Abstract
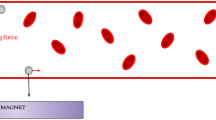
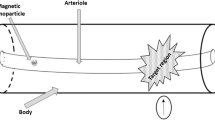
Among the proposed techniques for delivering drugs to specific locations within human body, magnetic drug targeting prevails due to its non-invasive character and its high targeting efficiency. Magnetic targeting drug delivery is a method of carrying drug-loaded magnetic nanoparticles to a target tissue target under the applied magnetic field. This method increases the drug concentration in the target while reducing the adverse side-effects. Although there have been some theoretical analyses for magnetic drug targeting, very few researchers have addressed the hydrodynamic models of magnetic fluids in the blood vessel. A mathematical model is presented to describe the hydrodynamics of ferrofluids as drug carriers flowing in a blood vessel under the applied magnetic field. In this model, magnetic force and asymmetrical force are added, and an angular momentum equation of magnetic nanoparticles in the applied magnetic field is modeled. Engineering approximations are achieved by retaining the physiclaly most significant items in the model due to the mathematical complexity of the motion equations. Numerical simulations are performed to obtain better insight into the theoretical model with computational fluid dynamics. Simulation results demonstrate the important parameters leading to adequate drug delivery to the target site depending on the magnetic field intensity, which coincident with those of animal experiments. Results of the analysis provide important information and suggest strategies for improving delivery in clinical application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jain K K. Targeted drug delivery for cancer[J]. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 2005, 4(4):311–313.
Fahmy T M, Fong P M, Goyal A, Saltzman W. Targeted for drug delivery[J]. Materials Today, 2005, 8(8):18–26.
Vasir J, Labhasetwar V. Targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy[J]. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 2005, 4(4):363–374.
Lübbe A S, Alexiou C. Bergemann C. Clinical application of magnetic drug targeting[J]. J Surg Res, 2001, 95(2):200–206.
Lübbe A S, Bergemann C, Riess H, Schriever F, et al. Clinical experiences with magnetic drug targeting: a phase I study with 4’-epidoxorubicin in 14 patients with advanced solid tumors[J]. Cancer Res, 1996, 56(20):4686–4693.
Alexiou C, Schmidt A, Klein R, Hulin P, Bergemann C, Arnold W. Magnetic drug targeting: biodistribution and dependency on magnetic field strength[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2002, 252(1–3):363–366.
Jurgons R, Seliger C, Hilpert A, Trahms L, Odenbach S, Alexiou C. Drug loaded magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy[J]. J Physics-Condensed Matte, 2006, 18(38):S2893–S2902.
Chen H, Ebner A, Kaminski M, Rosengart A, Ritter J. Analysis of magnetic drug carrier particle capture by a magnetizable intravascular stent-2: parametric study with multi-wire two-dimensional model[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 293(1):616–632.
Rosengart A, Kaminski M, Chen H, Caviness P, Ebner A, Ritter J. Magnetizable implants and functionalized magnetic carriers: a novel approach for noninvasive yet targeted drug delivery[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 293(1):633–638.
Ruuge E, Rusetski A. Magnetic fluids as drug carriers-targeted transport of drugs by a magneticfield[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 1993, 122(1–3):335–339.
Ramchand C, Pande P, Kopcansky P, Mehta R. Application of magnetic fluids in medicine and biotechnology[J]. Indian Pure Appl Phys, 2001, 39(10):683–686.
Asmatulu R, Zalich M, Claus R, Riffle J. Synthesis, characterization and targeting of biodegradable magnetic nanocomposite particles by external magnetic fields[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 292:108–119.
Alexiou C, Jurgons R, Schmid R, Erhardt W, Parak F, Bergemann C, Iro H. Magnetic drug targeting-a new approach in locoregional tumortherapy with chemotherapeutic agents, experimental animal studies[J]. HNO, 2005, 53(7):618–622.
Rotariu O, Iacob G, Strachan N, Chiriac H. Simulating the embolization of blood vessels using magnetic microparticles and acupuncture needle in a magnetic field[J]. Biotechnol Prog, 2004, 20(1):299–305.
Grief A, Richardson G. Mathematical modelling of magnetically targeted drug delivery[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 293(1):455–463.
Rotariu O, Strachan N. Modelling magnetic carrier particle targeting in the tumor microvasculature for cancer treatment[J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 293(1):639–646.
Rosensweig R E. Ferrohydrodynamics[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 1997, Chap. 6.
Versteeg H K, Malalasekera W. An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method[M]. New York: Wiley, 1995.
Fung Y C. Biodynamics: circulation[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
(Communicated by GUO Xing-ming)
Project supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2007CB936004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50875169)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han-dan, L., Wei, X., Shi-gang, W. et al. Hydrodynamic modeling of ferrofluid flow in magnetic targeting drug delivery. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 29, 1341–1349 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-008-1009-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-008-1009-y
Key words
- magnetic targeting drug delivery
- ferrofluids
- magnetic nanoparticles
- hydrodynamic modeling
- CFD simulation