Abstract
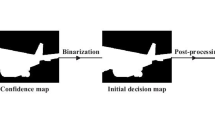
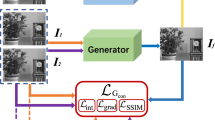
Multi-focus image fusion (MFIF) combines information by utilizing various image sequences of the same scenes at different of focus depths. The available MFIF method based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) lacks the feature complementarity of multi-focus images, resulting in the loss of details and noises in the generated decision maps. To resolve this problem, the learning framework of a joint distribution was developed via Siamese conditional generative adversarial network (SCGAN). This framework utilizes Siamese conditional generator that produces two-probabilistic feature maps from multi-focus images with complementary information. Additionally, the proposed framework also considers both the diversity of datasets and network convergence. The structural sparse objective function is designed to penalize the prediction of low confidence by sparse calculation of the rows and columns of the matrix. So, it endows a better Dice coefficient with higher values and improves the generalization capability of the GAN. Also, Wasserstein Divergence (DIV) is utilized to optimize the discrimination performance with stable training. In both quantitative and qualitative experiments, SCGAN has better scores on MFIF than other methods.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo X, Nie R, Cao J, Zhou D, Mei L, He K (2019) FuseGAN: learning to fuse multi-focus image via conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Transac Multimed 21:1982–1996
Fang SS, Chai ZY, Li YL (2021) Dynamic multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for IoT services. Appl Intell 51(1):1–24
Bai X, Zhang Y, Zhou F, Xue B (2015) Quadtree-based multi-focus image fusion using a weighted focus-measure. Inform Fusion 22:105–118
Daniel, Ebenezer (2018) Optimum Wavelet-Based Homomorphic Medical Image Fusion Using Hybrid Genetic–Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Sensors J:6804–6811
Zhou Z, Bo W, Sun L, Dong M 2016 (2016) “Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters,” Information Fusion, vol. 30.
Chi Y, Li J, Fan H (2022) Pyramid-attention based multi-scale feature fusion network for multispectral pan-sharpening[J]. Appl Intell 52(5):5353–5365
Fakhari F, Mosavi MR, Lajvardi MM (2017) Image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation: an image energy approach. IET Image Process 11(11):1041–1049
Xl A, Fz A, Htb C, Yc A, Wz A (2021) “Multi-focus image fusion based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform and residual removal,” Signal Processing, vol. 184
Chatterjee P, Ghoshal S, Biswas B et al (2015) Medical image fusion using Daubechies complex wavelet and near set[M]//transactions on computational science XXV. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 90–111
Kong W, Lei Y, Zhao H (2014) Adaptive fusion method of visible light and infrared images based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and fast non-negative matrix factorization. Infrared Phys Technol 67:161–172
Li S, Kang X, Fang L, Hu J, Yin H (2017) “Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art,” Information Fusion, vol. 33
Kumar S, K. B. (2015) Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter. Sig Image Video Proc 9(5):1193–1204
Kumar BKS (2013) “Multifocus and multispectral image fusion based on pixel significance using discrete cosine harmonic wavelet transform,” Signal,Image&Video Processing
Yang Y, Yang M, Huang S, Que Y, Ding M, Sun J (2017) Multifocus image fusion based on extreme learning machine and human visual system. IEEE Access 5:6989–7000
Dong Q, Zhou Z, Bo W, L Sun, "Weighted gradient-based fusion for multi-spectral image with steering kernel and structure tensor."
Wei H, Zhongliang, Jing (2007) “Evaluation of focus measures in multi-focus image fusion,” Pattern Recognition Letters
Li S, Kang X, Hu J (2013) Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2864–2875
Lewis JJ, O’Callaghan R, Nikolov SG, Bull DR, Canagarajah N (2007) Pixel- and region-based image fusion with complex wavelets. Inform Fusion 8(2):119–130
Tang L, Yuan J, Zhang H, Jiang X, Ma J (2022) PIAFusion: a progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inform Fusion 83:79–92
Wang J, Qu H, Wei Y, Xie M, Xu J, Zhang Z (2022) Multi-focus image fusion based on quad-tree decomposition and edge-weighted focus measure. Signal Process 198:108590
Ma B, Yin X, Wu D, Shen H, Ban X, Wang Y (2022) End-to-end learning for simultaneously generating decision map and multi-focus image fusion result. Neurocomputing 470:204–216
Liu Y, Chen X, Peng H, Wang Z (2017) Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network[J]. Inform Fusion 36:191–207
Tang H, Xiao B, Li W, Wang G (2018) “Pixel convolutional neural network for multi-focus image fusion,” INFORMATION SCIENCES, pp. S0020025517311647
Ma B, Zhu Y, Yin X, Ban X, Huang H, Mukeshimana M (2021) Sesf-fuse: an unsupervised deep model for multi-focus image fusion[J]. Neural Comput & Applic 33(11):5793–5804
Yu ZA, Yu LB, Peng SC, Han YA, Xz D, Li ZA (2020) IFCNN: a general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inform Fusion 54:99–118
Wu J, Huang Z, Thoma J, et al. (2018) Wasserstein divergence for gans[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV): 653–668
Miao QG, Cheng S, Xu PF, Yang M, Shi YB (2011) A novel algorithm of image fusion using shearlets. Opt Commun 284(6):1540–1547
Petrovic VS, Xydeas CS (2004) Gradient-based multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans Image Proc 13(2):228–237
Zhang Q, Guo B-l (2009) Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Signal Process 89(7):1334–1346
Peter J (2006) The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. Fund Pap Wavelet Theory 31(4):28
Nencini F, Garzelli A, Baronti S, Alparone L (2007) Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Information Fus 8(2):143–156
Yang B, Li S (2009) Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 59(4):884–892
Liu Y, Wang Z (2014) Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation. Image Processing Iet 9(5):347–357
Li S, Kang X, Hu J, Yang B (2013) Image matting for fusion of multi-focus images in dynamic scenes. Inform Fusion 14(2):147–162
Aslantas V, Kurban R (2010) Fusion of multi-focus images using differential evolution algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 37(12):8861–8870
Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z (2015) Multi-focus image fusion with dense SIFT. Inform Fusion 23:139–155
Li H, Wu X-J, Durrani T (2018) “Multi-focus noisy image fusion using low-rank representation,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.09325
Li J, Guo X, Lu G, Zhang B, Zhang D (2020) DRPL: Deep Regression Pair Learning for Multi-Focus Image Fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process PP(99):1–1
Zhang H, Xu H, Xiao Y, Guo X, Ma J (2020) Rethinking the image fusion: a fast unified image fusion network based on proportional maintenance of gradient and intensity. Proc AAAI ConfArtificial Intel 34(7):12797–12804
Zhang X (2021) Deep learning-based multi-focus image fusion: a survey and a comparative study. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Du C, Gao S (2017) Image segmentation-based multi-focus image fusion through multi-scale convolutional neural network. IEEE Access:1–1
Jiang L, Fan H, Li J (2022) A multi-focus image fusion method based on attention mechanism and supervised learning. Appl Intell 52(1):339–357
Guo J, Pang Z, Bai M, Xie P, Chen Y (2021) Dual generative adversarial active learning. Appl Intell 51(8):5953–5964
Zong X, Chen Z, Wang D (2021) Local-CycleGAN: a general end-to-end network for visual enhancement in complex deep-water environment. Appl Intell 51(4):1947–1958
Huang J, Ding W, Lv J, Yang J, Dong H, Del Ser J, Xia J, Ren T, Wong ST, Yang G (2022) Edge-enhanced dual discriminator generative adversarial network for fast MRI with parallel imaging using multi-view information. Appl Intell:1–18
Zhang H, Le Z, Shao Z, Xu H, Ma J (2021) MFF-GAN: an unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Inform Fusion 66:40–53
Ma J, Yu W, Liang P, Li C, Jiang J (2019) FusionGAN: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inform Fusion 48:11–26
Ma J, Xu H, Jiang J, Mei X, Zhang X-P (2020) DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4980–4995
Goodfellow IJ, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial networks. Adv Neural Inf Proces Syst 3:2672–2680
X. Mao, Q. Li, H. Xie, R. Y. Lau, Z. Wang, and S. Paul Smolley, "Least squares generative adversarial networks." pp. 2794–2802
X. Li, X. Sun, Y. Meng, J. Liang, F. Wu, and J. Li, “Dice loss for data-imbalanced NLP tasks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.02855, 2019
Mao X, Li Q, Xie H, et al. (2017) Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision: 2794–2802
Marszalek M, Schmid C (2007) "Accurate object localization with shape masks." pp. 1–8
Nejati M, Samavi S, Shirani S (2015) Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inform Fusion 25:72–84
Shreyamsha Kumar B (2013) Multifocus and multispectral image fusion based on pixel significance using discrete cosine harmonic wavelet transform. SIViP 7(6):1125–1143
Xu H, Ma J, Jiang J, Guo X, Ling H (2020) U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(1):502–518
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell G "Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation." pp. 1451–1460
Wang L, Lu H, Wang Y, Feng M, Wang D, Yin B, Ruan X, "Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision." pp. 136–145
KingaD A (2015) A methodforstochasticoptimization. Anon. InternationalConferenceon Learning Representations. SanDego, ICLR
Lin J (1991) Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 37(1):145–151
Tang S, Shen C, Zhang G (2016) Adaptive regularized scheme for remote sensing image fusion. Front Earth ence 10(2):236–244
Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou X, Zhang D, "A comprehensive evaluation of full reference image quality assessment algorithms." pp. 1477–1480
Hossny M, Nahavandi S, Creighton D (2008) Comments on 'Information measure for performance of image fusion'. Electron Lett 44(18):1066–1067
Alexandre EB (2017) IFT-SLIC: geração de superpixels com base em agrupamento iterativo linear simples e transformada imagem-floresta. Universidade de São Paulo
Marszalek M, Schmid C (2007) Accurate object localization with shape masks[C]//2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE: 1–8
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No.61662087, No.61966037, and No.61463052, the Research Foundation of Yunnan Province No.2019FA044, Provincial Foundation for Leaders of Disciplines in Science and Technology No.2019HB121, Postdoctoral fund of the Ministry of education of China No.2017 M621591 and No.2017 M621586, and in part by Yunnan University of the China Postgraduate Science Foundation under Grant 2020z77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Qian, W., Nie, R. et al. Siamese conditional generative adversarial network for multi-focus image fusion. Appl Intell 53, 17492–17507 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04406-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04406-2