Abstract
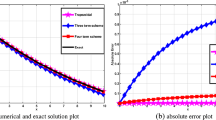
A novel method based on time-dependent stochastic orthogonal bases for stochastic response surface approximation is proposed to overcome the problem of significant errors in the utilization of the generalized polynomial chaos (GPC) method that approximates the stochastic response by orthogonal polynomials. The accuracy and effectiveness of the method are illustrated by different numerical examples including both linear and nonlinear problems. The results indicate that the proposed method modifies the stochastic bases adaptively, and has a better approximation for the probability density function in contrast to the GPC method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABGRALL, R. and CONGEDO, P. M. A semi-intrusive deterministic approach to uncertainty quantification in non-linear fluid flow problems. Journal of Computational Physics, 235, 828–845 (2013)
SIMON, F., GUILLEN, P., SAGAUT, P., and LUCOR, D. A GPC-based approach to uncertain transonic aerodynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 199, 1091–1099 (2010)
SEPAHVAND, K., MARBURG, S., and HARDTKE, H. J. Stochastic free vibration of orthotropic plates using generalized polynomial chaos expansion. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 331, 167–179 (2012)
CAPIEZ-LERNOUT, E., SOIZE, C., and MIGNOLET, M. P. Post-buckling nonlinear static and dynamical analyses of uncertain cylindrical shells and experimental validation. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 271, 210–230 (2014)
JACQUELIN, E., ADHIKARI, S., SINOU, J. J., and FRISWELL, M. I. Polynomial chaos expansion in structural dynamics: accelerating the convergence of the first two statistical moment sequences. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 356, 144–154 (2015)
ZHANG, J. and ELLINGWOOD, B. Effects of uncertain material properties on structural stability. Journal of Structural Engineering, 121, 705–716 (1995)
SINGH, B. N., IYENGAR, N., and YADAV, D. Effects of random material properties on buckling of composite plates. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 127, 873–879 (2001)
XIU, D. and KARNIADAKIS, G. E. The Wiener-Askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 24, 619–644 (2002)
XIU, D. Numerical Methods for Stochastic Computations: A Spectral Method Approach, Princeton University Press, Princeton (2010)
WAN, X. and KARNIADAKIS, G. E. Multi-element generalized polynomial chaos for arbitrary probability measures. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 28, 901–928 (2006)
GHANEM, R. G. and SPANOS, P. D. Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach, Dover Publications, Inc., New York (2003)
XIU, D. and HESTHAVEN, J. S. High-order collocation methods for differential equations with random inputs. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 27, 1118–1139 (2005)
MA, X. and ZABARAS, N. An adaptive hierarchical sparse grid collocation algorithm for the solution of stochastic differential equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 228, 3084–3113 (2009)
GANIS, B., KLIE, H., WHEELER, M. F., WILDEY, T., YOTOV, I., and ZHANG, D. Stochastic collocation and mixed finite elements for flow in porous media. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 197, 3547–3559 (2008)
NEGOITA, C., ZADEH, L., and ZIMMERMANN, H. Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1, 3–28 (1978)
KLIMKE, A. and WOHLMUTH, B. Computing expensive multivariate functions of fuzzy numbers using sparse grids. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 154, 432–453 (2005)
MOORE, R. E. Interval Analysis, Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, New York (1966)
IMPOLLONIA, N. and MUSCOLINO, G. Interval analysis of structures with uncertain-butbounded axial stiffness. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 200, 1945–1962 (2011)
YIN, S., YU, D., YIN, H., and XIA, B. Interval and random analysis for structure-acoustic systems with large uncertain-but-bounded parameters. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 305, 910–935 (2016)
SOIZE, C. Random matrix theory for modeling uncertainties in computational mechanics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 194, 1333–1366 (2005)
SOIZE, C. Random matrix theory and non-parametric model of random uncertainties in vibration analysis. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 263, 893–916 (2003)
XIU, D. and KARNIADAKIS, G. E. Modeling uncertainty in flow simulations via generalized polynomial chaos. Journal of Computational Physics, 187, 137–167 (2003)
BLATMAN, G. and SUDRET, B. Adaptive sparse polynomial chaos expansion based on least angle regression. Journal of Computational Physics, 230, 2345–2367 (2011)
ROSIĆ, B. V., LITVINENKO, A., PAJONK, O., and MATTHIES, H. G. Sampling-free linear Bayesian update of polynomial chaos representations. Journal of Computational Physics, 231, 5761–5787 (2012)
GERRITSMA, M., VAN DER STEEN, J. B., VOS, P., and KARNIADAKIS, G. Time-dependent generalized polynomial chaos. Journal of Computational Physics, 229, 8333–8363 (2010)
PANUNZIO, A. M., SALLES, L., and SCHWINGSHACKL, C. W. Uncertainty propagation for nonlinear vibrations: a non-intrusive approach. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 389, 309–325 (2017)
NAJM, H. N. Uncertainty quantification and polynomial chaos techniques in computational fluid dynamics. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 41, 35–52 (2009)
TOOTKABONI, M., ASADPOURE, A., and GUEST, J. K. Topology optimization of continuum structures under uncertainty—a polynomial chaos approach. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 201, 263–275 (2012)
GHANEM, R. and GHOSH, D. Efficient characterization of the random eigenvalue problem in a polynomial chaos decomposition. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 72, 486–504 (2007)
PASCUAL, B. and ADHIKARI, S. Hybrid perturbation-polynomial chaos approaches to the random algebraic eigenvalue problem. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 217, 153–167 (2012)
MANAN, A. and COOPER, J. Prediction of uncertain frequency response function bounds using polynomial chaos expansion. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 329, 3348–3358 (2010)
PENG, Y. B., GHANEM, R., and LI, J. Polynomial chaos expansions for optimal control of nonlinear random oscillators. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 329, 3660–3678 (2010)
WAN, X. and KARNIADAKIS, G. E. Long-term behavior of polynomial chaos in stochastic flow simulations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 195, 5582–5596 (2006)
ORSZAG, S. A. and BISSONNETTE, L. R. Dynamical properties of truncated Wiener-Hermite expansions. Physics of Fluids, 10, 2603–2613 (1967)
HEUVELINE, V. and SCHICK, M. A local time-dependent generalized polynomial chaos method for stochastic dynamical systems. Preprint (2011) https://doi.org/10.11588/emclpp.2011.04.11694
BECK, M. H., JÄCKLE, A., WORTH, G., and MEYER, H. D. The multiconfiguration timedependent Hartree (MCTDH) method: a highly efficient algorithm for propagating wavepackets. Physics Reports, 324, 1–105 (2000)
DE LATHAUWER, L., DE MOOR, B., and VANDEWALLE, J. A multilinear singular value decomposition. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 21, 1253–1278 (2000)
DE LATHAUWER, L., DE MOOR, B., and VANDEWALLE, J. On the best rank-1 and rank-(r 1, r 2, · · ·, r n) approximation of higher-order tensors. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 21, 1324–1342 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11632011, 11572189, and 51421092) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M601585)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, J., Zhang, Q., Wei, S. et al. Uncertainty quantification for stochastic dynamical systems using time-dependent stochastic bases. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 40, 63–84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2409-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2409-6
Key words
- uncertainty quantification
- stochastic response surface approximation
- time-dependent orthogonal bases
- polynomial chaos