Abstract
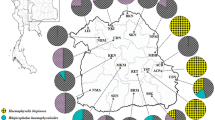
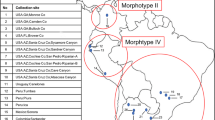
The taxonomy of ticks of the subgenus Boophilus has been extensively debated and is often complicated by the high intraspecific variation of morphological features between species. Notably, the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus is a species complex consisting of Rhipicephalus annulatus, Rhipicephalus australis and the three mitochondrial clades (A-C) of R. microplus. To gain insight into the taxonomic status of this species complex, we performed morphological and molecular analyses on these cattle ticks across four states in peninsular Malaysia. We morphologically identified 60 males and 104 females of R. microplus, 298 males and 374 females of R. australis, and one R. annulatus male in our field collection, of which the latter two species have never been recorded in Malaysia. However, all three morphologically identified species were molecularly assigned as R. microplus clade A based on the barcoding cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) analysis. The discrepancy between morphological and genetic data highlights an urgent need for further exploration and in-depth research into the taxonomic status of these sympatric tick species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschlimann A, Morel PC (1965) Boophilus geigyi n. sp. (Acarina: Ixodoidea), a new tick from cattle of West Africa. Acta Trop 22:162–168
Ali A, Parizi LF, Ferreira BR, da Silva Vaz Junior I (2016) A revision of two distinct species of Rhipicephalus: R. microplus and R. australis. Ciência Rural 46:1240–1248
Anastos G (1950) The scutate, or Ixodidae, of Indonesia. Entomol Am 30:1–144
Arthur DR (1960) Ticks, a monograph of the Ixodoidea. Part V—on the genera Dermacentor, Anocentor, Cosmiomma, Boophilus and Margaropus. Cambridge University Press, London
Bakkes DK, Ropiquet A, Chitimia-Dobler L, Matloa DE, Apanaskevich DA, Horak IG, Mans BJ, Matthee CA (2021) Adaptive radiation and speciation in Rhipicephalus ticks: a medley of novel hosts nested predator-prey food webs off-host periods and dispersal along temperature variation gradients. Mol Phylogenet Evol 162:162107178
Barker SC, Walker AR (2014) Ticks of Australia: the species that infest domestic animals and humans. Zootaxa 3816(1):1–144
Berry CM (2017) Resolution of the taxonomic status of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Dissertation, University of Glasgow
Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC (2014) Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol Phylogenet Evol 76:241–253
Davey RB, Osburn RL, Castillo C (1983) Longevity and mating behavior in males and parthenogenesis in females in hybridized Boophilus ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 20:614–617
Doeve W (1923) De teek op Celebes. Nederland Indisch Bl Diergeneesk 34:17–23
Estrada-Peña A, Venzal JM, Nava S, Mangold A, Guglielmone AA, Labruna MB, de la Fuente J (2012) Reinstatement of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) australis Fuller, the Australian cattle tick (Acari: Ixodidae) with redescription of the adult and larval stages. J Med Entomol 49:794–802
Fuller C (1899) Notes on the Queensland cattle tick and its relationship to the red water tick and the blue tick of Cape Colony (South Africa). Qld Agric J 4:389–394
Graham OH, Price MA, Trevino JL (1972) Cross-mating experiments with Boophilus annulatus and B. microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 9:531–537
Guglielmone AA, Robbins RG, Apanaskevich DA, Petney TN, Estrada-Peña A, Horak IG (2014) The hard ticks of the world (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae). Springer, New York
Guzmán PEE, Cuétara CF, Cano Argüelles AL, Castillo AF, Martínez YG, Fernández RR, Afonso YF, Soto YB, Alfaro YG, Méndez L, García AD, Estrada MP, Rodríguez-Mallon A (2021) Characterization of two Cuban colonies of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Rep 25:100591
Heyne H (1987) Differentiation of Boophilus decoloratus and Boophilus microplus. J S Afr Vet Assoc 57:251–252
Hoogstraal H (1956) African Ixodoidea 1. Ticks of the Sudan (with special reference to Equatoria Province and with preliminary reviews of Boophilus, Margaropus and Hyalomma). Department of the Navy, Bureau of Medicine and Surgery, Washington DC
Hoogstraal H, Kaiser MN (1960) Boophilus kohlsi n. sp. (Acarina: Ixodidae) from sheep and goats in Jordan. J Parasitol 46:441–448
Kaewmongkol S, Kaewmongkol G, Inthong N, Lakkitjaroen N (2015) Variation among Bm86 sequences in ticks collected from cattle across Thailand. Exp Appl Acarol 66:1–10
Katoh K, Rozewicki J, Yamada KD (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 20:1160–1166
Kohls GM (1957) Malaysian parasites. 18. Ticks (Ixodoidea) of Borneo and Malaya. Stud Institut Med Res 28:65–94
Koningsberger JC (1900) Onderzoekingen betreffende de teken (Ixodidae) van Nederlandsch-Indië. Teysmannia 11:56–64
Kovalev SY, Mikhaylishcheva MS, Mukhacheva TA (2015) Natural hybridization of the ticks Ixodes persulcatus and Ixodes pavlovskyi in their sympatric populations in Western Siberia. Infect Genet Evol 32:388–395
Kovalev SY, Golovljova IV, Mukhacheva TA (2016) Natural hybridization between Ixodes ricinus and Ixodes persulcatus ticks evidenced by molecular genetics methods. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 7:113–118
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Krantz GW, Walter DE (2009) A manual of acarology. Texas Tech University Press, Texas
Krijgsman BJ, Ponto SAS (1931) Die Verbreitung der Zecken in Niederländisch-Ostindien. Z Parasitenkd 4:140–146
Krijgsman BJ, Ponto SAS (1932) De teken van den Oost-Indischen Archipel. Veeartsenijk Meded 79:1–62
Lancaster WE (1939) Report of the Veterinary Department of the Federated Malay States. Fed Malay States 49–52
Lempereur L, Geysen D, Madder M (2010) Development and validation of a PCR–RFLP test to identify African Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) ticks. Acta Trop 114:55–58
Londt JGH, Arthur DR (1975) The structure and parasitic life cycle of Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1888) in South Africa (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Entomol Soc South Afr 38:321–340
Low VL, Tay ST, Kho KL, Koh FX, Tan TK, Lim YAL, Ong BL, Chandrawathani P, Yusoff NR, Mohd SA (2015) Molecular characterisation of the tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Malaysia: new insights into the cryptic diversity and distinct genetic assemblages throughout the world. Parasites Vectors 8:1–10
Ma M, Chen Z, Liu A, Ren Q, Liu J, Liu Z, Li Y, Yin H, Guan G, Luo J (2016) Biological parameters of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) fed on rabbits, sheep, and cattle. Korean J Parasitol 54:301–305
Minning W (1934) Beiträge zur Systematik und Morphologie der Zeckengattung Boophilus Curtice. Zeitschrift Parasitenk 7:1–43
Minning W (1935) Zur Kenntnis des Genus Boophilus Curtice I. Zeitschrift Parasitenk 7:719–721
Minning W (1936) Zur Kenntnis des Genus Boophilus Curtice II. Zeitschrift Parasitenk 8:365–370
Murrell A, Barker SC (2003) Synonymy of Boophilus Curtice, 1891 with Rhipicephalus Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae). Syst Parasitol 56:169–172
Nava S, Venzal JM, González-Acuña D, Martins TF, Guglielmone AA (2017) Ticks of the southern cone of America. Diagnosis, distribution, and hosts with taxonomy, ecology and sanitary importance. Academic Press, Cambridge
Neumann LG (1897) Revision de la famille des Ixodides. Mem Soc Zool Fr 10:324–420
Neumann LG (1901) Revision de la famille des Ixodides. Mem Soc Zool Fr 14:249–372
Nieschulz O (1924) Haemaphysalis bispinosa Neum., nieuw voor de fauna van Nederl-Indie. Tijdschr Diergeneesk 51:195
Puillandre N, Brouillet S, Achaz G (2021) ASAP: assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol Ecol Resour 21:609–620
Roy BC, Estrada-Peña A, Krücken J, Rehman A, Nijhof AM (2018) Morphological and phylogenetic analyses of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Myanmar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 9:1069–1079
Salmon DE, Stiles CW (1901) The cattle ticks (Ixodoidea) of the United States. Annual report of the United States. Department of Agriculture, Bureau of Animal Industry, Washington, pp 380–491
Sharif M (1928) A revision of the Indian Ixodidae with special reference to the collection in the Indian Museum. Records Indian Mus 30:217–344
Spickett AM, Malan JR (1978) Genetic incompatibility between Boophilus decoloratus (Koch, 1844) and Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1888) and hybrid sterility of Australian and South African Boophilus microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae). Onderstepoort J Vet Res 45:149–153
Stiles CW, Hassell A (1901) Notes on Parasites, 56: Boophilus australis present in Cuba, Porto Rico, Venezuela, and India. Bureau of Animal Industry, United States Department of Agriculture, Washington
Thompson GD, Osburn RL, Davey RB, Drummond RO, Price MA (1981) Hybrid sterility in cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Experientia 37:127–128
Uilenberg G (1962) Boophilus (Uroboophilus) fallax Minning, 1934 synonyme de Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1887) (Ixodidae). Rev Elev Med Vet Pays Trop 15:387–398
Walker AR, Bouattour A, Camicas JL (2003) Ticks of domestic animals in Africa: a guide to identification of species. The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to explicitly express their gratitude to Dr. Sangeetha A/P Sarvananthan from Pusat Ternakan Haiwan (PTH) Ulu Lepar, Pn. Aznida binti Che Ali from Ladang 16, Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), Pn. Suriaty binti Ramli from Institut Biodiversiti Veterinar Kebangsaan (IBVK), Pn. Sabariah binti Basir and Dr. Mohd Asraf bin Asmat from Institut Veterinar Malaysia (IVM), En. Taufik Mohd Noor and En. Muhammad Lutfi Zakaria for giving their permissions to visit the farm sites. Sincere thanks to IMMB for the laboratory facilities provided in this study. This study was supported by the Higher Institution Centre of Excellence (HICoE) program (MO002-2019) and Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine from Hamburg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazim, A.R., Low, V.L., Tappe, D. et al. Rhipicephalus annulatus, R. australis or R. microplus? Discordance between morphological and genetic data among three cattle tick species. Exp Appl Acarol 87, 119–131 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-022-00726-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-022-00726-7