Abstract
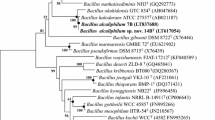
An alkaliphilic and moderately halophilic strain, designated YSP-3T, characterised by optimal growth at pH 9.0 and at 8.0% (w/v) NaCl, was isolated from Yangshapao Lake, Jilin Province, China. Cells of this strain is Gram-positive, straight rods and form a central or sub-terminal ellipsoidal endospore. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that it was grouped in the genus Bacillus with Bacillus aurantiacus K1-5T and Bacillus populi FJAT-45347T as the close relative (97.5 and 97.2% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity, respectively). Genomic relatedness between strain YSP-3T and its close relative was evaluated using average nucleotide identity, digital DNA–DNA hybridization and average amino acid identity with the values of 70.3–85.1%, 19.7–20.1% and 71.5–71.6%, respectively. Comparative genomics analysis showed that strain YSP-3T has distinct amino acid bias and significantly differences from foreign invasion events during evolution relative to the reference strains. Cell-wall peptidoglycan contains meso-diaminopimelic acid. The predominant polar lipids are phosphatidylethanolamine, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol. The predominant quinone is menaquinone-7. The major fatty acids of strain YSP-3T are anteiso-C15:0, iso-C15:0, iso-C16:0, anteiso-C17:0 and Iso-C14:0. DNA G + C content of strain YSP-3T is 48.3 mol%. Based on genomics analysis, physiological, biochemical and chemotaxonomic data, strain YSP-3T represent a novel species, for which the name Bacillus lacisalsi sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is YSP-3T ( = ACCC 60365T = KCTC 33934T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ash C, Farrow JAE, Wallbanks S, Collins MD (1991) Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus revealed by comparative analysis of small-subunit-ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett Appl Microbiol 13:202–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.1991.tb00608.x
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2002) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Pearson Education, Inc., Benjamin Cummings
Chen GQ, Jiang XR (2018) Next generation industrial biotechnology based on extremophilic bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 50:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.11.016
Chen Y, Chen XY, Du HT, Zhang X, Ma YM et al (2019) Chromosome engineering of the TCA cycle in Halomonas bluephagenesis for production of copolymers of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 3-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV). Metab Eng 54:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.03.006
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of isoprenoid quinones. Methods Microbiol 18:329–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70480-X
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Determination of biochemical properties. In: Dong XZ, Cai MY (eds) Manual for the systematic identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398 (in Chinese)
Embley TM (1996) The linear PCR reaction: a simple and robust method for sequencing amplified rRNA genes. Lett Appl Microbiol 13:171–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.1991.tb00600.x
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA et al (1981) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 25–29
Gregersen T (1978) Rapid method for distinction of gram-negative from gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 5:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498806
Hasegawa T, Takizawa M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 29:319–322. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.29.319
Hille F, Richter H, Wong SP, Bratovič M, Ressel S, Charpentier E (2018) The biology of CRISPR-Cas: backward and forward. Cell 172:1239–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.032
Kämpfer P (1994) Limits and possibilities of total fatty acid analysis for classification and identification of Bacillus species. Syst Appl Microbiol 17:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80035-4
Kämpfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Micobiol 42:989–1005. https://doi.org/10.1139/m96-128
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-society colour council-national bureau of standards colour-name charts illustrated with centroid colours published in US. US Government Printing Office, Washington
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.064931-0
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005) Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 187:6258–6264. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6258-6264.2005
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Logan NA, de Vos P, Genus I (2009) Bacillus. In: de Vos P, Garrity G, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W et al (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3. Springer, New York, pp 21–128
Luo C, Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) MyTaxa: an advanced taxonomic classifier for genomic and metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 42:e73. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku169
McDonald JH, Grasso AM, Rejto LK (1999) Patterns of temperature adaptation in proteins from Methanococcus and Bacillus. Mol Biol Evol 16:1785–1790. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026090
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbbiol Methods 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W182–W185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm321
Ohta H, Hattori T (1983) Agromonas oligotrophica gen. nov., sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing oligotrophic bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 49:429–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399322
Overbeek R, Olson R, Pusch GD, Olsen GJ, Davis JJ et al (2014) The SEED and the rapid annotation of microbial genomes using subsystems technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res 42:D206–D214. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1226
Parte AC (2018) LPSN—list of Prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature (bacterio.net), 20 years on. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1825–1829. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002786
Pettersson B, Lembke F, Hammer P, Stackebrandt E, Priest FG (1996) Bacillus sporothermodurans, a new species producing highly heat-resistant endospores. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-46-3-759
Qin QL, Xie BB, Zhang XY, Chen XL, Zhou BC et al (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01688-14
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Rosselló-Móra R, Trujillo ME, Sutcliffe IC (2017) Introducing a digital protologue: a timely move towards a database-driven systematics of archaea and bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:455–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0841-7
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. Mol Biol Evol 9:945. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040771
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.moldev.a040454
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Sorokin DY, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2011) The microbial sulfur cycle at extremely haloalkaline conditions of soda lakes. Front Microbiol 2:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2011.00044
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152
Täubel M, Kämpfer P, Buczolits S, Lubitz W, Busse HJ (2003) Bacillus barbaricus sp. nov., isolated from an experimental wall painting. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02304-0
Wang HF, Li QL, Zhang YG, Xiao M, Zhou XK et al (2017) Bacillus capparidis sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from roots of Capparis spinosa L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:282–287. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001616
Wang S, Dong L, Zhao B, Xu S, Wu K et al (2018) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus sp. strain YSP-3, a halophilic, alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Microbiol Resour Announc 7:e00882-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.00882-18
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O et al (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01872.x
Wu S, Zhu Z, Fu L, Niu B, Li W (2011) WebMGA: a customizable web server for fast metagenomic sequence analysis. BMC Genom 12:444. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-444
Xu L, Wu YH, Zhou P, Cheng H, Liu Q, Xu XW (2018) Investigation of the thermophilic mechanism in the genus Porphyrobacter by comparative genomic analysis. BMC Genom 19:385. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4789-4
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017a) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017b) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Zhang S, Li Z, Yan Y, Zhang C, Li J et al (2016) Bacillus urumqiensis sp. nov., a moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2305–2312. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001028
Zhao B, Yan Y, Chen S (2014) How could haloalkaliphilic microorganisms contribute to biotechnology? Can J Microbiol 60:717–727. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0233
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31300101) and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (Grant No. 1610042018005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL and WS wrote the main manuscript text. WH designed the experiments. DL and WS carried out the experiments. WH, ZB and ZX analysed the data. All authors approved and read the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this manuscript.
Ethical approval
No specific ethical or institutional permits were required to conduct sampling and the experimental studies did not involve endangered or protected species.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Wang, S., Cao, H. et al. Bacillus lacisalsi sp. nov., a moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a saline–alkaline lake. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 113, 127–136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01322-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01322-3