Abstract
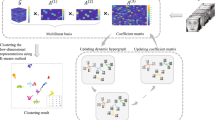
Tensor ring (TR) decomposition is a highly effective tool for obtaining the low-rank character of multi-way data. Recently, nonnegative tensor ring (NTR) decomposition combined with manifold learning has emerged as a promising approach for exploiting the multi-dimensional structure and extracting features from tensor data. However, an existing method such as graph regularized tensor ring (GNTR) decomposition only models the pair-wise similarities of objects. The graph cannot precisely encode similarity relationships for tensor data with a complex manifold structure. In this paper, to sufficiently utilize the high-dimensional and complex similarities among objects, we add a novel hypergraph regulation into the NTR framework to further enhance feature extraction. Based on this, we propose a hypergraph regularized nonnegative tensor ring decomposition (HGNTR) model. To reduce computational complexity and suppress noise, we apply the low-rank approximation trick to accelerate HGNTR (called LraHGNTR). Our experiment results demonstrate that the proposed HGNTR and LraHGNTR algorithms outperform other state-of-the-art algorithms; additionally, LraHGNTR significantly reduces running time without sacrificing accuracy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee D D, Seung H S (1999) Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 401(6755):788–791
Sheng Y, Wang M, Wu T, Xu H (2019) Adaptive local learning regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for data clustering. Appl Intell 49(6):2151–2168
Belkin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwani V (2006) Manifold regularization: A geometric framework for learning from labeled and unlabeled examples. J Machine Learn Res 7(11)
Chen S-B, Ding CHQ, Luo B (2014) Similarity learning of manifold data. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(9):1744–1756
Zhang L, Liu Z, Pu J, Song B (2020) Adaptive graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for data representation. Appl Intell 50(2):438–447
Li S, Li W, Hu J, Li Y (2021) Semi-supervised bi-orthogonal constraints dual-graph regularized nmf for subspace clustering. Appl Intell:1–22
Shu Z, Weng Z, Yu Z, You C, Liu Z, Tang S, Wu X (2021) Correntropy-based dual graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization with lp smoothness for data representation. Appl Intell:1–17
Cai D, He X, Han J, Huang T S (2010) Graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for data representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(8):1548–1560
Cichocki A, Mandic D, De Lathauwer L, Zhou G, Zhao Q, Caiafa C, Phan H A (2015) Tensor decompositions for signal processing applications: From two-way to multiway component analysis. IEEE Signal Process Mag 32(2):145–163
Zhao Q, Sugiyama M, Yuan L, Cichocki A (2019) Learning efficient tensor representations with ring-structured networks. IEEE, pp 8608–8612. ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
Yuan L, Li C, Mandic D, Cao J, Zhao Q (2019) Tensor ring decomposition with rank minimization on latent space: An efficient approach for tensor completion, vol 33. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 9151–9158
Peng W, Li T (2011) On the equivalence between nonnegative tensor factorization and tensorial probabilistic latent semantic analysis. Appl Intell 35(2):285–295
Zhang T, Zhao J, Sun Q, Zhang B, Chen J, Gong M (2021) Low-rank tensor completion via combined tucker and tensor train for color image recovery. Appl Intell:1–16
Zhou G, Cichocki A, Zhao Q, Xie S (2014) Nonnegative matrix and tensor factorizations: An algorithmic perspective. IEEE Signal Proc Mag 31(3):54–65
Yu Y, Zhou G, Zheng N, Xie S, Zhao Q (2020) Graph regularized nonnegative tensor ring decomposition for multiway representation learning. arXiv:http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05657
Yu J, Tao D, Wang M (2012) Adaptive hypergraph learning and its application in image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(7):3262–3272
Bretto A (2013) Hypergraph theory. An introduction. Mathematical Engineering. Springer, Cham
Zhou D, Huang J, Schölkopf B (2006) Learning with hypergraphs: Clustering, classification, and embedding. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:1601–1608
Zeng K, Yu J, Li C, You J, Jin T (2014) Image clustering by hyper-graph regularized non-negative matrix factorization. Neurocomputing 138:209–217
Wu W, Kwong S, Zhou Y, Jia Y, Gao W (2018) Nonnegative matrix factorization with mixed hypergraph regularization for community detection. Inf Sci 435:263–281
Tenenbaum J B, De Silva V, Langford J C (2000) A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290(5500):2319–2323
Martinsson P-G, Rokhlin V, Tygert M (2011) A randomized algorithm for the decomposition of matrices. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 30(1):47–68
Zhou G, Cichocki A, Xie S (2012) Fast nonnegative matrix/tensor factorization based on low-rank approximation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 60(6):2928–2940
Zhou G, Cichocki A, Zhao Q, Xie S (2015) Efficient nonnegative tucker decompositions: Algorithms and uniqueness. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):4990–5003
Kolda T G, Bader B W (2009) Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev 51 (3):455–500
Zhao Q, Zhou G, Xie S, Zhang L, Cichocki A (2016) Tensor ring decomposition. arXiv:http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05535
Chen Y, He W, Yokoya N, Huang T-Z, Zhao X-L (2019) Nonlocal tensor-ring decomposition for hyperspectral image denoising. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(2):1348–1362
Oseledets I V (2011) Tensor-train decomposition. SIAM J Sci Comput 33(5):2295–2317
He W, Yokoya N, Yuan L, Zhao Q (2019) Remote sensing image reconstruction using tensor ring completion and total variation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(11):8998–9009
Yu J, Zhou G, Sun W, Xie S (2021) Robust to rank selection: Low-rank sparse tensor-ring completion. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Yu J, Zhou G, Li C, Zhao Q, Xie S (2020) Low tensor-ring rank completion by parallel matrix factorization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Xu Y, Wu Z, Chanussot J, Wei Z (2020) Hyperspectral images super-resolution via learning high-order coupled tensor ring representation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(11):4747–4760
He W, Chen Y, Yokoya N, Li C, Zhao Q (2022) Hyperspectral super-resolution via coupled tensor ring factorization. Pattern Recogn 122:108280
Pan Y, Xu J, Wang M, Ye J, Wang F, Bai K, Xu Z (2019) Compressing recurrent neural networks with tensor ring for action recognition, vol 33. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 4683–4690
Hong C, Yu J, Li J, Chen X (2013) Multi-view hypergraph learning by patch alignment framework. Neurocomputing 118:79–86
Wang C, Yu J, Tao D (2013) High-level attributes modeling for indoor scenes classification. Neurocomputing 121:337–343
Huang Y, Liu Q, Lv F, Gong Y, Metaxas D N (2011) Unsupervised image categorization by hypergraph partition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(6):1266–1273
Tian Z, Hwang T, Kuang R (2009) A hypergraph-based learning algorithm for classifying gene expression and arraycgh data with prior knowledge. Bioinformatics 25(21):2831–2838
Jin T, Ji R, Gao Y, Sun X, Zhao X, Tao D (2018) Correntropy-induced robust low-rank hypergraph. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2755–2769
Gao Y, Zhang Z, Lin H, Zhao X, Du S, Zou C (2020) Hypergraph learning: Methods and practices. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence
Huang S, Wang H, Ge Y, Huangfu L, Zhang X, Yang D (2018) Improved hypergraph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization with sparse representation. Pattern Recogn Lett 102:8–14
Drineas P, Kannan R, Mahoney M W (2006) Fast monte carlo algorithms for matrices ii: Computing a low-rank approximation to a matrix. SIAM J Comput 36(1):158–183
Halko N, Martinsson P-G, Tropp J A (2011) Finding structure with randomness: Probabilistic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions. SIAM Rev 53(2):217–288
Mahoney M W (2010) Randomized algorithms for matrices and data. Mach Learn 3(2):123–224
Caiafa C F, Cichocki A (2010) Generalizing the column–row matrix decomposition to multi-way arrays. Linear Algebra Appl 433(3):557–573
Vannieuwenhoven N, Vandebril R, Meerbergen K (2011) On the truncated multilinear singular value decomposition. Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics Section
Qiu Y, Zhou G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Xie S (2020) A generalized graph regularized non-negative tucker decomposition framework for tensor data representation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics
Sofuoglu S E, Aviyente S (2020) Graph regularized tensor train decomposition. IEEE, pp 3912–3916. ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)
Rodríguez-Fdez I, Canosa A, Mucientes M, Bugarín A (2015) STAC: a web platform for the comparison of algorithms using statistical tests. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Guangdong Key R&D Project of China (Grant 2019B010121001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 62073087, Grant U1911401, Grant 62071132, and Grant 61973090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Yu, Y., Zhou, G. et al. Fast hypergraph regularized nonnegative tensor ring decomposition based on low-rank approximation. Appl Intell 52, 17684–17707 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03346-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03346-1