flow Turbul. Combust. 92(1), 299–317 (2014)
Baumann, M., Di Mare, F., Janicka, J.: On the validation of large eddy simulation applied to internal combustion engine flows part II: numerical analysis. Flow Turbul. Combust. 92(1–2), 299–317 (2014)
Bolla, M., Impagnatiello, M., Keskinen, K., Giannakopoulos, G.K., Frouzakis, C.E., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K.: Development of an algebraic wall heat transfer model for LES in IC engines using DNS data. Proc. Combust. Inst. 38, 5811–5819 (2021)
Borée, J., Miles, P.C.: In-cylinder Flow. In: Encyclopedia of Automotive Engineering. Wiley (2014)
Borman, G., Nishiwaki, K.: Internal combustion engine heat transfer. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 13(1), 1–46 (1987)
Bose, S.T., Park, G.I.: Wall-modeled large-eddy simulation for complex turbulent flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 50, 535–561 (2018)
Bradshaw, P., Huang, G.P.: The law of the wall in turbulent flow. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 451, 165–188 (1995)
Buhl, S., Hain, D., Hartmann, F., Hasse, C.: A comparative study of intake and exhaust port modeling strategies for scale-resolving engine simulations. Int. J. Engine Res. 19(3), 282–292 (2017)
Buhl, S., Gleiss, F., Köhler, M., Hartmann, F., Messig, D., Brücker, C., Hasse, C.: A combined numerical and experimental study of the 3D tumble structure and piston boundary layer development during the intake stroke of a gasoline engine. Flow Turbul. Combust. 98(2), 579–600 (2017)
Catchirayer, M., Boussuge, J.-F., Sagaut, P., Montagnac, M., Papadogiannis, D., Garnaud, X.: Extended integral wall-model for large-eddy simulations of compressible wall-bounded turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 30(6), 065106 (2018)
Chiodi, M., Bargende, M.: Improvement of engine heat-transfer calculation in the three-dimensional simulation using a phenomenological heat-transfer model. SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-3601 (2001)
Choi, K.-S., Lumley, J.L.: The return to isotropy of homogeneous turbulence. J. fluid Mech. 436, 59–84 (2001)
Deville, M.O., Fischer, P.F., Mund, E.H.: High-Order Methods for Incompressible Fluid Flow. High-Order Methods for Incompressible Fluid Flow, Cambridge (2002)
Frouzakis, C.E., Giannakopoulos, G.K., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K., Schmitt, M., Tomboulides, A.G.: Direct numerical simulations for internal combustion premixed gas engines: first steps, challenges and prospects. In: Leipert, A. (ed.) Engine Combustion Processes—Current Problems and Modern Techniques, pp. 267–284. ESYTEC-Verlag, Erlangen (2017)
Giannakopoulos, G.K., Frouzakis, C.E., Boulouchos, K., Fischer, P.F., Tomboulides, A.G.: Direct numerical simulation of the flow in the intake pipe of an internal combustion engine. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 68(421), 257–268 (2017)
Giannakopoulos, G.K., Frouzakis, C.E., Fischer, P.F., Tomboulides, A.G., Boulouchos, K.: LES of the gas-exchange process inside an internal combustion engine using a high-order method. Flow Turbul. Combust. 104, 673–692 (2020)
Han, Z., Reitz, R.D.: A temperature wall function formulation for variable-density turbulent flows with application to engine convective heat transfer modeling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 40(3), 613–625 (1997)
Hasse, C., Sohm, V., Durst, B.: Numerical investigation of cyclic variations in gasoline engines using a hybrid URANS/LES modeling approach. Comput. Fluids 39(1), 25–48 (2010)
Hattori, H., Nagano, Y.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent heat transfer in plane impinging jet. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 25(5), 749–758 (2004)
Haworth, D.C.: Large-eddy simulation of in-cylinder flows. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 54(2), 175–185 (1999)
He, C., Leudesdorff, W., Mare, F.D., Sadiki, A., Janicka, J.: Analysis of in-cylinder flow field anisotropy in IC engine using large eddy simulation. Flow Turbul. Combust. 99(2), 353–383 (2017)
Heywood, J.B.: Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals. McGraw-Hill, New York (1988)
Ho, L.W., Patera, A.T.: A Legendre spectral element method for simulation of unsteady incompressible viscous free-surface flows. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 80(1–3), 355–366 (1990)
Hohenberg, G.F.: Advanced approaches for heat transfer calculations. SAE Transactions, 2788–2806 (1979)
Huang, P.C., Coleman, G.N., Bradshaw, P.: Compressible turbulent channel flows: DNS results and modelling. J. Fluid Mech. 305, 185–218 (1995)
Impagnatiello, M., Bolla, M., Keskinen, K., Giannakopoulos, G., Frouzakis, C.E., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K.: Systematic assessment of data-driven approaches for wall heat transfer modelling for LES in IC engines using DNS data. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 183, 122109 (2022)
Jainski, C., Lu, L., Dreizler, A., Sick, V.: High-speed micro particle image velocimetry studies of boundary-layer flows in a direct-injection engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 14(3), 247–259 (2013)
Janas, P., Ribeiro, M.D., Kempf, A., Schild, M., Kaiser, S.: Penetration of the Flame Into the Top-Land Crevice—Large-Eddy Simulation and Experimental High-Speed Visualization. SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-1907 (2015)
Janas, P., Wlokas, I., Böhm, B., Kempf, A.: On the evolution of the flow field in a spark ignition engine. Flow Turbul. Combust. 98(1), 237–264 (2017)
Keskinen, K., Nuutinen, M., Kaario, O., Vuorinen, V., Koch, J., Wright, Y.M., Larmi, M., Boulouchos, K.: Hybrid LES/RANS with wall treatment in tangential and impinging flow configurations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 65, 141–158 (2017)
Keskinen, K., Koch, J., Wright, Y.M., Schmitt, M., Nuutinen, M., Kaario, O., Vuorinen, V., Larmi, M., Boulouchos, K.: Numerical assessment of wall modelling approaches in scale-resolving in-cylinder simulations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 74, 154–172 (2018)
Kim, J., Moin, P., Moser, R.: Turbulence statistics in fully developed channel flow at low Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 177, 133–166 (1987)
Larsson, J., Kawai, S., Bodart, J., Bermejo-Moreno, I.: Large eddy simulation with modeled wall-stress: recent progress and future directions. Mech. Eng. Rev. 3(1), 15–00418 (2016)
Lav, C., Sandberg, R.D., Tanimoto, K., Terakado, K.: Pulsed impinging jets: momentum and heat-transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 187, 122548 (2022)
Liu, K., Haworth, D.C.: Development and assessment of POD for analysis of turbulent flow in piston engines. SAE Technical Paper 2011-01-0830 (2011)
Lumley, J.L.: Engines: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Ma, P.C., Ewan, T., Jainski, C., Lu, L., Dreizler, A., Sick, V., Ihme, M.: Development and analysis of wall models for internal combustion engine simulations using high-speed micro-PIV measurements. Flow Turbul. Combust. 98(1), 283–309 (2016)
Ma, P.C., Greene, M., Sick, V., Ihme, M.: Non-equilibrium wall-modeling for internal combustion engine simulations with wall heat transfer. Int. J. Eng. Res. 18(1–2), 15–25 (2017)
Mare, F.D., Knappstein, R., Baumann, M.: Application of LES-quality criteria to internal combustion engine flows. Comput. Fluids 89, 200–213 (2014)
Min, K., Cheng, W.K., Heywood, J.B.: The Effects of Crevices on the Engine-Out Hydrocarbon Emissions in SI Engines. SAE Trans. 103(3), 371–385 (1994)
Monty, J.P., Harun, Z., Marusic, I.: A parametric study of adverse pressure gradient turbulent boundary layers. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 32(3), 575–585 (2011)
Müller, S.H.R., Böhm, B., Gleißner, M., Grzeszik, R., Arndt, S., Dreizler, A.: Flow field measurements in an optically accessible, direct-injection spray-guided internal combustion engine using high-speed PIV. Exp. Fluids 48, 281–290 (2010)
NEK5000 Version v17.0. Argonne National Laboratory, IL, U.S.A. Available at https://nek5000.mcs.anl.gov
Nguyen, T., Janas, P., Lucchini, T., D’Errico, G., Kaiser, S., Kempf, A.: LES of Flow Processes in an SI Engine Using Two Approaches: OpenFoam and PsiPhi. SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-1121 (2014)
Nguyen, T.M., Proch, F., Wlokas, I., Kempf, A.M.: Large eddy simulation of an internal combustion engine using an efficient immersed boundary technique. Flow Turbul. Combust. 97, 191–230 (2016)
Noorani, A., Khoury, G.K.E., Schlatter, P.: Evolution of turbulence characteristics from stright to curved pipes. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 41, 16–26 (2013)
Park, G.I.: Wall-modeled large-eddy simulation of a high Reynolds number separating and reattaching flow. AIAA J. 55, 3709–3721 (2017)
Patel, A., Peeters, J.W.R., Boersma, B.J., Pecnik, R.: Semi-local scaling and turbulence modulation in variable property turbulent channel flows. Phys. Fluids 27(9), 095101 (2015)
Patel, S., Fischer, P.F., Min, M., Tomboulides, A.G.: A characteristic-based spectral element method for moving-domain problems. J. Sci. Comput. 79(1), 564–592 (2018)
Peterson, B., Baum, E., Böhm, B., Sick, V., Dreizler, A.: High-speed PIV and LIF imaging of temperature stratification in an internal combustion engine. Proc. Combust. Inst. 34(2), 3653–3660 (2013)
Plengsaard, C., Rutland, C.: Improved Engine Wall Models for Large Eddy Simulation (LES). SAE Technical Paper 2013-01-1097 (2013)
Plengsaard, C., Rutland, C.: Improved engine wall models for large eddy simulation (LES). SAE Technical Paper 2013-01-1097 (2013)
Pope, S.B.: Turbulent Flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Renaud, A., Ding, C.-P., Jakirlic, S., Dreizler, A., Böhm, B.: Experimental characterization of the velocity boundary layer in a motored IC engine. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 71, 366–377 (2018)
Rutland, C.J.: Large-eddy simulations for internal combustion engines—a review. Int. J. Engine Res. 12(421), 421–451 (2011)
Schiffmann, P., Gupta, S., Reuss, D., Sick, V., Yang, X., Kuo, T.W.: TCC-III engine benchmark for large-eddy simulation of IC engine flows. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 71(1), 3 (2016)
Schmitt, M., Boulouchos, K.: Role of the intake generated thermal stratification on the temperature distribution at top dead center of the compression stroke. Int. J. Engine Res. 17(8), 836–845 (2016)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C.E., Tomboulides, A.G., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of multiple cycles in a valve/piston assembly. Phys. Fluids 26(3), 035105 (2014)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C.E., Tomboulides, A.G., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of the compression stroke under engine-relevant conditions: evolution of the velocity and thermal boundary layers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 91, 948–960 (2015)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C.E., Wright, Y.M., Tomboulides, A.G., Boulouchos, K.: Investigation of wall heat transfer and thermal stratification under engine-relevant conditions using DNS. Int. J. Engine Res. 17, 63–75 (2015)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C.E., Tomboulides, A.G., Wright, Y.M., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of the effect of compression on the flow, temperature and composition under engine-like conditions. Proc. Combust. Inst. 35(3), 3069–3077 (2015)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C.E., Wright, Y.M., Tomboulides, A.G., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of the compression stroke under engine relevant conditions: local wall heat flux distribution. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 91, 948–960 (2015)
Shekhawat, Y., Paltrinieri, S., Schiffmann, P., Haworth, D., Fontanesi, S., Reuss, D., Sick, V.: An experimental and simulation study of turbulent flow in a homogeneous-charge spark-ignition engine. In: LES for Internal Combustion Engine Flows (LES4ICE)—Rueil-Malmaison (2014)
Spalding, D.B.: A single formula for the “law of the wall’’. J. Appl. Mech. 28(3), 455–458 (1961)
Tomboulides, A.G., Lee, J., Orszag, S.: Numerical simulation of low Mach number reactive flows. J. Sci. Comput. 12, 139–167 (1997)
Trelis CFD v16.3. Csimsoft. https://www.csimsoft.com/trelis-cfd
Trettel, A., Larsson, J.: Mean velocity scaling for compressible wall turbulence with heat transfer. Phys. Fluids 28(2), 026102 (2016)
Welch, C., Schmidt, M., Keskinen, K., Giannakopoulos, G., Boulouchos, K., Dreizler, A., Böhm, B.: The effects of intake pressure on in-cylinder gas velocities in an optically accessible single-cylinder research engine. SAE Technical Paper, No. 2020-01-0792 (2020)
Werner, H., Wengle, H.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over and around a cube in a plate channel. In: Turbulent Shear Flows 8, pp. 155–168. Springer (1993)
Woschni, G.: A universally applicable equation for the instantaneous heat transfer coefficient in the internal combustion engine. SAE Technical paper 670931 (1967)
Yang, X.I., Lv, Y.: A semi-locally scaled eddy viscosity formulation for les wall models and flows at high speeds. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 32(5), 617–627 (2018)
Yang, X.I., Sadique, J., Mittal, R., Meneveau, C.: Integral wall model for large eddy simulations of wall-bounded turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 27(2), 025112 (2015)
Yang, X.I., Park, G.I., Moin, P.: Log-layer mismatch and modeling of the fluctuating wall stress in wall-modeled large-eddy simulations. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2(10), 104601 (2017)
Funding
Financial support from the Forschungsvereinigung Verbrennungskraftmaschinen (FVV, Project No. 1286: “Wall heat transfer processes in spark ignition engines”), the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (BfE, Contract No. SI/501615-01) and the Swiss Competence Center for Energy Research - Efficient Technologies and Systems for Mobility (SCCER Mobility) is gratefully acknowledged. C.E.F. acknowledges the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Center of Excellence in Combustion (CoEC) project, grant Agreement No. 952181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GG, KK, JK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review and Editing. YMW, CF, KB: Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
N/A
Computational resources
This research used resources of the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility, which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility supported under Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357. Preliminary simulations were performed at the Swiss National Supercomputing Center (CSCS) under project ID 753.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Giannakopoulos, G.K., Keskinen, K., Koch, J. et al. Characterizing the Evolution of Boundary Layers in IC Engines by Combined Direct Numerical and Large-Eddy Simulations. Flow Turbulence Combust 110, 209–238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-022-00383-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-022-00383-1