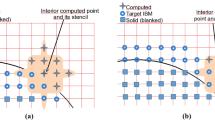
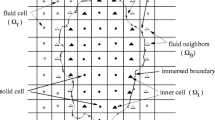
Abstract
An efficient Cartesian cut-cell/level-set method based on a multiple grid approach to simulate turbulent turbomachinery flows is presented. The finite-volume approach in an unstructured hierarchical Cartesian setup with a sharp representation of the complex moving boundaries embedded into the computational domain, which are described by multiple level-sets, ensures a strict conservation of mass, momentum, and energy. Furthermore, an efficient kinematic motion level-set interface method for the rotation of embedded boundaries described by multiple level-set fields on a computational domain distributed over several processors is introduced. This method allows the simulation of multiple boundaries rotating relatively to each other in a fixed frame of reference. To demonstrate the efficiency of the numerical method and the quality of the computed findings the generic test problem of a rotating cylinder surrounded by a stationary hull and the flow over a ducted rotating axial fan with a stationary turbulence generating grid at the inflow are simulated. The computational results of the axial fan show a good agreement with the experimental data.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blais, B., Lassaigne, M., Goniva, C., Fradette, L, Bertrand, F.: A semi-implicit immersed boundary method and its application to viscous mixing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 85, 136–146 (2016)
Blades, E., Marcum, D.: A sliding interface method for unsteady unstructured flow simulations. AIAA, 2005–5233 (2005)
Ferziger, J. H., Peric, M.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2002)
Mittal, R., Iaccarino, G.: Immersed boundary methods. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 37(1), 239–261 (2005)
Peskin, C. S.: Flow patterns around heart valves: A numerical method. J. Comput. Phys. 10(2), 252–271 (1972)
Peskin, C. S.: Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart. J. Comput. Phys. 25(3), 220–252 (1977)
Goldstein, D., Handler, R., Sirovich, L.: Modeling a no-slip flow boundary with an external force field. J. Comput. Phys. 105(2), 354–366 (1993)
Peskin, C. S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numerica 11, 479–517 (2002)
LeVeque, R., Li, Z.: The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31(4), 1019–1044 (1994)
Verzicco, R., Mohd-Yusof, J., Orlandi, P., Haworth, D.: Large eddy simulation in complex geometric configurations using boundary body forces. AIAA J. 38(3), 427–433 (2000)
Mohd-Yusof, J.: Combined immersed-boundary/b-spline methods for simulations of flow in complex geometries. Center Turb Res Ann Res Briefs, 317–327 (1997)
Hartmann, D., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: An adaptive multilevel multigrid formulation for Cartesian hierarchical grid methods. Comput. Fluids 37(9), 1103–1125 (2008)
Johansen, H., Colella, P.: A Cartesian grid embedded boundary method for Poisson’s equation on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 147, 60–85 (1998)
McCorquodale, P., Colella, P., Johansen, H.: A Cartesian grid embedded boundary method for the heat equation on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 173, 620–635 (2001)
Udaykumar, H., Mittal, R., Shyy, W.: Computation of solid–liquid phase fronts in the sharp interface limit on fixed grids. J. Comput. Phys. 153(2), 535–574 (1999)
Schneiders, L., Hartmann, D., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: An accurate moving boundary formulation in cut-cell methods. J. Comput. Phys. 235, 786–809 (2013)
Murman, S. M., Aftosmis, M. J., Berger, M. J.: Implicit approaches for moving boundaries in a 3-d Cartesian method. AIAA Paper, 2003–1119 (2003)
Iaccarino, G., Verzicco, R.: Immersed boundary technique for turbulent flow simulations. Appl. Mech. Rev. 56(3), 331–347 (2003)
Günther, C., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: A flexible level-set approach for tracking multiple interacting interfaces in embedded boundary methods. Comput. Fluids 102, 182–202 (2014)
Hartmann, D., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Differential equation based constrained reinitialization for level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 227(14), 6821–6845 (2008)
Hartmann, D., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: The constrained reinitialization equation for level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 229(5), 1514–1535 (2010)
Pogorelov, A., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Cut-cell method based large-eddy simulation of tip-leakage flow. Phys. Fluids 27(7), 075106 (2015)
Pogorelov, A., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Effects of tip-gap width on the flow field in an axial fan. IntJ Heat Fluid Flow. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2016.06.009 (2016)
Pogorelov, A., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Impact of periodic boundary conditions on the flow field in an axial fan. AIAA Paper, 2016–0610 (2016)
Schneiders, L., Günther, C., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: An efficient conservative cut-cell method for rigid bodies interacting with viscous compressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 311, 62–86 (2016)
You, D., Mittal, R., Wang, M., Moin, P.: Computational methodology for large-eddy simulation of tip-clearance flows. AIAA J. 42(2), 271–279 (2004)
You, D., Wang, M., Moin, P., Mittal, R.: Effects of tip-gap size on the tip-leakage flow in a turbomachinery cascade. Phys. Fluids 18(10), 105102 (2006)
You, D., Wang, M., Moin, P., Mittal, R.: Large-eddy simulation analysis of mechanisms for viscous losses in a turbomachinery tip-clearance flow. J. Fluid Mech. 586, 177–204 (2007)
You, D., Wang, M., Moin, P., Mittal, R.: Vortex dynamics and low-pressure fluctuations in the tip-clearance flow. J. Fluids Eng. 129(8), 1002–1014 (2007)
Tyagi, M., Acharya, S.: Large eddy simulation of turbulent flows in complex and moving rigid geometries using the immersed boundary method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 48, 691–722 (2005)
Posa, A., Lippolis, A., Verzicco, R., Balaras, E.: Large-eddy simulations in mixed-flow pumps using an immersed-boundary method. Comput. Fluids 47, 33–43 (2011)
Fadlun, E. A., Verzicco, R., Orlandi, P., Mohd-Yusof, J.: Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three dimensional complex flow simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 161, 35–60 (2000)
Hirt, C. W., Amsden, A. A., Cook, J. L.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian computing method for all flow speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 14(3), 227–253 (1974)
Sutherland, W.: The viscosity of gases and molecular force. Philos. Mag. 36, 507–531 (1893)
Udaykumar, H. S., Mittal, R., Rampunggoon, P., Khanna, A.: A sharp interface cartesian grid method for simulating flows with complex moving boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 174(1), 345–380 (2001)
Lintermann, A., Schlimpert, S., Grimmen, J. H., Günther, C., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Massively parallel grid generation on hpc systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 277, 131–153 (2014)
Boris, J. P., Grinstein, F. F., Oran, E. S., Kolbe, R. L.: New insights into large eddy simulation. Fluid Dyn. Res. 10(4-6), 199–228 (1992)
Alkishriwi, N., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: A large-eddy simulation method for low Mach number flows using preconditioning and multigrid. Comput. Fluids 35 (10), 1126–1136 (2006)
Meinke, M., Schröder, W., Krause, E., Rister, T.: A comparison of second- and sixth-order methods for large-eddy simulation. Comput. Fluids 31(4–7), 695–718 (2002)
Renze, P., Schröder, W., Meinke, M.: Large-eddy simulation of film cooling flows at density gradients. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29(1), 18–34 (2008)
Rütten, F., Schröder, W., Meinke, M.: Large-eddy simulation of low frequency oscillations of the Dean vortices in turbulent pipe. Phys. Fluids 17(3), 035107 (2005)
Mavriplis, D. J.: Revisiting the least-squares procedure for gradient reconstruction on unstructured meshes. AIAA, 2003–3986 (2003)
Liou, M. -S., Steffen, C.J. Jr: A new flux splitting scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 107(1), 23–39 (1993)
Berger, M. J., Aftosmis, M. J.: Progress towards a Cartesian cut-cell method for viscous compressible flow. AIAA, 2012–1301 (2012)
Hartmann, D., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: A strictly conservative Cartesian cut-cell method for compressible viscous flows on adaptive grids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200(9–12), 1038–1052 (2011)
Jameson, A., Mavriplis, D.: Finite volume solution of the two-dimensional Euler equations on a regular triangular mesh. AIAA J. 24(4), 616–618 (1986)
Schneiders, L., Günther, C., Grimmen, J., Meinke, M., Schröder, W.: Sharp resolution of complex moving geometries using a multi-cut-cell viscous flow solver. AIAA Paper, 2015–3427 (2015)
Sturm, M., Carolus, T.: Tonal fan noise of an isolated axial fan rotor due to inhomogeneous coherent structures at the intake. Noise Control Eng. J. 60(6), 699–706 (2012)
Zhu, T., Carolus, T. H.: Experimental and numerical investigation of the tip clearance noise of an axial fan. In: Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2013 (GT2013-94100). San Antonio (2013)
Acknowledgements
This study was funded under Grant No. 17747N (L238) by the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology via the ”Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen Otto von Guericke e.V. ” (AiF) and the ”Forschungsvereinigung Luft- und Trocknungstechnik e.V.” (FLT). Computing resources were provided by the High Performance Computing Center Stuttgart (HLRS) and by the Jülich Supercomputing Center (JSC) within a Large-Scale Project of the Gauss Center for Supercomputing (GCS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pogorelov, A., Schneiders, L., Meinke, M. et al. An Adaptive Cartesian Mesh Based Method to Simulate Turbulent Flows of Multiple Rotating Surfaces. Flow Turbulence Combust 100, 19–38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-017-9827-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-017-9827-9