Abstract
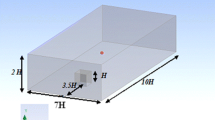
The objective of the present paper is to provide a detailed experimental and numerical investigation on the turbulent flow past a hemispherical obstacle (diameter D). For this purpose, the bluff body is exposed to a thick turbulent boundary layer of the thickness δ = D/2 at Re = 50,000. In the experiment this boundary layer thickness is achieved by specific fences placed in the upstream region of the wind tunnel. A detailed measurement of the upstream flow conditions by laser-Doppler and hot-film probes allows to mimic the inflow conditions for the complementary large-eddy simulation of the flow field using a synthetic turbulence inflow generator. These clearly defined boundary and operating conditions are the prerequisites for a combined experimental and numerical investigation of the flow field relying on the laser-Doppler anemometry and a finite-volume Navier-Stokes solver for block-structured curvilinear grids. The results comprise an analysis on the unsteady flow features observed in the vicinity of the hemisphere as well as a detailed discussion of the time-averaged flow field. The latter includes the mean velocity field as well as the Reynolds stresses. Owing to the proper description of the oncoming flow and supplementary numerical studies guaranteeing the choice of an appropriate grid and subgrid-scale model, the results of the measurements and the prediction are found to be in close agreement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acarlar, M.S., Smith, C.R.: A study of hairpin vortices in a laminar boundary layer. Part 1. Hairpin vortices generated by a hemisphere protuberance. J. Fluid Mech. 175, 1–41 (1987)
Adrian, R.J., Yao, C.S.: Power spectra of fluid velocities measured by laser-Doppler velocimetry. Exp. Fluid 5(1), 17–28 (1986)
Baker, C.J.: The turbulent horseshoe vortex. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 6(1), 9–23 (1980)
Benedict, L.H., Nobach, H., Tropea, C.: Estimation of turbulent velocity spectra from laser-Doppler data. Meas. Sci. Technol. 11(8), 1089–1104 (2000)
Bennington, J.L.: Effects of various shaped roughness elements in two-dimensional high Reynolds number turbulent boundary layers. Master thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg (2004)
Breuer, M., De Nayer, G., Münsch, M., Gallinger, T., Wüchner, R.: Fluid-structure interaction using a partitioned semi-implicit predictor-corrector coupling scheme for the application of large-eddy simulation. J Fluids Struct. 29, 107–130 (2012)
Broersen, P.M.T, de Waele, S., Bos, R.: The accuracy of time series analysis for laser-Doppler velocimetry. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Application of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon (2000)
Byun, G., Simpson, R.L.: Structure of three-dimensional separated flow on an axisymmetric bump. AIAA J. 44(5), 999–1008 (2006)
Byun, G., Simpson, R.L.: Surface-pressure fluctuations from separated flow over an axisymmetric bump. AIAA J. 48(10), 2397–2405 (2010)
Cheng, C.M., Fu, C.L.: Characteristic of wind loads on a hemispherical dome in smooth flow and turbulent boundary layer flow. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 98(6), 328–344 (2010)
Counihan, J.: An improved method of simulating an atmospheric boundary layer in a wind tunnel. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 3(2), 197–214 (1969)
Counihan, J.: Adiabatic atmospheric boundary layers: A review and analysis of data from the period 1880–1972. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 9(10), 871–905 (1975)
Durst, F., Schäfer, M.: A parallel block-structured multigrid method for the prediction of incompressible flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 22(6), 549–565 (1996)
Durst, F., Schäfer, M., Wechsler, K.: Efficient simulation of incompressible viscous flows on parallel computers. In: Hirschel, E.H. (ed.) Flow Simulation with High-Performance Computers II, Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics, vol. 52(1), pp 87–101, Vieweg (1996)
Ferziger, J.H., Perić, M.: Computational methods for fluid dynamics, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2002)
García-Villalba, M., Li, N., Rodi, W., Leschziner, M.A.: Large-eddy simulation of separated flow over a three-dimensional axisymmetric hill. J. Fluid Mech. 627, 55–96 (2009)
Germano, M., Piomelli, U., Moin, P., Cabot, W.H.: A dynamic subgrid-scale eddy viscosity model. Phys. Fluids A 3, 1760–1765 (1991)
Jacobs, W.: Strömung hinter einem einzelnen Rauhigkeitselement. Ingenieur-Archiv 9(5), 343–355 (1938)
Kharoua, N., Khezzar, L.: Large-eddy simulation study of turbulent flow around smooth and rough domes. Proc. IME C. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 227(12), 2686–2700 (2013)
Khosla, P.K., Rubin, S.G.: A diagonally dominant second-order accurate implicit scheme. Comput. Fluids 2(2), 207–209 (1974)
Kim, W.W., Menon, S.: Application of the localized dynamic subgrid-scale model to turbulent wall-bounded flows. AIAA Paper No. AIAA-97-0210 (1997)
Klein, M., Sadiki, A., Janicka, J.: A digital filter based generation of inflow data for spatially–developing direct numerical or large–eddy simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 186, 652–665 (2003)
Lawson, T.V.: Methods of producing velocity profiles in wind tunnels. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 2(1), 73–76 (1968)
Lilly, D.K.: A proposed modification of the Germano subgrid-scale closure method. Phys. Fluids A 4, 633–635 (1992)
Lund, T.S., Wu, X., Squires, K.D.: Generation of turbulent inflow data for spatially–developing boundary layer simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 140, 223–258 (1998)
Maher, F.J.: Wind loads on basic dome shapes. J. Struct. Div. 91(3), 219–228 (1965)
Manhart, M.: Vortex shedding from a hemisphere in a turbulent boundary layer. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 12(1), 1–28 (1998)
Martinuzzi, R., Tropea, C.: The flow around surface-mounted, prismatic obstacles placed in a fully developed channel flow. J. Fluids Eng. 115(1), 85–92 (1993)
Meroney, R.N., Letchford, C.W., Sarkar, P.P.: Comparison of numerical and wind tunnel simulation of wind loads on smooth, rough and dual domes immersed in a boundary layer. Wind Struct. 5(2–4), 347–358 (2002)
Nicoud, F., Ducros, F.: Subgrid-scale stress modelling based on the square of the velocity gradient tensor. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 62(3), 183–200 (1999)
Okamoto, S., Sunabashiri, Y.: Vortex shedding from a circular cylinder of finite length placed on a ground plane. J. Fluids Eng. 114(4), 512–521 (1992)
Pattenden, R.J., Turnock, S.R., Zhang, X.: Measurements of the flow over a low-aspect-ratio cylinder mounted on a ground plane. Exp. Fluids 39(1), 10–21 (2005)
Piomelli, U., Chasnov, J.R.: Large–eddy simulations: theory and applications. In: Hallbäck, M., Henningson, D., Johansson, A., Alfredson, P. (eds.) Turbulence and transition modeling, pp 269–331. Kluwer (1996)
Rhie, C.M., Chow, W.L.: Numerical study of the turbulent flow past an airfoil with trailing-edge separation. AIAA J. 21(11), 1525–1532 (1983)
Sakamoto, H., Arie, M.: Vortex shedding from a rectangular prism and a circular cylinder placed vertically in a turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 126, 147–165 (1983)
Sargison, J.E., Walker, G.J., Bond, V., Chevalier, G.: Experimental review of devices to artificially thicken wind tunnel boundary layers. In: Behnia, M., Lin, W., McBain, G.D. (eds.) Proceedings of the Fifteenth Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference (CD-ROM). AFMC00091. The University of Sydney, Sydney (2004)
Savory, E., Toy, N.: Hemisphere and hemisphere-cylinders in turbulent boundary layers. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 23, 345–364 (1986)
Savory, E., Toy, N.: The separated shear layers associated with hemispherical bodies in turbulent boundary layers. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 28(1), 291–300 (1988)
Scheit, C., Nusser, K., Hager, G., Becker, S., Zeiser, T., Wellein, G.: Optimizing the FASTEST-3D CFD code for massive parallelism. In: 26th International Conference on Comparative Fluid Dynamics, ParCFD, p 2014. Trondheim, Norway (2014)
Schlatter, P., Orlu, R., Li, Q., Brethouwer, G., Fransson, J.H.M., Johansson, A.V., Alfredsson, P.H., Henningson, D.S.: Turbulent boundary layers up to Re 𝜃 =2500 studied through simulation and experiment. Physics of Fluids 21(5), 51,702 (2009)
Schmidt, S., Breuer, M.: Extended synthetic turbulence inflow generator within a hybrid LES–URANS methodology for the prediction of non–equilibrium wall–bounded flows. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 95(4), 669–707 (2015).
Schmidt, S., Breuer, M.: Application and extension of a synthetic turbulence inflow generator within a hybrid LES–URANS methodology. In: Fröhlich, J., Kuerten, H., Geurts, B.J., Armenio, V. (eds.) ERCOFTAC Series, Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation X, 10th International ERCOFTAC Workshop on Direct and Large–Eddy Simulation: DLES-10, Limassol, Cyprus, May 27–29, 2015. Springer Science+Business Media B.V. To appear (2016)
Sergent, E.: Vers une methodologie de couplage entre la simulation des grandes echelles et les modeles statistiques. Ph.D. thesis, Ecully, Ecole Centrale de Lyon (2002)
Simpson, R.L., Long, C.H., Byun, G.: Study of vortical separation from an axisymmetric hill. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 23(5), 582–591 (2002)
Smagorinsky, J.: General circulation experiments with the primitive equations I: the basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 91(3), 99–165 (1963)
Spalart, P.R., Allmaras, S.R.: A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. AIAA J 94, 92–439 (1992)
Tamai, N., Asaeda, T., Tanaka, N.: Vortex structures around a hemispheric hump. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 39(3), 301–314 (1987)
Tamura, T., Kuwahara, K., Suzuki, M.: Numerical study of wind pressures on a domed roof and near wake flows. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 36, 1001–1010 (1990)
Taniguchi, S., Sakamoto, H., Kiya, M., Arie, M.: Time-averaged aerodynamic forces acting on a hemisphere immersed in a turbulent boundary. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 9(3), 257–273 (1982)
Tavakol, M.M., Abouali, O., Yaghoubi, M.: Large eddy simulation of turbulent flow around a wall mounted hemisphere. Appl. Math. Model. 39(13), 3596–3618 (2015)
Tavakol, M.M., Yaghoubi, M., Masoudi Motlagh, M.: Air flow aerodynamic on a wall-mounted hemisphere for various turbulent boundary layers. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 34(5), 538–553 (2010)
Taylor, T.J.: Wind pressures on a hemispherical dome. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 40(2), 199–213 (1992)
Toy, N., Moss, W.D., Savory, E.: Wind tunnel studies on a dome in turbulent boundary layers. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 11(1), 201–212 (1983)
Wilcox, D.C.: Turbulence modeling for CFD, 2nd edn. DCW Industries, Inc., La Cañada (1998)
Yaghoubi, M.A.: Air flow patterns around domed roof buildings. Renew. Energy 1(3), 345–350 (1991)
Yakhot, V., Orszag, S.A., Thangam, S., Gatski, T.B., Speziale, C.G.: Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique. Phys. Fluids 4(7), 1510–1520 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, J.N., De Nayer, G., Schmidt, S. et al. Experimental Investigation and Large-Eddy Simulation of the Turbulent Flow past a Smooth and Rigid Hemisphere. Flow Turbulence Combust 97, 79–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-015-9690-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-015-9690-5