Abstract
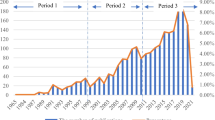
Probabilistic preference decision-making (PPDM) is a branch of uncertain decision-making, which identifies decision-makers’ preferences with probability to deal with uncertain decision-making problems more comprehensively. In order to understand the status and development process of publications related to PPDM, this paper conducts a bibliometric study. Based on the Web of Science (WoS) core collection, a total of 487 publications are obtained. Firstly, this paper makes a general analysis of the basic characteristics of PPDM, including the type of articles, the number of annual publications and the research directions. Secondly, according to the information of the country/region/institution/author/journal regarding the publications, the publication structure is analyzed, the most productive items are explored, and the partnership of each item is detected with the VOSviewer. The paper then examines the citation structure of PPDM publications, uses the VOSviewer to visualize the citation network and discusses the most influential items. Finally, VOSviewer and Bibliometrix are used to analyze the keywords and study the work focus and current hot topics of PPDM. The keywords are divided into three stages in chronological order to analyze the development trend and theme evolution of the research topics. Based on a series of analyses, we further discuss the characteristics of PPDM publications, give some reasonable suggestions and draw some main conclusions. This research thoroughly analyzes and summarizes the essential features, research status and development trend of PPDM publications, which is helpful for the interested researchers to carry out further scientific research.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Pang Q, Wang H, Xu ZS (2016) Probabilistic linguistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf Sci 369:128–143
Chen SJ, Hwang CL, Hwang FP (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision-making-methods and applications. Lect Notes Econ Math Syst 375:1-531
Xu ZS, Zhou W (2017) Consensus building with a group of decision makers under the hesitant probabilistic fuzzy environment. Special issue in the journal Fuzzy Optim Decis Making: Fuzzy Approaches in Intelligent Decision Making and Consensus 16(4):481–503
Li J, Chen QX, Niu LL, Wang ZX (2020) An ORESTE approach for multi-criteria decision-making with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet 11:1591–1609
Wu B, Ye Y, BSPR (2020) Basket-sensitive personalized ranking for product recommendation. Inf Sci 541:185–206
Ramadass S, Krishankumar R, Ravichandran KS, Liao H, Kar S, Herrera-Viedma E. (2020) Evaluation of cloud vendors from probabilistic linguistic information with unknown/partial weight values. Applied Soft Comput 97
Lin MV, Xu ZS, Zhai YL, Yao ZQ (2018) Multi-attribute group decision-making under probabilistic uncertain linguistic environment. J Oper Res Soc 69(2):157–170
Zhang YX, Xu ZS, Wang H, Liao HC (2016) Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Appl Soft Comput 49:817–833
Wu XL, Liao HC (2019) A consensus-based probabilistic linguistic gained and lost dominance score method. Eur J Oper Res 272:1017–1027
Wu XL, Liao HC (2018) An approach to quality function deployment based on probabilistic linguistic term sets and ORESTE method for multi-expert multi-criteria decision making. Inf Fusion 43:13–26
Wu XL, Liao HC, Xu ZS, Hafezalkotob A, Herrera F (2018) Probabilistic linguistic MULTIMOORA: a multicriteria decision making method based on the probabilistic linguistic expectation function and the improved Borda Rule. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26:3688–3702
Pritchard A (1969) Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. J Doc 25:348
He XR, Wu YY, Yu DJ, Merigo JM (2017) Exploring the ordered weighted averaging operator knowledge domain: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Intell Syst 32:1151–1166
Chen CM, CiteSpace II (2006) Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 57:359–377
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84:523–538
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr 11:959–975
van Eck NJ, Waltman L, CitNetExplorer (2014) A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J Informetr 8:802–823
Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2012) SciMAT: A new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 63:1609–1630
Cancino CA, Merigo JM, Coronado F, Dessouky Y, Dessouky M (2017) Forty years of computers & industrial engineering: a bibliometric analysis. Comput Ind Eng 113:614–629
Valenzuela L, Merigo JM, Johnston WJ, Nicolas C, Jaramillo JF (2017) Thirty years of the Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing: a bibliometric analysis. J Bus Ind Mark 32:1–18
Wang XX, Chang YR, Xu ZS, Wang ZD, Kadirkamanathan V (2020) 50th anniversary of International Journal of Systems Science: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Int J Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207721.2020.1862937
Yu DJ, Xu ZS, Fujita H (2019) Bibliometric analysis on the evolution of applied intelligence. Appl Intell 49(2):449–462
Shi YH, Wang SM, Ma YQ, Macleod J, Chen M, Yang HH (2019) Research on the hotspots and trends of learning analytics based on CiteSpace. In: Cheung SKS, Lee LK, Simonova I, Kozel T, Kwok LF (eds) Blended Learning: Educational Innovation for Personalized Learning, Icbl 2019. Springer International Publishing Ag, Cham, pp 239–248
Yu DJ, Xu ZS, Wang XZ (2020) Bibliometric analysis of support vector machines research trend: a case study in China. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet 11:715–728
Gu DX, Li JJ, Li XG, Liang CY (2017) Visualizing the knowledge structure and evolution of big data research in healthcare informatics. Int J Med Inform 98:22–32
Wang XX, Xu ZS, Su SF, Zhou W (2021) A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of uncertain group decision making from 1980 to 2019. Inf Sci 547:328–353
Qin Y, Wang XX, Xu ZS, Skare M (2021) The impact of poverty cycles on economic research: evidence from econometric analysis. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja 34:152–171
Xu ZS, Wang XD, Wang XX, Skare M (2021) A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of entrepreneurship and crisis. J Bus Res 135:304–318
Zhang K, Liang QM (2020) Recent progress of cooperation on climate mitigation: A bibliometric analysis. J Clean Prod 277
Lopez-Robles JR, Cobo MJ, Gutierrez-Salcedo M, Martinez-Sanchez MA, Gamboa-Rosales NK, Herrera-Viedma E (2021) 30th Anniversary of Applied Intelligence: A combination of bibliometrics and thematic analysis using SciMAT. Appl Intell 51:6547–6568
Hirsch JE (2007) Does the h index have predictive power? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19193–19198
Kohler J, Baravalle M (2019) Risk-based decision making and the calibration of structural design codes - prospects and challenges. Civ Eng Environ Syst 36:55–72
Shahbaz M, Bashir MF, Bashir MA, Shahzad L (2021) A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review of tourism-environmental degradation nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Liu J, Wu NQ, Qiao Y, Li ZW (2021) A scientometric review of research on traffic forecasting in transportation. IET Intel Transp Syst 15:1–16
Marx SM, Weber EU, Orlove BS, Leiserowitz A, Krantz DH, Roncoli C et al (2007) Communication and mental processes: Experiential and analytic processing of uncertain climate information. Glob Environ 17:47–58
Beer M, Ferson S, Kreinovich V (2013) Imprecise probabilities in engineering analyses. Mech Syst Signal Process 37:4–29
Gou XJ, Xu ZS (2016) Novel basic operational laws for linguistic terms, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and probabilistic linguistic term sets. Inf Sci 372:407–427
Guo JJ, Pandey S, Doyle J, Bian BY, Lis Y, Raisch DW (2010) A review of quantitative risk-benefit methodologies for assessing drug safety and efficacy-report of the ISPOR risk-benefit management working group. Value Health 13:657–666
Moeini-Aghtaie M, Abbaspour A, Fotuhi-Firuzabad M (2012) Incorporating large-scale distant wind farms in probabilistic transmission expansion planning-part I: theory and algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Syst 27:1585–1593
Liao HC, Jiang LS, Xu ZS, Xu JP, Herrera F (2017) A linear programming method for multiple criteria decision making with probabilistic linguistic information. Inf Sci 415:341–355
Zhang YX, Xu ZS, Liao HC (2017) A consensus process for group decision making with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 414:260–275
Zhang J, Yu Q, Zheng FS, Long C, Lu ZX, Duan ZG (2016) Comparing keywords plus of WoS and author keywords: A case study of patient adherence research. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol 67:967–972
Linnenluecke MK, Marrone M, Singh AK (2020) Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Aust J Manag 45:175–194
Tang M, Liao HC, Su SF (2018) A bibliometric overview and visualization of the International Journal of Fuzzy Systems Between 2007 and 2017. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20:1403–1422
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 72071135 and 71771155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Lei, T. & Qin, Y. An overview of probabilistic preference decision-making based on bibliometric analysis. Appl Intell 52, 15368–15386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03189-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03189-w