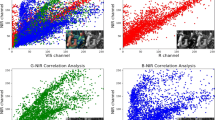
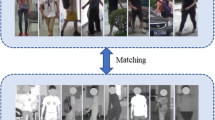
Abstract
Visible-infrared cross-modality person re-identification is an important task in the night video surveillance system, the huge difference between infrared and visible light images makes this work quite challenging. Unlike traditional person re-identification, a cross-modality mission needs to solve intra-class differences and inter-class variations. To solve the problem of huge modality discrepancy, in this paper, we propose a channel-based partition network which can unify the features of the two modes in an end-to-end way. Firstly, to handle the lack of discriminative information, we introduce newly generated samples to help the network improve its ability to learn cross modal features. Secondly, at the feature level, we propose a distinctive method of learning local features, in which the set of feature maps is parted on the channel. At the end of the proposed framework, we add a lightweight feature converter to further eliminate modality differences. The experimental results on the two popular datasets prove the effectiveness of our work.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengio Y, Courville A, Vincent P (2013) Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(8):1798–1828
Bottou L (2010) Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In: Proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010. Springer, pp 177–186
Chen Y, Zhu X, Gong S (2017) Person re-identification by deep learning multi-scale representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, pp 2590–2600
Choi S, Lee S, Kim Y, Kim T, Kim C (2020) Hi-cmd: Hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 10257–10266
Choi Y, Choi M, Kim M, Ha JW, Kim S, Choo J (2018) Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8789–8797
Dai P, Ji R, Wang H, Wu Q, Huang Y (2018) Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: IJCAI, vol 1, p 2
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’05), vol 1. IEEE, pp 886–893
Feng Z, Lai J, Xie X (2019) Learning modality-specific representations for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:579–590
Gatys LA, Ecker AS, Bethge M (2016) Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2414–2423
Gheissari N, Sebastian T B, Hartley R (2006) Person reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance. In: 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’06), vol 2. IEEE, pp 1528–1535
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2672–2680
Gray D, Tao H (2008) Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 262–275
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B (2017) In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv:1703.07737
Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1125–1134
Jüngling KK, Arens M (2010) Local feature based person reidentification in infrared image sequences. In: 2010 7th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance. IEEE, pp 448–455
Koestinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Roth PM, Bischof H (2012) Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 2288–2295
Li D, Wei X, Hong X, Gong Y (2020) Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: AAAI, pp 4610–4617
Li W, Zhu X, Gong S (2017) Person re-identification by deep joint learning of multi-loss classification. arXiv:1705.04724
Li W, Zhu X, Gong S (2018) Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2285–2294
Liao S, Li SZ (2015) Efficient psd constrained asymmetric metric learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3685–3693
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X, Li SZ (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2197–2206
Liu J, Sun C, Xu X, Xu B, Yu S (2019) A spatial and temporal features mixture model with body parts for video-based person re-identification. Appl Intell 49(9):3436–3446
Luo H, Gu Y, Liao X, Lai S, Jiang W (2019) Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 0–0
Ly W et al (2017) Unsupervised learning of multi-level descriptors for person re-identification
Ma B, Su Y, Jurie F (2014) Covariance descriptor based on bio-inspired features for person re-identification and face verification. Image Vis Comput 32(6-7):379–390
Nguyen D T, Hong H G, Kim K W, Park K R (2017) Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3):605
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Song W, Zheng J, Wu Y, Chen C, Liu F (2020) Discriminative feature extraction for video person re-identification via multi-task network. Appl Intell :1–16
Sun Y, Zheng L, Deng W, Wang S (2017) Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3800–3808
Sun Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S (2018) Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 480–496
Van Den Oord A, Vinyals O, et al. (2017) Neural discrete representation learning. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 6306–6315
Wang G, Yang Y, Cheng J, Wang J, Hou Z (2019a) Color-sensitive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 28th international joint conference on artificial intelligence. AAAI Press, pp 933–939
Wang G, Zhang T, Cheng J, Liu S, Yang Y, Hou Z (2019b) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3623–3632
Wang GA, Yang TZ, Cheng J, Chang J, Liang X, Hou Z et al (2020a) Cross-modality paired-images generation for rgb-infrared person re-identification. arXiv:200204114
Wang H, Peng J, Chen D, Jiang G, Zhao T, Fu X (2020b) Attribute-guided feature learning network for vehicle reidentification. IEEE MultiMed 27(4):112–121
Wang H, Peng J, Zhao Y, Fu X (2020c) Multi-path deep cnns for fine-grained car recognition. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 69(10):10484–10493
Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Fu X, Zhuo L, Xu M, Wang M (2020d) Kernelized multiview subspace analysis by self-weighted learning. IEEE Trans Multimed
Wang H, Peng J, Jiang G, Xu F, Fu X (2021) Discriminative feature and dictionary learning with part-aware model for vehicle re-identification. Neurocomputing 438:55–62
Wang Z, Wang Z, Zheng Y, Chuang YY, Satoh S (2019c) Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 618–626
Wu A, Zheng WS, Yu HX, Gong S, Lai J (2017) Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 5380– 5389
Wu J, Liao S, Wang X, Yang Y, Li S Z et al (2019) Clustering and dynamic sampling based unsupervised domain adaptation for person re-identification. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp 886–891
Yang Y, Yang J, Yan J, Liao S, Yi D, Li SZ (2014) Salient color names for person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 536–551
Yang Y, Lei Z, Wang J, Li S Z (2019) In defense of color names for small-scale person re-identification. In: 2019 international conference on biometrics (ICB). IEEE, pp 1–6
Ye M, Lan X, Li J (2018a) Yuen, PC. In: AAAI. Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification
Ye M, Wang Z, Lan X, Yuen P C (2018b) Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. In: IJCAI, vol 1, p 2
Zhao J, Mathieu M, LeCun Y (2016) Energy-based generative adversarial network. arXiv:1609.03126
Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2016) Person re-identification: Past, present and future. arXiv:1610.02984
Zheng W S, Gong S, Xiang T (2012) Reidentification by relative distance comparison. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(3):653–668
Zheng Z, Yang X, Yu Z, Zheng L, Yang Y, Kautz J (2019) Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2138–2147
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Luo Z, Li S, Yang Y (2019) Invariance matters: Exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 598–607
Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2223–2232
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61702278, in part by Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and in part by Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province KYCX18_0890.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Song, W., Chen, C. et al. Cross-modality person re-identification via channel-based partition network. Appl Intell 52, 2423–2435 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02548-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02548-3