Abstract
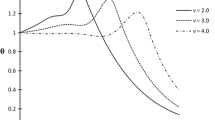
In this work, a model of two-temperature generalized thermoelasticity without energy dissipation for an elastic half-space with constant elastic parameters is constructed. The Laplace transform and state-space techniques are used to obtain the general solution for any set of boundary conditions. The general solutions are applied to a specific problem of a half-space subjected to a moving heat source with a constant velocity. The inverse Laplace transforms are computed numerically, and the comparisons are shown in figures to estimate the effects of the heat source velocity and the two-temperature parameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- λ, μ :
-
Lamé’s constants
- ρ :
-
density
- C E :
-
specific heat at constant strain
- t :
-
time
- T :
-
dynamical temperature
- T 0 :
-
reference temperature
- θ :
-
dynamical temperature increment (T−T 0)
- φ :
-
conductive temperature
- Q :
-
heat source
- α T :
-
coefficient of linear thermal expansion
- Γ :
-
stress-temperature coefficient (3λ+2μ)αT
- σ ij :
-
components of stress tensor
- e ij :
-
components of strain tensor
- u i :
-
components of displacement vector
- K*:
-
characteristic of theorem
- c 0 :
-
longitudinal wave speed \(\sqrt {\frac{{\lambda + 2\mu }} {\rho }}\)
- η :
-
thermal viscosity \(\frac{{\rho C_E }} {{K^* }}\)
- ɛ T :
-
dimensionless thermoelastic coupling constant \(\frac{{\gamma c_0^2 }} {{K^* }}\)
- C T :
-
dimensionless conductive-dynamical heat coupling constant ηc 20
- a :
-
two-temperature parameter
- β :
-
dimensionless two-temperature parameter ac 20 η 2
- b :
-
dimensionless mechanical coupling constant \(\frac{{\gamma T_0 }} {{\lambda + 2\mu }}\)
- v :
-
heat source velocity
References
Green, A. E. and Naghdi, P. M. Thermoelasticity without energy dissipation. Journal of Elasticity, 31, 189–208 (1993)
Green, A. E. and Naghdi, P. M. A re-examination of the basic postulate of thermomechanics. Proceeding of the Royal Society A, 432, 171–194 (1991)
Hetnarski, R. B. and Eslami, M. R. Thermal Stresses Advanced Theory and Applications, Springer, New York (2009)
Chandrasekharaiah, D. S. and Srinath, K. S. Thermoelastic waves without energy dissipation in an unbounded body with a spherical cavity. International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Science, 23(8), 555–562 (2000)
Kumar, R. and Deswal, S. Surface wave propagation in a micropolar thermoelastic medium without energy dissipation. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 256(1), 173–178 (2002)
Quintanilla, R. Thermoelasticity without energy dissipation of materials with microstructure. Journal of Applied Mathematical Modeling, 26, 1125–1137 (2002)
Roychoudhuri, S. K. and Dutta, P. S. Thermo-elastic interaction without energy dissipation in an infinite solid with distributed periodically varying heat sources. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 42, 4192–4203 (2005)
Roychoudhuri, S. K. and Bandyopadhyay, N. Radially symmetric thermo-elastic wave propagation without energy dissipation in an infinitely extended thin plate with a circular hole. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation, 179(1), 267–281 (2006)
Youssef, H. M. Theory of two-temperature generalized thermoelasticity. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 34(2), 138–146 (2011)
Youssef, H. M. State-space approach of two-temperature generalized thermoelastic medium subjected to moving heat source and ramp-type heating. Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures, 4(9), 1637–1649 (2009)
Youssef, H. M. Two-temperature generalized thermoelastic infinite medium with cylindrical cavity subjected to moving heat source. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 80(11), 1213–1224 (2010)
Youssef, H. M. Generalized thermoelastic infinite medium with spherical cavity subjected to moving hear source. Journal of Computational Mathematics and Modeling, 21(2), 212–225 (2010)
Charles, G. C. Matrices and Linear Transformations, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, New Jersey (1972)
Tzou, D. Macro-to-Micro Heat Transfer, Taylor & Francis, Washington, D. C. (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, H.M. State-space approach to two-temperature generalized thermoelasticity without energy dissipation of medium subjected to moving heat source. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 34, 63–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1653-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1653-7