Abstract
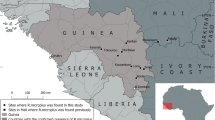
The invasive character of Rhipicephalus microplus was observed in Benin, the second West-African country from which this ticks species has been collected after the initial confirmed record in Ivory Coast in 2007. A cross-sectional study was carried out in the Department of Mono to examine the presence of the tick R. microplus. The survey covered 9 herds (villages) in an agro-ecological zone inhabited by agro-pastoralists, including the State Farm of Kpinnou that imported Girolando cattle from Brazil. Almost 800 ticks were sampled from 36 cattle, on average four cattle per village. The morphological identification revealed ticks of two different genera: Rhipicephalus and Amblyomma. Rhipicephalus microplus was the only representative of the species previously known as Boophilus or blue ticks. Its taxonomic identity was confirmed molecularly by PCR–RFLP. A comparison was made with the situation of R. microplus in Brazil.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus BM (1996) The history of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus in Australia and achievements in its control. Int J Parasitol 26:1341–1355
Baffi MA, de Souza GR, de Sousa CS, Ceron CR, Bonetti AM (2008) Esterase enzymes involved in pyrethroid and organophosphate resistance in a Brazilian population of Riphicephallus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari, Ixodidae). Mol Biochem Parasitol 160(1):70–73. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.03.009
Beugnet F, Costa R, Chardonnet L (1994) Adaptations des méthodes de lutte contre les tiques à l’extension du phénomène de chimiorésistance: exemple de Boophilus microplus en Nouvelle-Calédonie. Rev Méd Vét 145:931–940
Cardellino RA (2000) Animal genetic resources in southern Brazil. Arch Zootec 49:327–331
Castilho C, Gambini AL, Fernandes P, Trinca LA, Teixeira AB, Barros CM (2000) Synchronization of ovulation in crossbred dairy heifers using gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist, prostaglandin F2alpha and human chorionic gonadotrophin or estradiol benzoate. Braz J Med Biol Res 33(1):91–101
Coetzer CAW, Tustin RC (2004) Infectious diseases of livestock, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Graf JF, Gogolewski R, Leach-Bing N, Sabatini GA, Molento MB, Bordin EL, Arantes GJ (2004) Tick control: an industry point of view. Parasitology 129(S1):S427–S442
Jongejan F, Uilenberg G (2004) The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 129(supplement):S3–S14
Lempereur L, Geysen D, Madder M (2010) Development and validation of a PCR-RFLP test to identify African Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) ticks. Acta Trop 114(1):55–58
Li AY, Davey RB, Miller RJ, George JE (2005) Mode of inheritance of amitraz resistance in a Brazilian strain of the southern cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 37(3–4):183–198
Madder M, Thys E, Geysen D, Baudoux C, Horak I (2007) Boophilus microplus ticks found in West Africa. Exp Appl Acarol 43:233–234
Madder M, Thys E, Achi L, Toure A, De Deken R (2011) Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus: a most successful invasive tick species in West-Africa. Exp Appl Acarol 53(2):139–145
Martins JR, Furlong J (2001) Avermectin resistance of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus in Brazil. Vet Rec 149:64
Mendes MC, Lima CKP, Nogueira AHC, Yoshihara E, Chiebao DP, Gabriel FHL, Ueno TEH, Namindome A, Klafke GM (2011) Resistance to cypermethrin, deltamethrin and chlorpyriphos in populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) from small farms of the State of Sao Paulo. Braz Vet Parasitol 178(3–4):383–388
Temeyer KB, Pound JM, Miller JA, Chen AC, Pruett JH Jr, Guerrero F et al (2004) Organophosphate resistance in Mexican strains of Boophilus microplus: a major threat to the U.S. cattle industry. South Assoc Agric Sci Bull Biochem Biotechnol 17:43–51
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Belgian Development Cooperation (BDC) for the financial support of this research project as part of a Masters programme offered by the Institute of Tropical Medicine in Antwerp, Belgium. Also Nestor Ahomadegbe, herdsman at the state farm in Kpinnou is thanked for his assistance during the collection of field samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madder, M., Adehan, S., De Deken, R. et al. New foci of Rhipicephalus microplus in West Africa. Exp Appl Acarol 56, 385–390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9522-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9522-4