Abstract
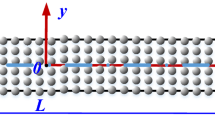
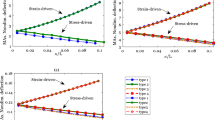
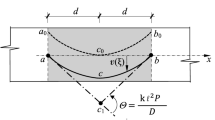
This study shows that it is possible to develop a well-posed size-dependent model by considering the effect of both nonlocality and surface energy, and the model can provide another effective way of nanomechanics for nanostructures. For a practical but simple problem (an Euler-Bernoulli beam model under bending), the ill-posed issue of the pure nonlocal integral elasticity can be overcome. Therefore, a well-posed governing equation can be developed for the Euler-Bernoulli beams when considering both the pure nonlocal integral elasticity and surface elasticity. Moreover, closed-form solutions are found for the deflections of clamped-clamped (C-C), simply-supported (S-S) and cantilever (C-F) nano-/micro-beams. The effective elastic moduli are obtained in terms of the closed-form solutions since the transfer of physical quantities in the transition region is an important problem for span-scale modeling methods. The nonlocal integral and surface elasticities are adopted to examine the size-dependence of the effective moduli and deflection of Ag beams.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SRINIVASA, A. R. and REDDY, J. N. An overview of theories of continuum mechanics with nonlocal elastic response and a general framework for conservative and dissipative systems. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 69(3), 031401 (2017)
AIFANTIS, E. C. Update on a class of gradient theories. Mechanics of Materials, 35(3), 259–280 (2003)
ERINGEN, A. C. On differential equations of nonlocal elasticity and solutions of screw dislocation and surface waves. Journal of Applied Physics, 54(9), 4703–4710 (1983)
GURTIN, M. E. and MURDOCH, A. I. A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 57, 291–323 (1975)
ERINGEN, A. C. Nonlocal Continuum Field Theories, Springer-Verlag, New York (2002)
AYDOGDU, M. Axial vibration of the nanorods with the nonlocal continuum rod model. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 41(5), 861–864 (2009)
REDDY, J. N. Nonlocal theories for bending, buckling and vibration of beams. International Journal of Engineering Science, 45(2–8), 288–307 (2007)
AIFANTIS, E. C. On the gradient approach—relation to Eringen’s nonlocal theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 49(12), 1367–1377 (2011)
CHALLAMEL, N. Variational formulation of gradient or/and nonlocal higher-order shear elasticity beams. Composite Structures, 105, 351–368 (2013)
LIM, C.W., ZHANG, G., and REDDY, J. N. A higher-order nonlocal elasticity and strain gradient theory and its applications in wave propagation. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 78, 298–313 (2015)
LI, L., HU, Y., and LI, X. Longitudinal vibration of size-dependent rods via nonlocal strain gradient theory. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 115, 135–144 (2016)
LI, L., LI, X., and HU, Y. Free vibration analysis of nonlocal strain gradient beams made of functionally graded material. International Journal of Engineering Science, 102, 77–92 (2016)
EBRAHIMI, F. and BARATI, M. R. A nonlocal strain gradient refined beam model for buckling analysis of size-dependent shear-deformable curved FG nanobeams. Composite Structures, 159, 174–182 (2017)
LU, L., GUO, X., and ZHAO, J. Size-dependent vibration analysis of nanobeams based on the nonlocal strain gradient theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 116, 12–24 (2017)
XU, X. J., WANG, X. C., ZHENG, M. L., and MA, Z. Bending and buckling of nonlocal strain gradient elastic beams. Composite Structures, 160, 366–377 (2017)
ZHANG, B., SHEN, H., LIU, J., WANG, Y., and ZHANG, Y. Deep postbuckling and nonlinear bending behaviors of nanobeams with nonlocal and strain gradient effects. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(4), 515–548 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2482-9
LI, L., TANG, H., and HU, Y. The effect of thickness on the mechanics of nanobeams. International Journal of Engineering Science, 123, 81–91 (2018)
GHAYESH, M. H. and FARAJPOUR, A. A review on the mechanics of functionally graded nanoscale and microscale structures. International Journal of Engineering Science, 137, 8–36 (2019)
TANG, H., LI, L., HU, Y., MENG, W., and DUAN, K. Vibration of nonlocal strain gradient beams incorporating Poisson’s ratio and thickness effects. Thin-Walled Structures, 137, 377–391 (2019)
YANG, F., CHONG, A., LAM, D. C., and TONG, P. Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 39(10), 2731–2743 (2002)
AKGÖZ, B. and CIVALEK, Ö. A novel microstructure-dependent shear deformable beam model. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 99, 10–20 (2015)
AKGÖZ, B. and CIVALEK, Ö. A size-dependent shear deformation beam model based on the strain gradient elasticity theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 70, 1–14 (2013)
KARAMI, B., SHAHSAVARI, D., JANGHORBAN, M., and LI, L. Influence of homogenization schemes on vibration of functionally graded curved microbeams. Composite Structures, 216, 67–79 (2019)
HE, J. and LILLEY, C. M. Surface effect on the elastic behavior of static bending nanowires. Nano Letters, 8(7), 1798–1802 (2008)
WANG, G. F. and FENG, X. Q. Timoshenko beam model for buckling and vibration of nanowires with surface effects. Journal of Physics D, Applied Physics, 42, 155411 (2009)
LIM, C. W. and HE, L. H. Size-dependent nonlinear response of thin elastic films with nano-scale thickness. Internation Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 46, 1715–1726 (2004)
LU, P., HE, L. H., LEE, H. P., and LU, C. Thin plate theory including surface effects. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 43, 4631–4647 (2006)
STEIGMANN, D. J. and OGDEN, R. W. Elastic surface-substrate interactions. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A-Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 455, 437–474 (1999)
GAO, X., HUANG, Z. P., QU, J. M., and FANG, D. N. A curvature-dependent interfacial energy-based interface stress theory and its applications to nano-structured materials, (i) general theory. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 66, 59–77 (2014)
CHEN, S. H. and YAO, Y. Elastic theory of nanomaterials based on surface-energy density. ASME Journal of Applied Mechanics, 81, 121002 (2014)
PAPARGYRI-BESKOU, S., TSEPOURA, K. G., POLYZOS, D., and BESKOS, D. E. Bending and stability analysis of gradient elastic beams. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 40, 385–400 (2003)
LEE, H. L. and CHANG, W. J. Surface effects on frequency analysis of nanotubes using nonlocal Timoshenko beam theory. Journal of Applied Physics, 108, 093503 (2010)
GAO, X. L. and MAHMOUD, F. F. A new Bernoulli-Euler beam model incorporating microstructure and surface energy effects. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP, 65, 393–404 (2014)
PREETHIA, K., RAJAGOPALA, A., and REDDY, J. N. Surface and non-local effects for nonlinear analysis of Timoshenko beams. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 76, 100–111 (2015)
LU, L., GUO, X., and ZHAO, J. On the mechanics of Kirchhoff and Mindlin plates incorporating surface energy. International Journal of Engineering Science, 124, 24–40 (2018)
LU, L., GUO, X., and ZHAO, J. A unified size-dependent plate model based on nonlocal strain gradient theory including surface effects. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 68, 583–602 (2019)
REDDY, J. N. and PANG, S. D. Nonlocal continuum theories of beams for the analysis of carbon nanotubes. Journal of Applied Physics, 103, 023511 (2008)
CHALLAMEL, N. and WANG, C. M. The small length scale effect for a non-local cantilever beam, a paradox solved. Nanotechnology, 19, 345703 (2008)
PEDDIESON, J., BUCHANAN, G., and MCNITT, R. Application of nonlocal continuum models to nanotechnology. International Journal of Engineering Science, 41, 305–312 (2003)
FERNÁNDEZ-SÁEZ, J. and ZAERA, R. Vibrations of Bernoulli-Euler beams using the two-phase nonlocal elasticity theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 119, 232–248 (2017)
EPTAIMEROS, K., KOUTSOUMARIS, C., and TSAMASPHYROS, G. Nonlocal integral approach to the dynamical response of nanobeams. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 115–116, 68–80 (2016)
ZHU, X., WANG, Y., and DAI, H. Buckling analysis of Euler-Bernoulli beams using Eringen’s two-phase nonlocal model. International Journal of Engineering Science, 116, 130–140 (2017)
KOUTSOUMARIS, C., EPTAIMEROS, K., and TSAMASPHYROS, G. A different approach to Eringen’s nonlocal integral stress model with applications for beams. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 112, 222–238 (2017)
WANG, Y., ZHU, X., and DAI, H. Exact solutions for the static bending of Euler-Bernoulli beams using Eringen’s two-phase local/nonlocal model. AIP Advances, 6(8), 085114 (2016)
FERNÁNDEZ-SÁEZ, J., ZAERA, R., LOYA, J., and REDDY, J. N. Bending of Euler-Bernoulli beams using Eringen’s integral formulation: a paradox resolved. International Journal of Engineering Science, 99, 107–116 (2016)
ROMANO, G., BARRETTA, R., DIACO, M., and MAROTTI DE SCIARRA, F. Constitutive boundary conditions and paradoxes in nonlocal elastic nanobeams. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 121, 151–156 (2017)
ERINGEN, A. C. Linear theory of nonlocal elasticity and dispersion of plane waves. International Journal of Engineering Science, 10(5), 425–435 (1972)
KHODABAKHSHI, P. and REDDY, J. N. A unified integro-differential nonlocal model. International Journal of Engineering Science, 95, 60–75 (2015)
POLIZZOTTO, C. Nonlocal elasticity and related variational principles. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 38(42), 7359–7380 (2001)
ALTAN, S. B. Uniqueness of initial-boundary value problems in nonlocal elasticity. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 25(11), 1271–1278 (1989)
BARRETTA, R., FAZELZADEH, S., FEO, L., GHAVANLOO, E., and LUCIANO, R. Nonlocal inflected nano-beams: a stress-driven approach of bi-Helmholtz type. Composite Structures, 200, 239–245 (2018)
BARRETTA, R., CAPORALE, A., FAGHIDIAN, S. A., LUCIANO, R., DE SCIARRA, F. M., and MEDAGLIA, C. M. A stress-driven local-nonlocal mixture model for Timoshenko nanobeams. Composites Part B: Engineering, 164, 590–598 (2019)
GURTIN, M. E. and MURDOCH, A. I. Surface stress in solids. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 14, 431–440 (1978)
SHIM, H. W., ZHOU, L., HUANG, H., and CALE, T. S. Nanoplate elasticity under surface reconstruction. Applied Physics Letters, 86(15), 151912 (2005)
ZHOU, L. and HUANG, H. Are surfaces elastically softer or stiffer? Applied Physics Letters, 84(11), 1940–1942 (2004)
ZHANG, L. and HUANG, H. Young’s moduli of ZnO nanoplates: Ab initio determinations. Applied Physics Letters, 89(18), 183111 (2006)
KULKARNI, A., ZHOU, M., and KE, F. Orientation and size dependence of the elastic properties of zinc oxide nanobelts. Nanotechnology, 16(12), 2749–2756 (2005)
CAO, G. and CHEN, X. Energy analysis of size-dependent elastic properties of ZnO nanofilms using atomistic simulations. Physical Review B, 76(16), 165407 (2007)
CHEBAKOV, R., KAPLUNOV, J., and ROGERSON, G. A. A non-local asymptotic theory for thin elastic plates. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A-Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 473, 20170249 (2017)
SAJADI, B., GOOSEN, H., and VAN KEULEN, F. Capturing the effect of thickness on size-dependent behavior of plates with nonlocal theory. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 115–116, 140–148 (2017)
POLYANIN, A. D. and MANZHIROV, A. V. Handbook of Integral Equations, CRC Press, New York (2008)
TANG, H., LI, L., and HU, Y. Coupling effect of thickness and shear deformation on size-dependent bending of micro/nano-scale porous beams. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 66, 527–547 (2019)
HEARN, E. J. Mechanics of Materials 1, an Introduction to the Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural Materials, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1997)
LI, L., HU, Y., and LING, L. Wave propagation in viscoelastic single-walled carbon nanotubes with surface effect under magnetic field based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 75, 118–124 (2016)
ZHU, X. and LI, L. Closed form solution for a nonlocal strain gradient rod in tension. International Journal of Engineering Science, 119, 16–28 (2017)
LI, L., TANG, H., and HU, Y. Size-dependent nonlinear vibration of beam-type porous materials with an initial geometrical curvature. Composite Structures, 184, 1177–1188 (2018)
ZHU, X. and LI, L. On longitudinal dynamics of nanorods. International Journal of Engineering Science, 120, 129–145 (2017)
ZHU, X. and LI, L. Longitudinal and torsional vibrations of size-dependent rods via nonlocal integral elasticity. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 133, 639–650 (2017)
KAMITAKAHARA, W. and BROCKHOUSE, B. Crystal dynamics of silver. Physics Letters A, 29(10), 639–640 (1969)
CUENOT, S., FŔETIGNY, C., DEMOUSTIER-CHAMPAGNE, S., and NYSTEN, B. Surface tension effect on the mechanical properties of nanomaterials measured by atomic force microscopy. Physical Review B, 69(16), 165410 (2004)
JING, G., DUAN, H., SUN, X., ZHANG, Z., XU, J., LI, Y., WANG, J., and YU, D. Surface effects on elastic properties of silver nanowires, contact atomic-force microscopy. Physical Review B, 73(23), 235409 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: ZHU, X. W. and LI, L. A well-posed Euler-Bernoulli beam model incorporating nonlocality and surface energy effect. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(11), 1561–1588 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2541-5
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51605172), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (No. 2016CFB191), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 2722019JCG06 and 2015MS014)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Li, L. A well-posed Euler-Bernoulli beam model incorporating nonlocality and surface energy effect. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 40, 1561–1588 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2541-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2541-5