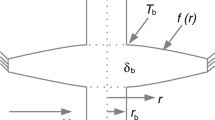
Abstract
The thermal analysis of the annular rectangular profile fins with variable thermal properties is investigated by using the homotopy analysis method (HAM). The thermal conductivity and heat transfer coefficient are assumed to vary with a linear and power-law function of temperature, respectively. The effects of the thermal-geometric fin parameter and the thermal conductivity parameter variations on the temperature distribution and fin efficiency are investigated for different heat transfer modes. Results from the HAM are compared with numerical results of the finite difference method (FDM). It can be seen that the variation of dimensionless parameters has a significant effect on the temperature distribution and fin efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraus, A. D., Aziz, A., and Welty, J. Extended Surface Heat Transfer, Wiley, New York (2001)
Aziz, A. and Enamul Hug, S. M. Perturbation solution for convecting fin with variable thermal conductivity. ASME Journal of Heat Transfer, 97, 300–301 (1975)
Ganji, D. D., Ganji, Z. Z., and Ganji, H. D. Determination of temperature distribution for annular fins with temperature dependent thermal conductivity by HMP. Thermal Science, 15(1), 111–115 (2011)
Kim, S. and Huang, C. H. A series solution of the non-linear fin problem with temperature dependent thermal conductivity and heat transfer coefficient. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 40(9), 2979–2987 (2007)
Bouaziz, M. N. and Aziz, A. Simple and accurate solution for convective adiative fin with temperature dependent thermal conductivity using double optimal linearization. Energy Conversion and Management, 51, 2776–2782 (2010)
Ganji, D. D., Rahimi, M., Rahgoshay, M., Jafari, M., and Babaelahi, M. Analytical and numerical investigation of fin efficiency and temperature distribution of conductive, convective, and radiative straight fins. Heat Transfer-Asian Research, 40(3), 233–245 (2011)
Chang, M. H. Decomposition solution for fins with temperature dependent surface heat flux. International Journal of Heat Mass Transfer, 48(9), 1819–1824 (2005)
Liao, S. J. Homotopy analysis method: a new analytical technique for nonlinear problems. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2(2), 95–100 (1997)
Liao, S. Homotopy analysis method: a new analytical method for nonlinear problems. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 19(10), 957–962 (1998) DOI 10.1007/BF02457955
Liao, S. J. Beyond Perturbation: Introduction to the Homotopy Analysis Methods, Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton (2003)
Liao, S. J. On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 147(2), 499–513 (2004)
Liao, S. J. Comparison between the homotopy analysis method and homotopy perturbation method. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 169(2), 1186–1194 (2005)
Liao, S. J. and Tan, Y. A general approach to obtain series solutions of nonlinear differential equations. Studies in Applied Mathematics, 119(4), 297–354 (2007)
Liao, S. J. Notes on the homotopy analysis method: some definitions and theorems. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14(4), 983–997 (2009)
Inc, M. Application of homotopy analysis method for fin efficiency of convective straight fins with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 79(2), 189–200 (2008)
Arslantürk, C. Analysis of thermal performance of annular fins with variable thermal conductivity by homotopy analysis method. Journal of Thermal Science Technology, 30(2), 1–7 (2010)
Khani, F. and Aziz, A. Thermal analysis of a longitudinal fin with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and heat transfer coefficient. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 15(3), 590–601 (2010)
Chowdhury, M. S. H., Hashim, I., and Abdulaziz, O. Comparison of homotopy analysis method and homotopy-perturbation method for purely nonlinear fin-type problems. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14(2), 371–378 (2009)
Khani, F., Raji, M. A., and Nejad, H. H. Analytical solutions and efficiency of the nonlinear fin problem with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and heat transfer coefficient. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14(8), 3327–3338 (2009)
Molabahrami, A. and Khani, F. The homotopy analysis method to solve the Burgers-Huxley equation. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 10(2), 589–600 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksoy, I.G. Thermal analysis of annular fins with temperature-dependent thermal properties. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 34, 1349–1360 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1750-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1750-8