Abstract
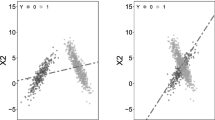
Visual recognition has become inevitable in applications such as object detection, biometric tracking, autonomous vehicles, and social media platforms. The images have multiple factors such as image resolution, illumination, perspective and noise, resulting in a significant mismatch between the training and testing domains. Unsupervised Domain adaptation (DA) has proven an effective way to reduce the differences by adapting the knowledge from a richly labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. But the real-time datasets are non-linear and high-dimensional. Though kernelization can handle the non-linearity in data, the dimension needs to be reduced as the salient features of the data lie in a low-dimensional subspace. Current dimensionality reduction approaches in DA preserve either the global or local part of information of manifold data. Specifically, the data manifold’s static (subject-invariant) and dynamic (intra-subject variant) information need to be considered during knowledge transfer. Therefore, to preserve both parts of information Globality-Locality Preserving Projection (GLPP) method is applied to the labeled source domain. The other objectives are preserving the discriminant information and variance of target data, and minimizing the distribution and subspace differences between the domains. With all these objectives, we propose a unique method known as Kernelized Global-Local Discriminant Information Preservation for unsupervised DA (KGLDIP). KGLDIP aims to reduce the discrimination discrepancy geometrically and statistically between the two domains after calculating two projection matrices for each domain. Intensive experiments are conducted using five standard datasets and the analysis reveals that the proposed algorithm excels the other state-of-the-art DA approaches.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Q (2022) Breckon TP (2022) Cross-domain structure preserving projection for heterogeneous domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 123:108362
Shao L, Zhu F, Li X (2014) Transfer learning for visual categorization: a survey. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(5):1019–1034
Zhang J, Li W, Ogunbona P (2017) Joint geometrical and statistical alignment for visual domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 1859–1867
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2013) Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp 2200–2207
Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K (2012) Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, pp 2066–2073
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M, Tuytelaars T (2013) Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. pp 2960–2967
Gou J, Yang Y, Yi Z, Lv J, Mao Q, Zhan Y (2020) Discriminative globality and locality preserving graph embedding for dimensionality reduction. Expert Syst Appl 144:113079
Sanodiya RK, Sharma C, Mathew J (2019) Unified framework for visual domain adaptation using globality-locality preserving projections. In: Neural Information Processing: 26th International Conference, ICONIP 2019, Sydney, NSW, Australia, December 12–15, 2019, Proceedings, Part I 26. Springer, pp 340–351
Zhao J, Li L, Deng F, He H, Chen J (2022) Discriminant Geometrical and Statistical Alignment With Density Peaks for Domain Adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 52(2):1193–1206. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2994875
Pilancı M, Vural E (2022) Domain Adaptation on graphs by learning aligned graph bases. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 34(2):587–600. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.2984212
Huang S, Elgammal A, Huangfu L, Yang D, Zhang X (2014) Globality-locality preserving projections for biometric data dimensionality reduction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. pp. 15–20
Sanodiya RK, Yao L (2020) Linear discriminant analysis via pseudo labels: a unified framework for visual domain adaptation. IEEE Access 8:200073–200090
Pan SJ, Tsang IW, Kwok JT, Yang Q (2010) Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 22(2):199–210
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2014) Transfer joint matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 1410–1417
Lekshmi R, Sanodiya RK, Linda R, Jose BR, Mathew J (2021) Kernelized transfer feature learning on manifolds. In: International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Springer, pp 297–308
Liang J, He R, Sun Z, Tan T (2018) Aggregating randomized clustering-promoting invariant projections for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(5):1027–1042
Wang J, Feng W, Chen Y, Yu H, Huang M, Yu PS (2018) Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. pp 402–410
Liu J, Li J, Lu K (2018) Coupled local-global adaptation for multi-source transfer learning. Neurocomputing 275:247–254
Ghifary M, Balduzzi D, Kleijn WB, Zhang M (2016) Scatter component analysis: a unified framework for domain adaptation and domain generalization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(7):1414–1430
Zhang W, Wu D (2020) Discriminative joint probability maximum mean discrepancy (DJP-MMD) for domain adaptation. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE, pp 1–8
Sun B, Saenko K (2015) Subspace distribution alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. BMVC 4:24–1
Gholenji E, Tahmoresnezhad J (2020) Joint discriminative subspace and distribution adaptation for unsupervised domain adaptation. Appl Intell 50(7):2050–2066
Kang Q, Yao S, Zhou M, Zhang K, Abusorrah A (2020) Enhanced subspace distribution matching for fast visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst 7(4):1047–1057
Luo L, Chen L, Hu S, Lu Y, Wang X (2020) Discriminative and geometry-aware unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(9):3914–3927
Wei J, Liang J, He R, Yang J (2018) Learning discriminative geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 1–6
Liang J, He R, Sun Z, Tan T (2019) Exploring uncertainty in pseudo-label guided unsupervised domain adaptation. Pattern Recogn 96:106996
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, Jordan M (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, pp 97–105
Sun B, Saenko K (2016) Deep coral: Correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp 443–450
Sun H, Chen X, Wang L, Liang D, Liu N, Zhou H (2020) C2dan: An improved deep adaptation network with domain confusion and classifier adaptation. Sensors 20(12):3606
Luo Y, Ren C, Dai D, Yan H (2022) Unsupervised domain adaptation via discriminative manifold propagation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(03):1653–1669
Huang S, Yang D, Zhou J, Zhang X (2015) Graph regularized linear discriminant analysis and its generalization. Pattern Anal Appl 18:639–650
Balakrishnama S, Ganapathiraju A (1998) Linear discriminant analysis-a brief tutorial. Institute for Signal and information Processing 18(1998):1–8
He X, Niyogi P (2003) Locality preserving projections. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16
Li J, Jing M, Lu K, Zhu L, Shen HT (2019) Locality preserving joint transfer for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(12):6103–6115. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2924174
Dornaika F, Baradaaji A, El Traboulsi Y (2021) Joint Label Inference and Discriminant Embedding. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33(9):4413–4423
Huang S, Yang D, Yang F, Ge Y, Zhang X, Lu J (2013) Face recognition via globality-locality preserving projections. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/1311.1279
Huang S, Elgammal A, Lu J, Yang D (2015) Cross-speed gait recognition using speed-invariant gait templates and globality-locality preserving projections. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(10):2071–2083
Gretton A, Borgwardt K, Rasch M, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2006) A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. Adv Neural Inf Proces Syst 19
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2002) The CMU pose, illumination, and expression (PIE) database. In: Proceedings of Fifth IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition. IEEE, pp 53–58
Griffin G, Holub A, Perona P (2007) Caltech-256 object category dataset
Sanodiya RK, Yao L (2020) A subspace based transfer joint matching with laplacian regularization for visual domain adaptation. Sensors 20(16):4367
Nene SA, Nayar SK, Murase H et al (1996) Columbia object image library (COIL-100)
Huang L-Q, Liu Z-G, Dezert J (2021) Cross-domain pattern classification with distribution adaptation based on evidence theory. IEEE Trans Cybern
Venkateswara H, Eusebio J, Chakraborty S, Panchanathan S (2017) Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 5018–5027
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Pan SJ, Yu PS (2014) Adaptation regularization: a general framework for transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(5):1076–1089
Xu Y, Fang X, Wu J, Li X, Zhang D (2015) Discriminative transfer subspace learning via low-rank and sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(2):850–863
Herath S, Harandi M, Porikli F (2017) Learning an invariant Hilbert space for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 3845–3854
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S, Feng W, Shen Z (2017) Balanced distribution adaptation for transfer learning. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 1129–1134
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vision 115(3):211–252
Sanodiya RK, Mathew J, Paul B, Jose BA (2019) A kernelized unified framework for domain adaptation. IEEE Access 7:181381–181395
Li S, Song S, Huang G, Ding Z, Wu C (2018) Domain invariant and class discriminative feature learning for visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(9):4260–4273
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Saenko K, Darrell T (2014) Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3474
Lu H, Shen C, Cao Z, Xiao Y, van den Hengel A (2018) An embarrassingly simple approach to visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(7):3403–3417
Chen C, Chen Z, Jiang B, Jin X (2019) Joint domain alignment and discriminative feature learning for unsupervised deep domain adaptation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 33:3296–3303
Sanodiya RK, Mathew J, Saha S, Tripathi P (2020) Particle swarm optimization based parameter selection technique for unsupervised discriminant analysis in transfer learning framework. Appl Intell 50(10):3071–3089
Zhang L, Fu J, Wang S, Zhang D, Dong Z, Chen CLP (2020) Guide subspace learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(9):3374–3388
Noori Saray S, Tahmoresnezhad J (2021) Joint distinct subspace learning and unsupervised transfer classification for visual domain adaptation. SIViP 15(2):279–287
Tian L, Tang Y, Hu L, Ren Z, Zhang W (2020) Domain adaptation by class centroid matching and local manifold self-learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:9703–9718
Lu Y, Wang W, Yuan C, Li X, Lai Z (2020) Manifold transfer learning via discriminant regression analysis. IEEE Trans Multimedia 23:2056–2070
Shi K, Liu Z, Lu W, Ou W, Yang C (2022) Unsupervised domain adaptation based on adaptive local manifold learning. Comput Electr Eng 100:107941
Yu C, Wang J, Chen Y, Huang M (2019) Transfer learning with dynamic adversarial adaptation network. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 778–786
Zhou Q, Wang S et al (2021) Cluster adaptation networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. Image Vis Comput 108:104137
Long M, Zhu H, Wang J, Jordan MI (2017) Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, pp 2208–2217
Saito K, Watanabe K, Ushiku Y, Harada T (2018) Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 3723–3732
Sun B, Feng J, Saenko K (2017) Correlation alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. Domain Adaptation in Computer Vision Applications 153–171
Van der Maaten L, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using T-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9(11)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
R, L., Sanodiya, R.K., Jose, B.R. et al. Kernelized global-local discriminant information preservation for unsupervised domain adaptation. Appl Intell 53, 25412–25434 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04706-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-023-04706-1