Abstract
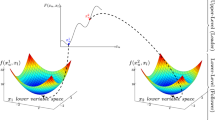
Bi-Level Optimization Problem (BLOP) is a class of challenging problems with two levels of optimization tasks. The main goal is to optimize the upper level problem, which has another optimization problem as a constraint. In this way, the evaluation of each upper level solution requires finding an optimal solution to the corresponding lower level problem, which is computationally so expensive. For this reason, most proposed bi-level resolution methods have been restricted to solve the simplest case (linear continuous BLOPs). This fact has attracted the evolutionary computation community to solve such complex problems. Besides, to enhance the search performance of Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs), reusing knowledge captured from past optimization experiences along the search process has been proposed in the literature, and was demonstrated much promise. Motivated by this observation, we propose in this paper, a memetic version of our proposed Co-evolutionary Decomposition-based Algorithm-II (CODBA-II), that we named M-CODBA-II, to solve combinatorial BLOPs. The main motivation of this paper is to incorporate transfer learning within our recently proposed CODBA-II scheme to make the search process more effective and more efficient. Our proposed hybrid algorithm is investigated on two bi-level production-distribution problems in supply chain management formulated to: (1) Bi-CVRP and (2) Bi-MDVRP. The experimental results reveal a potential advantage of memes incorporation in CODBA-II. Most notably, the results emphasize that transfer learning allows not only accelerating the convergence but also finding better solutions.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For more details about each part of the CODBA-II algorithm, the reader is invited to refer to [10].
SVD is a data reduction method that transforms correlated variables into a set of uncorrelated ones that better expose the various relationships among the original data items
References
Aiyoshi E, Shimizu K (1981) Hierarchical decentralized systems and its new solution by a barrier method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 6:444–449
Augerat P, Belenguer JM, Benavent E, Corberán A, Naddef D, Rinaldi G (1998) Computational results with a branch-and-cut code for the capacitated vehicle routing problem. Rapport de recherche- IMAG
Bard JF, Falk J (1982) An explicit solution to the multi-level programming problem. Comput Oper Res 9 (1):77–100
Borgwardt KM, Gretton A, Rasch MJ, Kriegel H-P, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2006) Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14):e49–e57
Bracken J, McGill J (1973) Mathematical programs with optimization problems in the constraints. Oper Res 21(1):37–44
Calvete HI, Galé C (2010) A multiobjective bilevel program for production-distribution planning in a supply chain. Springer, pp 155–165
Calvete HI, Galé C, Oliveros M (2011) Bilevel model for production–distribution planning solved by using ant colony optimization. Comput Oper Res 38(1):320–327
Calvete HI, Galé C, Oliveros M-J (2013) A hybrid algorithm for solving a bilevel production-distribution planning problem. In: Modeling and simulation in engineering, economics, and management. Springer, pp 138–144
Candler W, Norton R (1977) Multilevel programming. Tech. rep. Technical Report 20. World Bank Development Research, Washington D. C
Chaabani A, Bechikh S, Ben Said L, Azzouz R (2015) An improved co-evolutionary decomposition-based algorithm for bi-level combinatorial optimization. In: Proceedings of the companion publication of the 2015 annual conference on genetic and evolutionary computation. ACM, pp 1363–1364
Chaabani A, Bechikh S, Said LB (2015) A co-evolutionary decomposition-based algorithm for bi-level combinatorial optimization. In: 2015 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 1659–1666
Chen X, Ong Y-S, Lim M-H, Tan K (2011) A multi-facet survey on memetic computation. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 15(5):591–607
Christofides N, Eilon S (1969) An algorithm for the vehicle-dispatching problem. J Oper Res Soc 20 (3):309–318
Colson B, Marcotte P, Savard G (2007) An overview of bilevel optimization. Ann Oper Res 153 (1):235–256
Cordeau J-F, Gendreau M, Laporte G (1997) A tabu search heuristic for periodic and multi-depot vehicle routing problems. Networks 30(2):105–119
Deb K, Sinha A (2010) An efficient and accurate solution methodology for bilevel multi-objective programming problems using a hybrid evolutionary-local-search algorithm. Evol Comput 18(3):403–449
Dempe S (2003) Annotated bibliography on bilevel programming and mathematical programs with equilibrium constraints
Dempe S, Kalashnikov VV, Kalashnykova N (2006) Optimality conditions for bilevel programming problems. In: Optimization with multivalued mappings. Springer, pp 3–28
Eiben AE, Smit S (2011) Parameter tuning for configuring and analyzing evolutionary algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 1(1):19–31
El Ela AA, Abido M, Spea S (2010) Differential evolution algorithm for emission constrained economic power dispatch problem. Electr Power Syst Res 80(10):1286–1292
Feng L, Ong Y-S, Tan A-H, Tsang I (2015) Memes as building blocks: a case study on evolutionary optimization+ transfer learning for routing problems. Memetic Comput 7(3):159–180
Fliege J, Vicente L (2006) Multicriteria approach to bilevel optimization. J Optim Theory Appl 131 (2):209–225
Fortuny-Amat J, McCarl B (1981) A representation and economic interpretation of a two-level programming problem. J Oper Res Soc, 783–792
Gretton A, Bousquet O, Smola A, Schölkopf B (2005) Measuring statistical dependence with Hilbert-Schmidt norms. In: International conference on algorithmic learning theory, pp 63–77
Gretton A, Fukumizu K, Teo CH, Song L, Schölkopf B, Smola A (2008) A kernel statistical test of independence. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, 585–592
Kolstad C (1985) A review of the literature on bi-level mathematical programming. Tech rep., Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM
Kuhn H, Tucker A (1951a) Non linear programming. In: Proceedings of the second Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, Berkeley, University of California, pp 481–492
Lan H, Li R, Liu Z, Wang R (2011) Study on the inventory control of deteriorating items under vmi model based on bi-level programming. Expert Syst Appl 38(8):9287–9295
Legillon F, Liefooghe A, Talbi E-G (2012) Cobra: A cooperative coevolutionary algorithm for bi-level optimization. In: 2012 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation, 1–8
Marinakis Y, Marinaki M (2008) A bilevel genetic algorithm for a real life location routing problem. Int J Logist Res Appl 11(1):49–65
Mathieu R, Pittard L, Anandalingam G (1994) Genetic algorithm based approach to bi-level linear programming. Revue franċaise d’automatique, d’informatique et de recherche opérationnelle. Recherche Opérationnelle 28(1):1–21
Meng Q, Yang H, Bell M (2001) An equivalent continuously differentiable model and a locally convergent algorithm for the continuous network design problem. Transp Res B Methodol 35(1):83–105
Oduguwa V, Roy R (2002) Bi-level optimisation using genetic algorithm. In: IEEE International conference on artificial intelligence systems (ICAIS), pp 322–327
Ong Y-S, Krasnogor N, Ishibuchi H (2007) Special issue on memetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 37(1):2–5
Ong Y-S, Lim M-H, Neri F, Ishibuchi H (2009) Special issue on emerging trends in soft computing: memetic algorithms. Soft Comput- Fus Found Methodol Appl 13(8):739–740
Phadke MS (1995) Quality engineering using robust design. Prentice Hall PTR
Potvin J-Y, Bengio S (1996) The vehicle routing problem with time windows part ii: genetic search. INFORMS J Comput 8(2):165–172
Ross PJ (1988) Taguchi techniques for quality engineering: loss function, orthogonal experiments, parameter and tolerance design
Sinha A, Malo P, Frantsev A, Deb K (2014) Finding optimal strategies in a multi-period multi-leader–follower Stackelberg game using an evolutionary algorithm. Comput Oper Res 41:374–385
Stackelberg H (1952) The theory of the market economy. Oxford University Press, New York
Vicente LN, Calamai P (1994) Bilevel and multilevel programming: a bibliography review. J Global Optim 5(3):291–306
Wang Y, Jiao Y-C, Li H (2005) An evolutionary algorithm for solving nonlinear bilevel programming based on a new constraint-handling scheme. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C (Appl Rev) 35(2):221–232
Yin Y (2000) Genetic-algorithms-based approach for bilevel programming models. J Transp Eng 126(2):115–120
Gupta A, Ong YS, Feng L, Tan KC (2017) Multiobjective multifactorial optimization in evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(7):1652–1665
Wang, Li H, Wang L, Hei X, Li W, Jiang Q (2017) A decomposition-based chemical reaction optimization for multi-objective vehicle routing problem for simultaneous delivery and pickup with time windows. Memetic Comput, 1–18
Fazlollahtabar H, Hassanli S (2018) Hybrid cost and time path planning for multiple autonomous guided vehicles. Appl Intell 48(2):482–498
Feng L, Ong YS, Jiang S, Gupta A (2017) Autoencoding evolutionary search with learning across heterogeneous problems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 21(5):760–772
Gupta A, Mandziuk J, Ong YS (2016) Evolutionary multitasking in bi-level optimization. Complex Intell Syst 1(1-4):83–95
Handoko SD, Chuin LH, Gupta A, Soon OY, Kim HC, Siew TP (2015) Solving multi-vehicle profitable tour problem via knowledge adoption in evolutionary bi-level programming. In: IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC), pp 2713–2720
Dorigo M, Stützle T (2010) Ant colony optimization: overview and recent advances. In: Handbook of metaheuristics. Springer, Boston, pp 227–263
Sinha A, Malo P, Deb K (2018) A review on bilevel optimization: from classical to evolutionary approaches and applications. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 22(2):276–295
Islam MM, Singh HK, Ray T, Sinha A (2017) An enhanced memetic algorithm for single-objective bilevel optimization problems. Evol Comput 25(4):607–642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaabani, A., Said, L.B. Transfer of learning with the co-evolutionary decomposition-based algorithm-II: a realization on the bi-level production-distribution planning system. Appl Intell 49, 963–982 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1309-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1309-9