Abstract
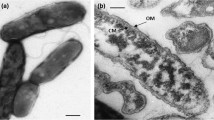
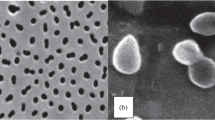
Three novel facultatively methylotrophic bacteria, strains 3CT, 1A, 8P, were isolated from activated sludges. The isolates were aerobic, Gram-stain-negative, non-motile, non-spore forming rods multiplying by binary fission. The predominant polar lipids were phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethylethanolamine, phosphatidylmonomethylethanolamine, and diphosphatidylglycerol. The major fatty acids of cells were С18:1ω7c, C19:0ω8c cyclo and C16:0. Levels of 16S rRNA gene similarity indicates that the closely relatives are representatives of the genera Starkeya, Ancylobacter, Angulomicrobium and Methylorhabdus (96.4–99.4%). Genomic comparisons of 3CT and its closest relatives, S. novella DSM 506T and S. koreensis Jip08T, shared 87.3 and 86.8% nucleotide identity and 28.3 and 26.8% digital DNA–DNA hybridization values, respectively. The average amino acid identities between the strain 3CT and representatives of Starkeya, Ancylobacter and Angulomicrobium were in the range of 75.6–84.3%, which combines these strains into a single genus and gives rise to their reclassification. Based on polyphasic analyses, the strains 3CT, 1A, 8P represents a novel species of the genus Ancylobacter, for which the name Ancylobacter moscoviensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is 3CT (= VKM B-3218T = KCTC 62336T). Furthermore, we also suggested the reclassification of Starkeya novella as Ancylobacter novellus comb. nov., Starkeya koreensis as Ancylobacter koreensis comb. nov., Angulomicrobium tetraedrale as Ancylobacter tetraedralis comb. nov., Angulomicrobium amanitiforme as Ancylobacter amanitiformis comb. nov. and Methylorhabdus multivorans as Ancylobacter multivorans comb. nov. with the emended description of the genus Ancylobacter.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agafonova NV, Kaparullina EN, Trotsenko YA, Doronina NV (2017) Ancylobacter sonchi sp. nov., a novel methylotrophic bacterium frоm roots of Sonchus arvensis L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(11):4552–4558. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002330
Andreoni V, Zanchi R, Cavalca L, Corsini A, Romagnoli C, Canzi E (2012) Arsenite oxidation in Ancylobacter dichloromethanicus As3-1b Strain: detection of genes involved in arsenite oxidation and CO2 fixation. Curr Microbiol 65(2):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0149-9
Atlas R (1993) Handbook of microbiological media. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Auch A, Von Jan M, Klenk H, Göker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genomic Sci 2(1):117–134. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.531120
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich A, Dvorkin M, Kulikov A, Lesin V, Nikolenko S, Pham S, Prjibelski A, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev M, Pevzner P (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol: J Comput Mol cell biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Camboim EKA, Tadra-Sfeir MZ, de Souza EM, Pedrosa FdO, Andrade PP, McSweeney CS, Riet-Correa F, Melo MA (2012) Defluorination of sodium fluoroacetate by bacteria from soil and plants in Brazil. Sci World J 2012. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/149893
Chaumeil P-A, Mussig AJ, Hugenholtz P, Parks DH (2020) GTDB-Tk: a toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 36(6):1925–1927. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz848
Chemodurova AA, Kaparullina EN, Machulin AV, Spröer C, Lang E, Doronina NV (2020) Ancylobacter lacus sp. nov. and Ancylobacter plantiphilus sp. nov., Novel Aerobic Facultative Methylotrophic Bacteria. Microbiology 89(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261720010051
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu X-W, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 68(1):461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of Isoprenoid Quinones. In: Bergan T (ed) Methods in Microbiology, Academic Press, pp 329–366
Doronina NV, Braus-Stromeyer SA, Leisinger T, Trotsenko YA (1995) Isolation and characterization of a new facultatively methylotrophic bacterium: description of Methylorhabdus multivorans, gen. nov., sp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 18(1):92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80454-6
Doronina NV, Gogleva AA, Trotsenko YA (2012) Methylophilus glucosoxydans sp. nov., a restricted facultative methylotroph from rice rhizosphere. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 62(1):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.024620-0
Doronina NV, Kaparullina EN, Chemodurova AA, Trotsenko YA (2018) Paracoccus simplex sp. nov., a new methylamine-utilizing facultative methylotroph. Microbiology 87(5):662–671. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261718050077
Doronina NV, Kaparullina EN, Trotsenko YA (2014) Methyloversatilis thermotolerans sp. nov., a novel thermotolerant facultative methylotroph isolated from a hot spring. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 64(Pt1):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.055046-0
Doronina NV, Trotsenko YA, Tourova TP, Kuznetsov BB, Leisinger T (2001) Albibacter methylovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel aerobic, facultatively autotrophic and methylotrophic bacterium that utilizes dichloromethane. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 51(3):1051–1058. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-3-1051
Dreyfus B, Garcia JL, Gillis M (1988) Characterization of Azorhizobium caulinodans gen. nov., sp. nov., a stem-nodulating nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from Sesbania rostrata. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 38(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-38-1-89
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Firsova J, Doronina N, Lang E, Spröer C, Vuilleumier S, Trotsenko Y (2009) Ancylobacter dichloromethanicus sp. nov. – a new aerobic facultatively methylotrophic bacterium utilizing dichloromethane. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(4):227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2009.02.002
Fritz I, Strömpl C, Abraham W-R (2004) Phylogenetic relationships of the genera Stella, Labrys and Angulomicrobium within the ‘Alphaproteobacteria’ and description of Angulomicrobium amanitiforme sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 54(3):651–657. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02746-0
Grouzdev DS, Rysina MS, Bryantseva IA, Gorlenko VM, Gaisin VA (2018) Draft genome sequences of ‘Candidatus Chloroploca asiatica’ and ‘Candidatus Viridilinea mediisalina’, candidate representatives of the Chloroflexales order: phylogenetic and taxonomic implications. Stand Genomic Sci 13(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-018-0329-8
Hoang DT, Chernomor O, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS (2018) UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol Biol Evol 35(2):518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
Hoang DT, Vinh LS, Flouri T, Stamatakis A, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2018) MPBoot: fast phylogenetic maximum parsimony tree inference and bootstrap approximation. BMC Evol Biol 18(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1131-3
Horneffer V, Haverkamp J, Janssen H-G, Notz R (2004) MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of bacterial spores: wet heat-treatment as a new releasing technique for biomarkers and the influence of different experimental parameters and microbiological handling. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 15(10):1444–1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasms.2004.06.017
Hördt A, López MG, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Weinhold L-M, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020) Analysis of 1,000 + type-strain genomes substantially improves taxonomic classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front Microbiol 11:468
Im W-T, Aslam Z, Lee M, Ten LN, Yang D-C, Lee S-T (2006) Starkeya koreensis sp. nov., isolated from rice straw. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 56(10):2409–2414. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64093-0
Irgens RL, Kersters K, Segers P, Gillis M, Staley JT (1991) Aquabacter spiritensis, gen. nov., sp. nov. an aerobic, gas-vacuolate aquatic bacterium. Arch Microbiol 155(2):137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248607
Jain C, Rodriguez-R LM, Phillippy AM, Konstantinidis KT, Aluru S (2018) High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat Commun 9(1):5114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07641-9
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14(6):587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kappler U, Nouwens A (2013) Metabolic adaptation and trophic strategies of soil bacteria—C1- metabolism and sulfur chemolithotrophy in Starkeya novella. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00304
Kelly DP, McDonald IR, Wood AP (2000) Proposal for the reclassification of Thiobacillus novellus as Starkeya novella gen. nov., comb. nov., in the alpha-subclass of the Proteobacteria. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 50(5):1797–1802. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-50-5-1797
Kelly D, Wood A (2005) Genus XIX. Starkeya (ex Starkey 1934) Kelly, McDonald and Wood 2000, 1800VP. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The Proteobacteria, Part C The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria 2nd edn edn. Springer, New York
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lane D (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Lang E, Swiderski J, Stackebrandt E, Schumann P, Spröer C, Sahin N (2008) Description of Ancylobacter oerskovii sp. nov. and two additional strains of Ancylobacter polymorphus. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 58(9):1997–2002. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65666-0
Lu P, Jin L, Liang B, Zhang J, Li S, Feng Z, Huang X (2011) Study of biochemical pathway and enzyme involved in Metsulfuron-Methyl Degradation by Ancylobacter sp. XJ-412-1 isolated from soil. Curr Microbiol 62(6):1718–1725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9919-z
Luo C, Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) MyTaxa: an advanced taxonomic classifier for genomic and metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 42(8):e73–e73. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku169
Marín P, Martirani-Von Abercron SM, Urbina L, Pacheco-Sánchez D, Castañeda-Cataña MA, Retegi A, Eceiza A, Marqués S (2019) Bacterial nanocellulose production from naphthalene. Microb Biotechnol 12(4):662–676. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13399
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Nguyen L-T, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32(1):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Nikitin D (1971) A new soil microorganism- Renobacter vacuolatum gen.nov. sp.nov. Dokl Acad Nauk SSSR (in Russian) 198:447–448
Oren A, Xu X-W (2014) The Family Hyphomicrobiaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: alphaproteobacteria and betaproteobacteria. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 247–281
Oren A (2014) The family Xanthobacteraceae. The Prokaryotes. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30197-1_258
Ørskov J (1928) Beschreibung eines neuen Mikroben, Microcyclus aquaticus. mit Eigentuemlicher Morphologie Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg Abt I 107:180–184
Poroshina MN, Doronina NV, Kaparullina EN, Kovalevskaya NP, Trotsenko YA (2013) Halophilic and halotolerant aerobic methylobacteria from the technogenic Solikamsk biotopes. Microbiology 82(4):490–498. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261713040097
Qin Q-L, Xie B-B, Zhang X-Y, Chen X-L, Zhou B-C, Zhou J, Oren A, Zhang Y-Z (2014) A Ppoposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196(12):2210–2215. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01688-14
Raj HD (1983) NOTES: proposal of Ancylobacter gen. nov. as a substitute for the bacterial genus microcyclus Ørskov 1928. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 33(2):397–398. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-33-2-397
Shi W, Sun Q, Fan G, Hideaki S, Moriya O, Itoh T, Zhou Y, Cai M, Kim S-G, Lee J-S, Sedlacek I, Arahal DR, Lucena T, Kawasaki H, Evtushenko L, Weir Bevan S, Alexander S, Dénes D, Tanasupawat S, Eurwilaichitr L, Ingsriswang S, Gomez-Gil B, Hazbón Manzour H, Riojas MA, Suwannachart C, Yao S, Vandamme P, Peng F, Chen Z, Liu D, Sun X, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Meng Z, Wu L, Ma J (2021) gcType: a high-quality type strain genome database for microbial phylogenetic and functional research. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D694–D705. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa957
Staley J, Jenkins C, Konopka A (2005) Genus III. Ancylobacter Raj 1983, 397VP. Springer, New York
Starkey RL (1934) Cultivation of organisms concerned in the oxidation of thiosulfate. J Bacteriol 28(4):365–386. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.28.4.365-386.1934
Suarez C, Ratering S, Schäfer J, Schnell S (2017) Ancylobacter pratisalsi sp. nov. with plant growth promotion abilities from the rhizosphere of Plantago winteri Wirtg. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 67(11):4500–4506. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002320
Sun L, Zhu S, Yang Z, Chen Q, Liu H, Zhang J, Hu G, Li S, Hong Q (2016) Degradation of monocrotophos by Starkeya novella YW6 isolated from paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(4):3727–3735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5606-0
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Ciufo S, Li W (2013) Prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US), Bethesda (MD)
Urakami T, Komagata K (1986) Methanol-utilizing ancylobacter strains and comparison of their cellular fatty acid compositions and quinone systems with those of Spirosoma, Flectobacillus, and Runella Species. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 36(3):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-36-3-415
Urakami T, Komagata K (1987) Cellular fatty acid composition with special reference to the existence of hydroxy fatty acids in Gram-negative methanol-, methane-, and methylamine-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Appl Microbiol 33(2):135–165. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.33.135
Varghese NJ, Mukherjee S, Ivanova N, Konstantinidis KT, Mavrommatis K, Kyrpides NC, Pati A (2015) Microbial species delineation using whole genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 43(14):6761–6771. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv657
Vasilyeva L (2015) Angulomicrobium. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria, pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118960608.gbm00812
Vasilyeva L, Semenov AM (1984) Labrys monahos, a new budding prosthecate bacterium with radial symmetry. Mikrobiologiya (Russian) 53:85–92
Vasil’eva L, Lafitskaya T, Namsaraev B (1979) Angulomicrobium tetraedrale, a new genus of budding bacteria with radial cell symmetry. Mikrobiologiya (Russian) 48:1033–1039
Wang Y, Wang G, Dai Y, Wang Y, Lee Y-W, Shi J, Xu J (2020) Biodegradation of deoxynivalenol by a novel microbial consortium. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02964
Wiegel J, Wilke D, Baumgarten J, Opitz R, Schlegel HG (1978) Transfer of the nitrogen-fixing hydrogen bacterium corynebacterium autotrophicum baumgarten to xanthobacter gen nov. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 28(4):573–581. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-28-4-573
Wijngaard AJvd K, KWvd P, Jvd, Pries F, Kazemier B, Janssen DB (1992) Degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane by Ancylobacter aquaticus and other facultative methylotrophs. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(3):976–983. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.58.3.976-983.1992
Wu L, Ma J (2019) The Global Catalogue of Microorganisms (GCM) 10K type strain sequencing project: providing services to taxonomists for standard genome sequencing and annotation. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 69(4):895–898. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003276
Xin YH, Zhou YG, Chen WX (2006) Ancylobacter polymorphus sp. nov. and Ancylobacter vacuolatus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 56(6):1185–1188. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64118-0
Xin YH, Zhou YG, Zhou HL, Chen WX (2004) Ancylobacter rudongensis sp. nov., isolated from roots of Spartina anglica. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 54(2):385–388. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02466-0
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol MicroBiol 67(5):1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Aharon Oren for his advice regarding the nomenclature. We are grateful to N.V. Prisyazhnaya (All-Russian Collection of Microorganisms, IBPM RAS) for MALDI analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, grant agreement № 075-15-2021-1051 and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1602002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.D.: isolation of cultures, formal analysis, data curation, original draft preparation, review and editing, visualization; A.Ch.: formal analysis; V.K.: genome sequencing of the type strain, the section on genome features; D.G.: genome sequencing of the type strain, the sections on bioinformatic phylogenomic analyses and genome features, review and editing; N.A.: original draft preparation, data curation, review and editing; W.S.: genome sequence and data analyses of Ancylobacter spp.; L.W.: genome of sequence and data analyses; E.K.: formal analysis, data curation, original draft preparation, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Doronina, N.V., Chemodurova, A.A., Grouzdev, D.S. et al. Ancylobacter moscoviensis sp. nov., novel facultatively methylotrophic bacteria from activated sludge and the reclassification of Starkeya novella (Starkey 1934) Kelly et al. 2000 as Ancylobacter novellus comb. nov., Starkeya koreensis Im et al. 2006 as Ancylobacter koreensis comb.nov., Angulomicrobium tetraedrale Vasil'eva et al. 1986 as Ancylobacter tetraedralis comb. nov., Angulomicrobium amanitiforme Fritz et al. 2004 as Ancylobacter amanitiformis comb. nov., and Methylorhabdus multivorans Doronina et al. 1996 as Ancylobacter multivorans comb. nov., and emended description of the genus Ancylobacter. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 116, 153–170 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-022-01788-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-022-01788-8