Abstract
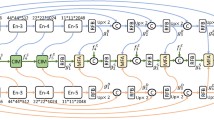
Previous RGB-D saliency detection methods adopt different fusion schemes to fuse the RGB images and depth maps or their saliency maps. However, both the feature maps from different modalities and the different features within the same maps are not of equal importance. To address this problem, We present a new precise RGB-D saliency detection framework in this work that selectively fuses features of different resolutions from two modalities, considering the global location and local detail complementarity. Depth data contains superior position discrimination, which has been shown to enhance saliency prediction. However, errors or missing areas in a depth map or random distribution along an object boundary will introduce negative effect. Therefore, we design a backbone network and an edge detection module that can select useful representations from RGB images and depth maps with attention mechanism and effectively integrate macroscopic and microscopic features from the two modalities. The accurate location of salient objects with fine edge details is realized by cross-modal selective fusion and complementation. We also propose a triple loss function to improve the credibility of the network for hard sample detection. Extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluation experiments on six benchmark datasets show that our method has a superior performance compared with 11 existing state-of-the-art methods with various evaluation metrics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borji A, Itti L (2013) State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Intell 35(1):185–207. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.89
Banks M S, Read J C A, Allison R S, Watt S J (2012) Stereoscopy and the human visual system. SMPTE Mot Imaging J 121(4):24–43. https://doi.org/10.5594/j18173
Wang H, Li Z, Li Y, Gupta B B, Choi C (2020) Visual saliency guided complex image retrieval. Pattern Recogn Lett 130:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.08.010
Wei S, Liao L, Li J, Zheng Q, Yang F, Zhao Y (2019) Saliency inside: learning attentive CNNs for content-based image retrieva. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(9):4580–4593. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2913513https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2913513
Yang S, Lin W, Jiang Q, Wang Y (2019) SGDNEt: An end-to-end saliency-guided deep neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. MM 2019 - Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 1383–1391
Jia S, Zhang Y (2018) Saliency-based deep convolutional neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. Multimed Tools Appl 77(12):14859–14872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5070-6https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5070-6
Sun F, Li W (2019) Saliency guided deep network for weakly-supervised image segmentation. Pattern Recogn Lett 120(Wenhui Li):62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.01.009
Zhou Y, Wang X, Jiao J, Darrell T, Yu F (2020) Learning saliency propagation for semi-supervised instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 10304–10313, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01032, (to appear in print)
Chen C, Li S, Qin H, Hao A (2015) Real-time and robust object tracking in video via low-rank coherency analysis in feature space. Pattern Recogn 48(9):2885–2905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.01.025https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.01.025
Babichev S A, Ries J, Lvovsky A I (2002) Quantum scissors: teleportation of single-mode optical states by means of a nonlocal single photon Preprint at arXiv:quant-ph/0208066v1
Beneke M, Buchalla G, Dunietz I (1997) Mixing induced CP asymmetries in inclusive B decays. Phys Lett B393:132–142. arXiv:https://arxiv.org/abs/0707.3168 [gr-gc]
Imamoglu N, Lin W, Fang Y (2013) A saliency detection model using low-level features based on wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Multimed 15(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2012.2225034https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2012.2225034
Cheng M M, Mitra N J, Huang X, Torr P H S, Hu S M (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401
Yang J, Yang M H (2017) Top-down visual saliency via joint CRF and dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(3):576–588. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2547384https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2547384
He S, Lau R W H (2016) Exemplar-driven top-down saliency detection via deep association. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 2016-Decem. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.617https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.617, pp 5723–5732
Deng Z, Hu X, Zhu L, Xu X, Qin J, Han B, Heng P-A (2018) r3net: recurrent residual refinement network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI-18), pp 684–690, DOI https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/95, (to appear in print)
Zhao T, Wu X (2019) Pyramid feature attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3085–3094, DOI https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1903.00179, (to appear in print)
Piao Y, Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Lu H (2019) Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 2019-Octob, pp 7254–7263, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00735, (to appear in print)
Tan Z, Gu X (2021) Depth scale balance saliency detection with connective feature pyramid and edge guidance. Appl Intell 51(8):5775–5792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02150-z
Wang J, Zhao Z, Yang S, Chai X, Zhang W, Zhang M (2021) Global contextual guided residual attention network for salient object detection. Applied Intelligence
Jiao J, Xue H, Ding J (2021) Non-local duplicate pooling network for salient object detection. Appl Intell 51(10):6881–6894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02147-8
Liu Z, Song T, Xie F (2019) Rgb-d image saliency detection from 3d perspective. Multimed Tools Appl 78(6):6787–6804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6319-4
Liu Z, Shi S, Duan Q, Zhang W, Zhao P (2019) Salient object detection for RGB-d image by single stream recurrent convolution neural network. Neurocomputing 363:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.012https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.012
Song H, Liu Z, Du H, Sun G, Le meur O, Ren T (2017) Depth-Aware salient object detection and segmentation via multiscale discriminative saliency fusion and bootstrap learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(9):4204–4216. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2711277https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2711277
Qu L, He S, Zhang J, Tian J, Tang Y, Yang Q (2017) RGBD Salient object detection via deep fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(5):2274–2285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2682981
Fan D P, Lin Z, Zhao J X, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Hou Q, Zhu M, Cheng M M (2019) Rethinking RGB-d salient object detection: models, datasets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(5):2075–2089. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2020.2996406https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2020.2996406
Huang P, Shen C H, Hsiao H F (2019) RGBD Salient object detection using spatially coherent deep learning framework. International Conference on Digital Signal Processing DSP 2018-November:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDSP.2018.8631584
Guo J, Ren T, Bei J (2016) Salient object detection for rgb-d image via saliency evolution. In: 2016 IEEE International conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2016.7552907https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2016.7552907
Han J (2018) Cnns-based rgb-d saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(11):3171–3183. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2761775
Wang N, Gong X (2019) Adaptive fusion for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Access 7:55277–55284. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913107https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913107
Chen H, Li Y (2018) Progressively complementarity-aware fusion network for rgb-d salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00322https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00322, pp 3051–3060
Chen H, Li Y, Su D (2019) Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-d salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 86:376–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.007
Liu N, Zhang N, Han J (2020) Learning selective self-mutual attention for RGB-d saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01377https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01377, pp 13753–13762
Li C, Cong R, Kwong S, Hou J, Fu H, Zhu G, Zhang D, Huang Q (2020) ASIF-Net: attention steered interweave fusion network for RGB-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 51 (1):88–100. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2969255
Huang N, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Han J (2021) Joint cross-modal and unimodal features for RGB-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:2428–2441. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.3011327https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.3011327
Zhang M, Ren W, Piao Y, Rong Z, Lu H (2020) Select, supplement and focus for RGB-d saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00353, pp 3472–3481
Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Piao Y, Lu H (2020) Accurate RGB-d Salient Object Detection Via Collaborative Learning vol 12363 LNCS, pp 52–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_4
Li G, Liu Z, Ye L, Wang Y, Ling H (2020) Cross-modal weighting network for RGB-d salient object detection. In: Computer vision - ECCV 2020: 16th european conference, pp 665–681, DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_39, (to appear in print)
Chen H, Li Y (2019) Three-stream attention-aware network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2825–2835. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2891104
Zhang Y, Jiang G, Yu M, Chen K (2010) Stereoscopic visual attention model for 3d video. In: Advances in multimedia modeling. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11301-7_33. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 314–324
Desingh K, K MK, Rajan D, Jawahar C (2014) Depth really matters: improving visual salient region detection with depth. pp 98–19811. https://doi.org/10.5244/c.27.98
Ju R, Liu Y, Ren T, Ge L, Wu G (2015) Depth-aware salient object detection using anisotropic center-surround difference. Signal Process Image Commun 38:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2015.07.002
Cheng Y, Fu H, Wei X, Xiao J, Cao X (2014) Depth enhanced saliency detection method. In: ACM International conference proceeding series, pp 23–27. https://doi.org/10.1145/2632856.2632866
Liu J J, Hou Q, Cheng M M, Feng J, Jiang J (2019) A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 2019-June, pp 3912–3921, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00404, (to appear in print)
Zhao J, Liu J J, Fan D P, Cao Y, Yang J, Cheng M M (2019) EGNEt: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision 2019-Octob(Iccv), pp 8778–8787, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00887https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00887, (to appear in print)
Feng M, Lu H, Ding E (2019) Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 2019-June. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00172, pp 1623–1632
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M (2019) Basnet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 7471–7481. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00766
Fu K, Fan D P, Ji G P, Zhao Q, Shen J, Zhu C (2021) Siamese network for RGB-d salient object detection and beyond. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14(8):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3073689
Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Fu X, Zhuo L, Xu M, Wang M (2021) Kernelized multiview subspace analysis by Self-Weighted learning. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:3828–3840. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.3032023
Deng R, Shen C, Liu S, Wang H, Liu X (2018) Learning to predict crisp boundaries. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 11210 LNCS:570–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01231-1_35
Liu Y, Cheng M M, Hu X, Bian J W, Zhang L, Bai X, Tang J (2019) Richer convolutional features for edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(8):1939–1946. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2878849
Chen Z, Xu Q, Cong R, Huang Q (2020) Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. In: Arxiv, DOI https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6633, (to appear in print)
Ren J, Gong X, Yu L, Zhou W, Yang M Y (2015) Exploiting global priors for RGB-d saliency detection. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recog Work 2015-Octob:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2015.7301391
Peng H, Li B, Xiong W, Hu W, Ji R (2014) RGBD Salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 8691 LNCS((PART 3)):92–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_7
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, Liu F (2012) Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 454–461, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247708, (to appear in print)
Li N, Ye J, Ji Y, Ling H, Yu J (2017) Saliency detection on light field. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(8):1605–1616. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2610425
Fu K, Fan DP, Ji G P, Zhao Q (2020) JL-DCF: Joint Learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for RGB-d salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3049–3059, DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00312, (to appear in print)
Borji A, Cheng M M, Jiang H, Li J (2015) Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2487833
Cheng M M, Fan D P (2021) Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. Int J Comput Vis 129(9):2622–2638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01490-8
Fan D P, Gong C, Cao Y, Ren B, Cheng M M, Borji A (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In: IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2018-July. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/97https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/97, pp 698–704
Cong R, Lei J, Zhang C, Huang Q, Cao X, Hou C (2016) Saliency detection for stereoscopic images based on depth confidence analysis and multiple cues fusion. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 23 (6):819–823. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2016.2557347
Zhao JX, Cao Y, Fan DP et al (2019) Contrast prior and Fluid pyramid integration for rgbd salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol 2019-June, pp 3922–3931. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00405
Liu D, Zhang K, Chen Z (2020) Attentive cross-modal fusion network for RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:967–981
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Zaozhuang University (No.1022004), Key Support Project of the National Natural Science Foundation Joint Fund of China (No.U2141239).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, W., Sun, X. & Qian, Y. RGB-D saliency detection via complementary and selective learning. Appl Intell 53, 7957–7969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03612-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03612-2