Abstract
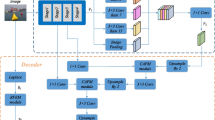
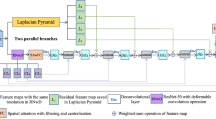
The goal of semantic segmentation is to classify each pixel in the image, so as to segment out the specific contour of the target. Most previous semantic segmentation models cannot generate enough semantic information for each pixel to understand the content of complex scenes. In this paper, we propose a novel semantic segmentation model Ince-DResAsppNet based on dense convoluted separation convolution. Unlike the previous model, our model revolves around reducing semantic information loss and enhancing detailed information. In the feature extraction part of the model, the idea of Dense and Ince is introduced to expand the number of channels on the basis of feature reuse. In the feature fusion part, Dense and Atrous’s idea of dense dilated based on coprime factors is introduced, combined with multi-scale feature information to expand the receptive field and collect more dense pixels. Experiments conducted on the dataset PASCAL VOC 2012 and the CityScapes dataset show that our method performs better than the existing semantic segmentation model. Our model achieves 83.3% and 78.1% segmentation accuracy on the mIoU indicator, which surpasses many classical semantic segmentation models.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I (2015) Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs. Comput Sci 4:357–361
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I (2016) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, Atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Xu X, Joo H, Mori G, Savva M (2021) D3D-HOI: dynamic 3D human-object interactions from videos. arXiv:2108.08420
Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G (2018) Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv:1802.02611
Liu J, Cheng S, Xu X, Xu B, Shuangyuan Y (2019) A spatial and temporal features mixture model with body parts for video-based person re-identification. Appl Intell 49(9):3436–3446
Xu X, Wang X, Kitani KM (2018) Error correction maximization for deep image hashing. In: British Machine Vision Conference
Yuan Y, Chen X, Wang J (2020) Object contextual representations for semantic segmentation. ECCV
Tao A, Sapra K, Catanzaro B (2020) Hierarchical multi-scale attention for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.10821
Zhang H, Wu C, Zhang Z et al (2020) Resnest: Split attention networks. arXiv:2004.08955
Mohan R, Valada A (2020) Efficientps: efficient panoptic segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 129:1551–1579
Hariharan B, Arbelaez P, Bourdev L, Maji S, Malik J (2011) Semantic contours from inverse detectors. ICCV
Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, Franke U, Roth S, Schiele B (2016) The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. CVPR
Papandreou G, Chen LC, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2015) Weakly- and semi-supervised learning of a dcnn for semantic image segmentation. ICCV
Chen LC, Yang Y, Wang J, Xu W, Yuille AL (2016) Attention to scale: Scale-aware semantic image segmentation. CVPR
Zhang F, Xu X, Nauata N, Furukawa Y (2021) Structured outdoor architecture reconstruction by exploration and classification. ICCV
Li X, Liu Z, Luo P, Loy CC, Tang X (2017) Not all pixels are equal: difficulty-aware semantic segmentation via deep layer cascade. arXiv:1704.01344
Vemulapalli R, Tuzel O, Liu MY, Chellappa R (2016) Gaussian conditional random field network for semantic segmentation. CVPR
Zheng S, Jayasumana S, Romera-Paredes B, Vineet V, Su Z, Du D, Huang C, Torr P (2015) Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. ICCV
Noh H, Hong S, Han B (2015) Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. ICCV
Dai J, He K, Sun J (2015) Boxsup: Exploiting bounding boxes to supervise convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. ICCV
Yu F, Koltun V (2016) Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions, ICLR
Chandra S, Kokkinos I (2016) Fast, exact and multi-scale inference for semantic image segmentation with deep Gaussian CRFs. arXiv:1603.08358
Kokkinos I (2016) Pushing the boundaries of boundary detection using deep learning. ICLR
Yan Z, Zhang H, Jia Y, Breuel T, Yu Y (2016) Combining the best of convolutional layers and recurrent layers: a hybrid network for semantic segmentation. arXiv:1603.04871
Ghiasi G, Fowlkes CC (2016) Laplacian reconstruction and refinement for semantic segmentation. arXiv: 1605. 02264
Lin G, Shen C, Reid I et al (2015) Efficient piecewise training of deep structured models for semantic segmentation. arXiv:1504.01013
Arnab A, Jayasumana S, Zheng S, Torr P (2015) Higher order potentials in end-to-end trainable conditional random fields. arXiv:1511.08119
Shen F, Zeng G (2016) Fast semantic image segmentation with high order context and guided filtering. arXiv:1605.04068
Wu Z, Shen C, van den Hengel A (2016) Bridging category-level and instance-level semantic image segmentation. arXiv:1605.06885
Sun H, Xie D, Pu S (2016) Mixed context networks for semantic segmentation. arXiv:1610.05854
Badrinarayanan V, Handa A, Cipolla R (2015) SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for robust semantic pixel-wise labelling. Comput Sci
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell G (2017) Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. arXiv:1702.08502
Uhrig J, Cordts M, Franke U, Brox T (2016) Pixel-level encoding and depth layering for instance-level semantic labeling. arXiv:1604.05096
Shellhamer E, Long J, Darrell T (2014) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):640–651
Fan H, Mei X, Prokhorov D, Ling H (2016) Multi-level contextual rnns with attention model for scene labeling. arXiv:1607.02537
Pohlen T, Hermans A, Mathias M, Leibe B (2016) Full resolution residual networks for semantic segmentation in street scenes. arXiv:1611.08323
Ozdemir F, Goksel O (2019) Extending pretrained segmentation networks with additional anatomical structures. Int J Comput Assisted Radiol Surg
Li X, Jie Z, Wang W, Liu C, Yang J, Shen X, Lin Z, Chen Q, Yan S, Feng J (2017) Foveanet: perspective-aware urban scene parsing. arXiv:1708.02421
Kreso I, Segvi’c S, Krapac J (2017) Ladder-style densenets for semantic segmentation of large natural images. ICCV
Jin X, Li X, Xiao H, Shen X, Lin Z, Yang J, Chen Y, Dong J, Liu L, Jie Z, Feng J, Yan S (2017) Video scene parsing with predictive feature learning, ICCV
Liang X, Zhou H, Xing E (2018) Dynamic-structured semantic propagation network. CVPR
Peng C, Zhang X, Yu G, Luo G, Sun J (2017) Large kernel matters - improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network. CVPR
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell GW (2018) Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. WACV
Yu C, Wang J, Peng C, Gao C, Yu G, Sang N (2018) Bisenet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.00897
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Cangzhou key research and development plan [204102013].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, E., Xu, X., Xu, B. et al. An enhancement model based on dense atrous and inception convolution for image semantic segmentation. Appl Intell 53, 5519–5531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03448-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03448-w