Abstract
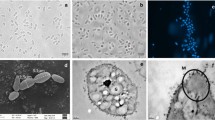
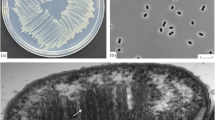
A gammaproteobacterial methanotroph, strain GJ1T, was isolated from a rhizosphere soil sample of rice in Nanjing, China. The cells were Gram-negative, motile rods with a single polar flagellum, and they contained type I intracytoplasmic membranes. The cells formed pink colonies. The strain possessed both the particulate methane monooxygenase enzyme (pMMO) and the soluble methane monooxygenase enzyme (sMMO). pxmABC, encoding a divergent methane monooxygenase (pXMO), and nifH, which encodes dinitrogenase reductase, were also present. Methane and methanol were utilized as sole carbon sources, while other carbon sources, including acetate, pyruvate, succinate, citrate, malate, glucose, urea, methylamine, ethanol and formate, could not be utilized by strain GJ1T. Cell grew optimally at 25–33 °C (range 16–37 °C), pH 6.0–8.0 (range 5.5–8.5) and 0–1.2% NaCl (no growth above 1.5% NaCl). Phylogenetic analyses based on the 16S rRNA gene, pmoA and nifH showed that the isolate belongs to the genus Methylomonas of the family Methylococcaceae within the class Gammaproteobacteria. The major quinone was determined to be MQ-8, and the major fatty acids were observed to be C16:1 and C14:0. The genome size of strain GJ1T is about 4.55 Mb, and the DNA G + C content of the strain was determined to be 53.67 mol% within the range of the genus Methylomonas (47–58 mol%) reported at present. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values between strain GJ1T and Methylomonas koyamae Fw12E-YT among the genus Methylomonas were the highest, and they were only 74.66% and 21.40%, respectively. In consequence, results of phenotypic characterization and phylogenetic analyses support strain GJ1T as a novel species within the genus Methylomonas, namely, Methylomonas rhizoryzae sp. nov.. The type strain is GJ1T (= ACCC 61706).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachelet D, Neue HU (1993) Methane emissions from wetland rice areas of Asia. Chemosphere 26:219–237
Bowman JP, Sly LI, Cox JM, Hayward AC (1990) Methylomonas fodinarum sp. nov. and Methylomonas aurantiaca sp.nov.: two closely related type I obligate methanotrophs. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:279–287
Bowman JP, Sly LI, Nichols PD, Hayward AC (1993) Revised taxonomy of the methanotrophs: description of Methylobacter gen. nov., emendation of Methylococcus, validation of Methylosinus and Methylocystis species, and a proposal that the family Methylococcaceae includes only the group I methanotrophs. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:735–753
Cleenwerck I, Vandemeulebroecke K, Janssens D, Swings J (2002) Re-examination of the genus Acetobacter, with descriptions of Acetobacter cerevisiae sp. nov. and Acetobacter malorum sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1551–1558
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of isoprenoid quinines. Method Microbiol 18:329–366
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Conrad R (2007) Microbial ecology of methanogens and methanotrophs. Adv Agron 96:1–63
Danilova OV, Kulichevskaya IS, Rozova ON, Detkova EN, Bodelier PLE, Trotsenko YA, Dedysh SN (2013) Methylomonas paludis sp. nov., the first acid-tolerant member of the genus Methylomonas, from an acidic wetland. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2282–2289
Dedysh SN, Dunfield PF (2014) Cultivation of methanotrophs. Springer, Berlin
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Artaxo P, Berntsen T, Averyt KB (2007) Changes in atmospheric constituents in radiative forcing. In: Fourth assessment report of the working group I Report, vol 2007, pp 129–234
Frenzel P (2000) Plant-associated methane oxidation in rice fields and wetlands. Adv Microb Ecol 16:85–114
Frindte K, Maarastawi SA, Lipski A, Hamacher J, Knief C (2017) Characterization of the first rice paddy cluster I isolate, Methyloterricola oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov. and amended description of Methylomagnum ishizawai. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4507–4514
Ghashghavi M, Belova SE, Bodelier PLE, Dedysh SN, Kox MAR, Speth DR, Frenzel P, Jetten MSM, Lucker S, Luke C (2019) Methylotetracoccus oryzae strain C50C1 is a novel Type Ib Gammaproteobacterial methanotroph adapted to freshwater environments. mSphere 4:0
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridizationvalues and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Groth I, Schumann P, Weiss N, Martin K, Rainey FA (1996) Agrococcus jenensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus of actinomycetes with diaminobutyric acid in the cell wall. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:234–239
Hanson RS, Hanson TE (1996) Methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiol Rev 60:439–471
Hoefman S, Heylen K, De Vos P (2014) Methylomonas lenta sp. nov., a methanotroph isolated from manure and a denitrification tank. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1210–1217
Kalyuzhnaya MG, Khmelenina VN, Kotelnikova S, Holmquist L, Pedersen K, Trotsenko YA (1999) Methylomonas scandinavica sp. nov., a new methanotrophic psychrotrophic bacterium isolated from deep igneous rock ground water of Sweden. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:565–572
Kim OS, Cho Y, Lee K et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Khatri K, Mohite JA, Pandit PS, Bahulikar R, Rahalkar MC (2020) Description of ‘Ca. Methylobacter oryzae’ KRF1, a novel species from the environmentally important Methylobacter clade 2. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:729–735
Knief C (2015) Diversity and habitat preferences of cultivated and uncultivated aerobic methanotrophic bacteria evaluated based on pmoA as molecular marker. Front microbiol 6:1346
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Ogiso T, Ueno C, Dianou D, Van Huy T, Katayama A, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2012) Methylomonas koyamae sp. nov., a type I methane-oxidizing bacterium from floodwater of a rice paddy field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1832–1837
Op den Camp HJ, Islam T, Stott MB, Harhangi HR, Hynes A et al (2009) Environmental, genomic and taxonomic perspectives on methanotrophic Verrucomicrobia. Env Microbiol Rep 1:293–306
Pandit PS, Rahalkar MC (2019) Renaming of ‘Candidatus Methylocucumis oryzae’ as Methylocucumis oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Type I methanotroph isolated from India. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:955–959
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newslett 20:1–6
Sieburth JM, Johnson PW, Eberhardt MA, Sieracki ME, Lidstrom M, Laux D (1987) The first methaneoxiding bacterium from the upper mixing layer of the deep ocean: Methylomonas pelagica sp. nov. Curr Microbiol 14:285–293
Takeda K, Tonouchi A, Mai T, Suko T, Suzuki S et al (2008) Characterization of cultivable methanotrophs from paddy soils and rice roots. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 54:876–885
Tamura K, Peterson DS, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tavormina PL, Orphan VJ, Kalyuzhnaya MG, Jetten MSM, Klotz MG (2011) A novel family of functional operons encoding methane/ammonia monooxygenase-related proteins in gammaproteobacterial methanotrophs. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:91–100
Vita N, Platsaki S, Basle A, Allen SJ, Paterson NG et al (2015) A four-helix bundle stores copper for methane oxidation. Nature 525:140–143
Wayne LG et al (1987) International Committee on SystematicBacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Whittenbury R, Davies SL, Davey JF (1970) Exospores and cysts formed by methane-utilizing. Microbiology 61:219–226
Whittenbury R, Krieg NR (1984) Family Methylococcaceae. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, pp 256–261
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Yoon S, Ha S, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800095, 31770125, 31970099) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180541).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PZ, MC, DP and YL performed experiments, PZ and MC performed data analysis and wrote the manuscript, XY designed research and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Cheng, M., Pei, D. et al. Methylomonas rhizoryzae sp. nov., a type I methanotroph isolated from the rhizosphere soil of rice. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 113, 2167–2176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01487-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01487-2