Abstract
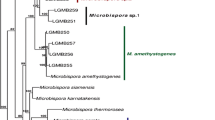
The family Vibrionaceae is classified into many clades based on their phylogenetic relationships. The Ponticus clade is one of its clades and consists of four species, Vibrio panuliri, V. ponticus, V. rhodolitus, and V. taketomensis. Two strains, CAIM 703 and CAIM 1902, were isolated from the diseased spotted rose snapper external lesion (Lutjanus guttatus), they were analyzed to determine their taxonomic position, a phylogenetic analysis was performed based on the 16S rRNA sequences proved that the two strains are members of the genus Vibrio and they belong to the Ponticus clade. Then, a phylogenomic analysis was performed with four type strains and four reference strains isolated from marine organisms and aquatic environments. Multilocus Sequence Analysis (MLSA) of 139 single-copy genes showed that CAIM 703 and CAIM 1902 belong to V. panuliri. The 16S rRNA sequence similarity value between CAIM 703 and CAIM 1902 was 99.61%. The Ponticus clade species showed Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) values between 78 to 80% against the two strains for ANIb, except V. panuliri LBS2T (99% and 100% similarity). Finally, this analysis represents the first phylogenomic analysis of the Ponticus clade where V. panuliri strains are reported from Mexico.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-saari N, Gao F, Rohul AA, Sato K, Sato K, Mino S, Suda W, Oshima K, Hattori M, Ohkuma M, Meirelles PM, Thompson FL, Thompson C, Filho GM, Gomez-Gil B, Sawabe T, Sawabe T (2015) Advanced microbial taxonomy combined with genome-based-approaches reveals that Vibrio astriarenae sp. Nov., an agarolytic marine bacterium, forms a new clade in vibrionaceae. PLOS ONE 10(8):e0136279. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136279
Auch AF, Von Jan M, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genomic Sci 2(1):117–134. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.531120
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Baker-Austin C, Trinanes J, Gonzalez-Escalona N, Martinez-Urtaza J (2017) Non-Cholera Vibrios: The Microbial Barometer of Climate Change. Trends Microbiol 25(1):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2016.09.008
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, Da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu X-W, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(1):461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Delmont TO, Quince C, Shaiber A, Esen ÖC, Lee ST, Rappé MS, McLellan SL, Lücker S, Eren AM (2018) Nitrogen-fixing populations of Planctomycetes and Proteobacteria are abundant in surface ocean metagenomes. Nat Microbiol 3(7):804–813. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-018-0176-9
Dikow RB (2011) Systematic relationships within the Vibrionaceae (Bacteria: Gammaproteobacteria): steps toward a phylogenetic taxonomy. Cladistics 27(1):9–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-0031.2010.00312.x
Enciso-Ibarra J, Roque A, Bolán-Mejia C, Enciso-Ibarra K, González-Castillo A, Gomez-Gil B (2023) Vibrio eleionomae sp. Nov., isolated from shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) pond water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 73(5):005866. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.005866
Eren AM, Esen ÖC, Quince C, Vineis JH, Morrison HG, Sogin ML, Delmont TO (2015) Anvi’o: An advanced analysis and visualization platform for ‘omics data. PeerJ 3:e1319. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1319
Galperin MY, Kristensen DM, Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2019) Microbial genome analysis: The COG approach. Brief Bioinform 20(4):1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx117
Giorgi FM, Ceraolo C, Mercatelli D (2022) The R Language: An Engine for Bioinformatics and Data Science. Life 12(5):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050648
González-Castillo A, Enciso-Ibarra J, Gomez-Gil B (2020) Genomic taxonomy of the Mediterranei clade of the genus Vibrio (Gammaproteobacteria). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113(6):851–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01396-4
González-Castillo A, Carballo JL, Bautista-Guerrero E (2021) Genomics and phylogeny of the proposed phylum ‘Candidatus Poribacteria’ associated with the excavating sponge Thoosa mismalolli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 114(12):2163–2174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01670-z
González-Castillo A, Carballo JL, Bautista-Guerrero E (2023) Genomics, Phylogeny, and in Silico Phenotyping of Nitrosopumilus Genus. Curr Microbiol 80(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03121-y
Goodfellow M, Manfio GP, Chun J, Claridge MF, Dawah HA, Wilson MR (1997) Towards A Practical Species Concept for Cultivable Bacteria (Species: The Units of Biodiversity). Chapman & Hall
Guerrero A, Gomez-Gil B, Lizarraga-Partida ML (2021) Genomic stability among O3:K6 V. parahaemolyticus pandemic strains isolated between 1996 to 2012 in American countries. BMC Genomic Data 22(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-021-00985-0
Hahn MW, Jezberová J, Koll U, Saueressig-Beck T, Schmidt J (2016) Complete ecological isolation and cryptic diversity in Polynucleobacter bacteria not resolved by 16S rRNA gene sequences. ISME J 10(7):1642–1655. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.237
Hall BG (2013) Building Phylogenetic Trees from Molecular Data with MEGA. Mol Biol Evol 30(5):1229–1235. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst012
Henz SR, Huson DH, Auch AF, Nieselt-Struwe K, Schuster SC (2005) Whole-genome prokaryotic phylogeny. Bioinformatics 21(10):2329–2335. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth324
Hyatt D, Chen G-L, LoCascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 11(1):119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-119
Jaspers E, Overmann J (2004) Ecological Significance of Microdiversity: Identical 16S rRNA Gene Sequences Can Be Found in Bacteria with Highly Divergent Genomes and Ecophysiologies. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(8):4831–4839. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.8.4831-4839.2004
Jiang C, Tanaka M, Nishikawa S, Mino S, Romalde JL, Thompson FL, Gomez-Gil B, Sawabe T (2022) Vibrio Clade 3.0: New Vibrionaceae Evolutionary Units Using Genome-Based Approach. Curr Microbiol 79(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02725-0
Kumari P, Poddar A, Schumann P, Das SK (2014) Vibrio panuliri sp. Nov., a marine bacterium isolated from spiny lobster, Panulirus penicillatus and transfer of Vibrio ponticus from Scophthalmi clade to the newly proposed Ponticus clade. Res Microbiol 165(10):826–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2014.10.012
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35(9):3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
MacFaddin J (2000) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins
Macián MC, Ludwig W, Aznar R, Grimont PA, Schleifer KH, Garay E, Pujalte MJ (2001) Vibrio lentus sp. Nov., isolated from Mediterranean oysters. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(4):1449–1456. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-4-1449
Macián MC, Garay E, Grimont PAD, Pujalte MJ (2004) Vibrio ponticus sp. Nov., a Neighbour of V. fluvialis-V. furnissii Clade, Isolated from Gilthead Sea Bream, Mussels and Seawater. Syst Appl Microbiol 27(5):535–540. https://doi.org/10.1078/0723202041748127
Mahato NK, Gupta V, Singh P, Kumari R, Verma H, Tripathi C, Rani P, Sharma A, Singhvi N, Sood U, Hira P, Kohli P, Nayyar N, Puri A, Bajaj A, Kumar R, Negi V, Talwar C, Khurana H, Nagar S, Sharma M, Mishra H, Singh AK, Dhingra G, Negi RK, Shakarad M, Singh Y, Lal R (2017) Microbial taxonomy in the era of OMICS: application of DNA sequences, computational tools and techniques. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110(10):1357–1371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0928-1
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Prakash O, Verma M, Sharma P, Kumar M, Kumari K, Singh A, Kumari H, Jit S, Gupta SK, Khanna M, Lal R (2007) Polyphasic approach of bacterial classification—An overview of recent advances. Indian J Microbiol 47(2):98–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-007-0022-x
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(45):19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Rodriguez-R LM, Gunturu S, Harvey WT, Rosselló-Mora R, Tiedje JM, Cole JR, Konstantinidis KT (2018) The Microbial Genomes Atlas (MiGA) webserver: Taxonomic and gene diversity analysis of Archaea and Bacteria at the whole genome level. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W282–W288. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky467
Rosselló-Mora R (2001) The species concept for prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25(1):39–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6445(00)00040-1
Sentausa E, Fournier P-E (2013) Advantages and limitations of genomics in prokaryotic taxonomy. Clin Microbiol Infect 19(9):790–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-0691.12181
Silva CSF, Walter JM, Nobrega MS, Calegario G, Appolinario LR, Leomil L, Cavalcanti G, Silva BS, Garcia GD, Tschoeke D, Swings J, Thompson FL, Thompson CC (2018) Genome Sequences of Vibrio maerlii sp. Nov. And Vibrio rhodolitus sp. Nov. Isolated from Rhodoliths. Microbiol Resour Announc 7(19):e01039-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01039-18
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tanaka M, Hongyu B, Jiang C, Mino S, Milet Meirelles P, Thompson F, Gomez-Gil B, Sawabe T (2020) Vibrio taketomensis sp. Nov. By genome taxonomy. Syst Appl Microbiol 43(1):126048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2019.126048
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44(14):6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Vesth T, Wassenaar TM, Hallin PF, Snipen L, Lagesen K, Ussery DW (2010) On the Origins of a Vibrio Species. Microb Ecol 59(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9596-7
Vesth T, Lagesen K, Acar Ö, Ussery D (2013) CMG-Biotools, a Free Workbench for Basic Comparative Microbial Genomics. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60120. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060120
Funding
This study was funded by Centro de Investigación en Alimentación y Desarrollo and Universidad Politécnica de Sinaloa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Alejandra de Jesús Chavarín-Meza. Writing - Original Draft and Formal analysis. Bruno Gómez-Gil. Funding acquisition and Conceptualization. Adrián González-Castillo: Formal analysis, Project administration and Resources. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Jesús Chavarín-Meza, A., Gómez-Gil, B. & González-Castillo, A. Phylogenomic analysis of the Ponticus clade: strains isolated from the spotted rose snapper (Lutjanus guttatus). Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 117, 59 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-024-01959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-024-01959-9