Abstract
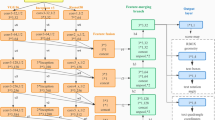
Scene text detection has drawn increasing attention due to its potential scalability to large-scale applications. Currently, a well-trained scene text detection model on a source domain usually has unsatisfactory performance when it is migrated to e large domain shift between them. To bridge this gap, this paper proposes a novel network integrates both text-specific Faster R-CNN (ts-FRCNN) and domain adaptation (ts-DA) into one framework. Compared to conventional FRCNN, ts-FRCNN designs a text-specific RPN to generate more accurate region proposals by considering the inherent characters of scene text, as well as text-specific RoI pooling to extract purer and sufficient fine-grained text features by adopting an adaptive asymmetric griding strategy. Compared to conventional domain adaptation, ts-DA adopts a triple-level alignment strategy to reduce the domain shift at the image, word and character levels, and builds a triple-consistency regularization among them, which significantly promotes domain-invariant text feature learning. We conduct extensive experiments on three representative transfer learning tasks: common-to-extreme scenes, real-to-real scenes and synthetic-to-real scenes. The experimental results demonstrate that our model consistently outperforms the previous methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun C, Ai Y, Wang S, Zhang W (2021) Mask-guided ssd for small-object detection. Appl Intell 51:3311–3322
Pal SK, Pramanik A, Maiti J, Mitra P (2021) Deep learning in multi-object detection and tracking: state of the art. Appl Intell 51:6400–6429
Serradilla O, Zugasti E, Rodriguez J, Zurutuza U (2022) Deep learning models for predictive maintenance: a survey, comparison, challenges and prospects. Appl Intell 52(10):10934–10964
Y. Liu, D. Jiang, C. Xu, Y. Sun, G. Jiang, B. Tao, X. Tong, M. Xu, G. Li, J. Yun, (2022) Deep learning based 3d target detection for indoor scenes, Appl Intell 1–14
Jhaldiyal A, Chaudhary N (2023) Semantic segmentation of 3d lidar data using deep learning: a review of projection-based methods. Appl Intell 53(6):6844–6855
Lin H, Yang P, Zhang F (2020) Review of scene text detection and recognition. Archives of computational methods in engineering 27(2):433–454
He W, Zhang X-Y, Yin F, Luo Z, Ogier J-M, Liu C-L (2020) Realtime multi-scale scene text detection with scale-based region proposal network. Pattern Recognition 98
Wang Y, Xie H, Zha Z, Tian Y, Fu Z, Zhang Y (2020) R-net: A relationship network for efficient and accurate scene text detection. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 23:1316–1329
Wang S, Liu Y, He Z, Wang Y, Tang Z (2020) A quadrilateral scene text detector with two-stage network architecture. Pattern Recognition 102 107230
Wu Q, Luo W, Chai Z, Guo G (2022) Scene text detection by adaptive feature selection with text scale-aware loss. Appl Intell 52(1):514–529
X. Ma, K. He, D. Zhang, D. Li, (2021) Pieed: Position information enhanced encoder-decoder framework for scene text recognition, Appl Intell 1–10
S. Xia, J. Kou, N. Liu, T. Yin, (2022) Scene text recognition based on two-stage attention and multi-branch feature fusion module, Appl Intell 1–14
Wu X, Tang B, Zhao M, Wang J, Guo Y (2023) Str transformer: a cross-domain transformer for scene text recognition. Appl Intell 53(3):3444–3458
W. Wu, N. Lu, E. Xie, Synthetic-to-real unsupervised domain adaptation for scene text detection in the wild, in: ACCV, 2020
F. Zhan, C. Xue, S. Lu, Ga-dan: Geometry-aware domain adaptation network for scene text detection and recognition, in: ICCV, 2019
Y. Chen, W. Wang, Y. Zhou, F. Yang, D. Yang, W. Wang, (2021) Self-training for domain adaptive scene text detection, in: ICPR, IEEE, pp. 850–857
G. Zeng, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhou, X. Yang, (2021) A cost-efficient framework for scene text detection in the wild, in: PRICAI, Springer, pp. 139–153
Z. Tian, C. Xue, J. Zhang, S. Lu, (2022) Domain adaptive scene text detection via subcategorization, arXiv:2212.00377
Khan T, Sarkar R, Mollah AF (2021) Deep learning approaches to scene text detection: a comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev 54:3239–3298
Liao M, Zou Z, Wan Z, Yao C, Bai X (2022) Real-time scene text detection with differentiable binarization and adaptive scale fusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 45(1):919–931
Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhou W, Wang Y, Yang Z, Bai X (2019) Textfield: Learning a deep direction field for irregular scene text detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 28(11):5566–5579
Liu Y, Jin L, Zhang S, Luo C, Zhang S (2019) Curved scene text detection via transverse and longitudinal sequence connection. Pattern Recognition 90:337–345
Liu X, Meng G, Pan C (2019) Scene text detection and recognition with advances in deep learning: a survey. Int J Doc Anal Recognit 22:143–162
B. Shi, X. Bai, S. Belongie, (2017) Detecting oriented text in natural images by linking segments, in: CVPR
Tang J, Yang Z, Wang Y, Zheng Q, Xu Y, Bai X (2019) Seglink++: Detecting dense and arbitrary-shaped scene text by instance-aware component grouping. Pattern recognition 96:106954
J. Ma, W. Shao, H. Ye, L. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Zheng, X. Xue, (2018) Arbitrary-oriented scene text detection via rotation proposals, IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 3111–3122
M.Liao, Z. Zhu, B. Shi, G.-s. Xia, X. Bai, (2018) Rotation-sensitive regression for oriented scene text detection, in: CVPR
X. Zhou, C. Yao, H. Wen, Y. Wang, S. Zhou, W. He, J. Liang, (2017) East: An efficient and accurate scene text detector, in: CVPR
Ma C, Sun L, Zhong Z, Huo Q (2021) Relatext: exploiting visual relationships for arbitrary-shaped scene text detection with graph convolutional networks. Pattern Recognition 111:107684
Zhang S, Liu Y, Jin L, Wei Z, Shen C (2020) Opmp: An omnidirectional pyramid mask proposal network for arbitrary-shape scene text detection. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 23:454–467
Naiemi F, Ghods V, Khalesi H (2021) A novel pipeline framework for multi oriented scene text image detection and recognition. Expert Systems with Applications 170:114549
C.-K. ChÃC. S. Chan, C.-L. Liu, (2020) Total-text: toward orientation robustness in scene text detection. Int J Doc Anal Recognit 23(1):31–52
W. Wang, E. Xie, X. Li, W. Hou, T. Lu, G. Yu, S. Shao, (2019) Shape robust text detection with progressive scale expansion network, in: CVPR
H. Wang, P. Lu, H. Zhang, M. Yang, X. Bai, Y. Xu, M. He, Y. Wang, W. Liu, 2020 All you need is boundary: Toward arbitrary-shaped text spotting, in: AAAI
Y. Liu, H. Chen, C. Shen, T. He, L. Jin, L. Wang, (2020) Abcnet: Real-time scene text spotting with adaptive bezier-curve network, in: CVPR
Wang X, Yi Y, Peng J, Wang K (2022) Arbitrary-shaped scene text detection by predicting distance map. Appl Intell 52(12):14374–14386
M. Liao, Z. Wan, C. Yao, K. Chen, X. Bai, (2020) Real-time scene text detection with differentiable binarization, in: AAAI
Zhu Y, Du J (2021) Textmountain: Accurate scene text detection via instance segmentation. Pattern Recognition 110 107336
Sun X, Xv H, Dong J, Zhou H, Chen C, Li Q (2020) Few-shot learning for domain-specific fine-grained image classification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 68(4):3588–3598
G. Yang, M. Ding, Y. Zhang, (2022) Bi-directional class-wise adversaries for unsupervised domain adaptation, Appl Intell 1–17
J. Zhao, X. Zhou, G. Shi, N. Xiao, K. Song, J. Zhao, R. Hao, K. Li, (2022) Semantic consistency generative adversarial network for cross-modality domain adaptation in ultrasound thyroid nodule classification, Appl Intell 1–15
D.-q. Xu, M.-a. Li, (2022) A dual alignment-based multi-source domain adaptation framework for motor imagery eeg classification, Appl Intell 1–23
Kang G, Wei Y, Yang Y, Zhuang Y, Hauptmann A (2020) Pixel-level cycle association: A new perspective for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:3569–3580
Zhang L, Wang X, Yang D, Sanford T, Harmon S, Turkbey B, Wood BJ, Roth H, Myronenko A, Xu D et al (2020) Generalizing deep learning for medical image segmentation to unseen domains via deep stacked transformation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 39(7):2531–2540
Wang Q, Gao J, Li X (2019) Weakly supervised adversarial domain adaptation for semantic segmentation in urban scenes. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 28(9):4376–4386
H. Chen, Y. Jiang, M. Loew, H. Ko, (2022) Unsupervised domain adaptation based covid-19 ct infection segmentation network, Appl Intell 1–14
Chen C, Wang G (2021) Iosuda: an unsupervised domain adaptation with input and output space alignment for joint optic disc and cup segmentation. Appl Intell 51:3880–3898
Flores CF, Gonzalez-Garcia A, van de Weijer J, Raducanu B (2019) Saliency for fine-grained object recognition in domains with scarce training data. Pattern Recognition 94:62–73
Song K, Wei X-S, Shu X, Song R-J, Lu J (2020) Bi-modal progressive mask attention for fine-grained recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 29:7006–7018
Wei X-S, Song Y-Z, Mac Aodha O, Wu J, Peng Y, Tang J, Yang J, Belongie S (2021) Fine-grained image analysis with deep learning: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 44(12):8927–8948
Wang X, Tang J, Tan S (2022) Three-way enhanced part-aware network for fine-grained sketch-based image retrieval. Appl Intell 52(10):10901–10916
Xia W, Yang Y, Xue J-H (2020) Unsupervised multi-domain multimodal image-to-image translation with explicit domain-constrained disentanglement. Neural Networks 131:50–63
Tan DS, Lin Y-X, Hua K-L (2020) Incremental learning of multi-domain image-to-image translations. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 31(4):1526–1539
G. Wang, H. Shi, Y. Chen, B. Wu, (2022) Unsupervised image-to-image translation via long-short cycle-consistent adversarial networks, Appl Intell 1–17
W. Li, X. Liu, Y. Yuan, (2022) Scan++: Enhanced semantic conditioned adaptation for domain adaptive object detection, IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
P. Oza, V. A. Sindagi, V. V. Sharmini, V. M. Patel, (2023) Unsupervised domain adaptation of object detectors: A survey, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Yin G, Yu M, Wang M, Hu Y, Zhang Y (2022) Research on highway vehicle detection based on faster r-cnn and domain adaptation. Appl Intell 52(4):3483–3498
Li S, Huang J, Hua X-S, Zhang L (2021) Category dictionary guided unsupervised domain adaptation for object detection. AAAI 35:1949–1957
J. Deng, W. Li, Y. Chen, L. Duan, (2021) Unbiased mean teacher for cross-domain object detection, in: CVPR, pp. 4091–4101
Y.-J. Li, X. Dai, C.-Y. Ma, Y.-C. Liu, K. Chen, B. Wu, Z. He, K. Kitani, P. Vajda, (2022) Cross-domain adaptive teacher for object detection, in: CVPR, pp. 7581–7590
Wang J, Shen T, Tian Y, Wang Y, Gou C, Wang X, Yao F, Sun C (2022) A parallel teacher for synthetic-to-real domain adaptation of traffic object detection. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles 7(3):441–455
Shi X, Li Z, Yu H (2021) Adaptive threshold cascade faster rcnn for domain adaptive object detection. Multimed Tools Appl 80:25291–25308
L. Zhao, L. Wang, (2022) Task-specific inconsistency alignment for domain adaptive object detection, in: CVPR, pp. 14217–14226
D. Liu, C. Zhang, Y. Song, H. Huang, C. Wang, M. Barnett, W. Cai, (2022) Decompose to adapt: Cross-domain object detection via feature disentanglement, IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Shan Y, Lu WF, Chew CM (2019) Pixel and feature level based domain adaptation for object detection in autonomous driving. Neurocomputing 367:31–38
R. Ramamonjison, A. Banitalebi-Dehkordi, X. Kang, X. Bai, Y. Zhang, (2021) Simrod: A simple adaptation method for robust object detection, in: ICCV, pp. 3570–3579
Munir MA, Khan MH, Sarfraz M, Ali M (2021) Ssal: Synergizing between self-training and adversarial learning for domain adaptive object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst 34:22770–22782
Y. Chen, W. Li, C. Sakaridis, D. Dai, V. L. Gool, (2018) Domain adaptive faster r-cnn for object detection in the wild, in: CVPR
C. Li, D. Du, L. Zhang, L. Wen, T. Luo, Y. Wu, P. Zhu, (2020) Spatial attention pyramid network for unsupervised domain adaptation, in: ECCV, Springer, pp. 481–497
Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Mao, (2021) Rpn prototype alignment for domain adaptive object detector, in: CVPR, pp. 12425–12434
W. Li, X. Liu, Y. Yuan, (2022) Sigma: Semantic-complete graph matching for domain adaptive object detection, in: CVPR, pp. 5291–5300
Y. Ganin, S. V. Lempitsky, (2015) Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation, in: ICML
S. Ren, K. He, B. R. Girshick, J. Sun, (2017) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 1137–1149
X. He, R. Wang, X. Li, X. Chen, C. Guo, L. Wen, C. Gao, L. Liu, (2019) Htstl: Head-and-tail search network with scale-transfer layer for traffic sign text detection, IEEE Access 118333–118342
N. Nayef, F. Yin, I. Bizid, H. Choi, Y. Feng, D. Karatzas, Z. Luo, U. Pal, C. Rigaud, J. Chazalon, W. Khlif, M. M. Luqman, J.-C. Burie, C.-L. Liu, J.-M. Ogier, (2017) Icdar2017 robust reading challenge on multi-lingual scene text detection and script identification - rrc-mlt, in: ICDAR
D. Karatzas, F. Shafait, S. Uchida, M. Iwamura, G. i. L. Bigorda, R. S. Mestre, J. Mas, F. D. Mota, A. J. Almaz n, P. d. l. L. Heras, (2013) Icdar 2013 robust reading competition, in: ICDAR
A. Gupta, A. Vedaldi, A. Zisserman, (2016) Synthetic data for text localisation in natural images, in: CVPR
F. Zhan, S. Lu, C. Xue, (2018) Verisimilar image synthesis for accurate detection and recognition of texts in scenes, in: ECCV, pp. 249–266
D. Chen, L. Lu, Y. Lu, R. Yu, S. Wang, L. Zhang, T. Liu, (2019) Cross-domain scene text detection via pixel and image-level adaptation, in: ICONIP, Springer, pp. 135–143
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U21A20518, No.61976086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Yuan, J., Li, M. et al. A Text-Specific Domain Adaptive Network for Scene Text Detection in the Wild. Appl Intell 53, 26827–26839 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04873-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04873-1