Abstract
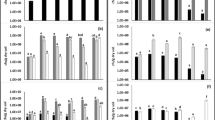
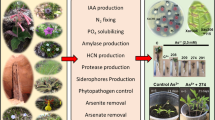
The functional diversity of endophytic and rhizospheric microorganisms associated with the promotion of plant growth includes increased availability of plant nutrients, phytohormone synthesis and phytopathogen suppression. We used the hypothesis that the unknown root and rhizospheric community associated with the Butia purpurascens palm, an endemic species of the Cerrado, could be composed of microbiota with great functional diversity. Thus, the potential of the isolates of this community for four functional traits was evaluated: solubilization of calcium phosphate (CaHPO4) and iron phosphate (FePO4), synthesis of indoleacetic acid (IAA) and suppression of seed- and fruit-spoilage fungi of B. purpurascens. A total of 166 bacterial isolates, most belonging to the phylum Proteobacteria (94%), and 46 fungal isolates (Ascomycota) were tested. None of the isolates showed the four functional traits tested, but 72% presented two traits (CaHPO4 solubilization and IAA synthesis). Fifteen fungi (27% of the isolates) presented only the trace for IAA, whereas the capacity for antibiosis was observed in only eight bacteria. CaHPO4-solubilization capacity was evidenced by all bacterial isolates and by some fungal isolates. The functional trait for IAA production was present in all isolates, and production levels were significantly above 100 μg mL−1 for some bacteria. Isolates of the genus Bacillus efficiently suppressed the growth of spoilage fungi tested, with relative inhibition rates reaching levels higher than 60% when using Bacillus subtilis. These results attest to the multifunctionality of the endophytic and rhizospheric isolates of B. purpurascens for the promotion of plant growth. This is the first study that sought to identify the root endophytic and rhizospheric microbiota associated with the B. purpurascens palm for the bioprospection of species with functional traits related to the promotion of plant growth, thus opening the way for in vivo tests in plants of commercial or ecological interest.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaszadeh-Dahaji P, Savaghebi GR, Asadi-Rahmani H, Rejali F, Farahbakhsh M, Moteshareh-Zadeh B, Omidvari M, Lindstrom K (2012) Symbiotic effectiveness and plant growth promoting traits in some Rhizobium strains isolated from Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Growth Regul 68:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9724-0
Alsohiby FAA, Yahya S, Humaid AA (2016) Screening of soil isolates of bacteria for antagonistic activity against plant pathogenic fungi. PSM Microbiol 1:05–09
Bacon CW, White JF Jr (2016) Functions, mechanisms and regulation of endophytic and epiphytic microbial communities of plants. Symbiosis 68:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0350-2
Barroso CB, Nahas E (2008) Solubilização do fosfato de ferro em meio de cultura. Pesq Agropec Bras 43:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2008000400012
Behera BC, Singdevsachan SK, Mishra RR, Dutta SK, Thatoi HN (2014) Diversity, mechanism and biotechnology of phosphate solubilizing microorganism in mangrove: a review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2013.09.008
Behie SW, Bidochka MJ (2014) Nutrient transfer in plant–fungal symbioses. Trends Plant Sci 19:734–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.06.007
Berthelot C, Blaudez D, Leyval C (2017) Differential growth promotion of poplar and birch inoculated with three dark septate endophytes in two trace element-contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 19:1118–1125. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1328392
Bilal L, Asaf S, Hamayun M, Gul H, Igbal A, Ullah I, Lee I-J, Hussain A (2018) Plant growth promoting endophytic fungi Aspergillus fumigatus TS1 and Fusarium proliferatum BRL1 produce gibberellins and regulates plant endogenous hormones. Symbiosis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0545-4
Bruto M, Prigent-Combaret C, Muller D, Moënne-Loccoz Y (2014) Analysis of genes contributing to plant-beneficial functions in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and related Proteobacteria. Sci Rep 4:6261. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06261
Cassán F, Vanderleyden J, Spaepen S (2014) Physiological and agronomical aspects of phytohormone production by model plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) belonging to the genus Azospirillum. J Plant Growth Regul 33:440–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9362-4
Chagas Junior AF, Oliveira LA, Oliveira AN, Willerding AL (2010) Capacidade de solubilização de fosfatos e eficiência simbiótica de rizóbios isolados de solos da Amazônia. Acta Sci Agron 32:359–366. https://doi.org/10.4025/actasciagron.v32i2.3185
Chen X, Zhang Y, Fu X, Li Y, Wang Q (2016) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PG12 for the biological control of apple ring rot. Postharvest Biol Technol 115:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.12.021
Cheng HR, Jiang N (2006) Extremely rapid extraction of DNA from bacteria and yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 28:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-4688-z
Coelho AR, Nóbrega GMA, Pagnocca FC, Hoffmann FL, Harada K, Hirooka EY (2011) Avaliação do potencial antagônico de leveduras, visando biocontrole de deterioração por Penicillium expansum. Semina Ciênc Agrár 32:1879–1892. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0359
Da Silva CF, Senabio JA, Pinheiro LC, Soares MA, Souchie EL (2015) Isolation and genetic characterization of endophytic and rhizospheric microorganisms from Butia purpurascens Glassman. Afr J Microbiol Res 9:1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2015.7477
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
De Silva ED (2016) Exploring plant associated fungi of Sri Lanka for biologically active metabolites. Chem Sri Lanka 33:13–16
Delfim J, Schoebitz M, Paulino L, Hirzel J, Zagal E (2018) Phosphorus availability in wheat, in volcanic soils inoculated with phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus thuringiensis. Sustainability 10:144. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010144
El-Bendary MA, Hamed HA, Moharam ME (2016) Potential of Bacillus isolates as bio-control agents against some fungal phytopathogens. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 5:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.02.001
Elshahawy IE, Saied NM, Morsy AA (2017) Fusarium proliferatum, the main cause of clove rot during storage, reduces clove germination and causes wilt of established garlic plants. Plant Pathol J 99:85–93. https://doi.org/10.4454/jpp.v99i1.3794
Esitken A, Yildiz HE, Ercisli S, Donmez MF, Turan M, Gunes A (2010) Effects of plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) on yield, growth and nutrient contents of organically grown strawberry. Sci Hortic 124:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.12.012
Estrada-De Los Santos P, Rojas-Rojaserika FU, Tapia-García Y, Vásquez-Murrieta MS, Hirsch AM (2016) To split or not to split: an opinion on dividing the genus Burkholderia. Ann Microbiol 66:1303–1314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1183-1
Esua JO, Chin NL, Yusof YA, Sukor R (2017) Antioxidant bioactive compounds and spoilage microorganisms of wax apple (Syzygium samarangense) during room temperature storage. Inter J Fruit Science 17:188–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/15538362.2017.1285263
Ferreira DF (2011) Sisvar: um sistema computacional de análise estatística. Ciênc Agrotecnol 35:1039–1042. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542011000600001
Gadagi RS, Sa T (2002) New isolation method for microorganisms solubilizing iron and aluminum phosphates using dyes. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 48:615–618. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2002.10409246
Gaggia F, Baffoni L, Gioia D, Accorsi M, Bosi S, Marotti I, Biavati B, Dinelli G (2013) Inoculation with microorganisms of Lolium perenne L.: evaluation of plant growth parameters and endophytic colonization of roots. N Biotechnol 30:695–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2013.04.006
Ghobad-Nejhad M, Meyn R, Langer E (2018) Endophytic fungi isolated from healthy and declining Persian oak (Quercus brantii) in western Iran. Nova Hedwigia. https://doi.org/10.1127/nova_hedwigia/2018/0470
Ghyselinck J, Velivelli SLS, Heylen K, O’Herlihy E, Franco J, Rojas M, Vos P, Prestwich BD (2013) Bioprospecting in potato fields in the Central Andean Highlands: screening of rhizobacteria for plant growth-promoting properties. Syst Appl Microbiol 36:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2012.11.007
Gordon SA, Weber RP (1951) Colorimetric estimation of indole acetic acid. Plant Physiol 26:192–195
Goswami D, Dhandhukia P, Patel P, Thakker JN (2014) Screening of PGPR from saline desert of Kutch: growth promotion in Arachis hypogea by Bacillus licheniformis A2. Microbiol Res 169:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.07.004
Gotor-Vila A, Teixidó N, Casals C, Torres R, De Cal A, Guijarro B, Usall J (2017) Biological control of brown rot in stone fruit using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CPA-8 under field conditions. Crop Prot 102:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2017.08.010
Guesmi-Jouini J, Garrido-Jurado I, López-Díaz C, Halima-Kamel MB, Quesada-Moraga E (2014) Establishment of fungal entomopathogens Beauveria bassiana and Bionectria ochroleuca (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) as endophytes on artichoke Cynara scolymus. J Invertebr Pathol 119:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2014.03.004
Guilherme FAG, Vasconcelos EI, Coelho CP, Ressel K, Batista NTF, Souza LF (2015) Vegetative and reproductive phenology of Butia purpurascens Glassman (Arecaceae) under the effects of leaf harvesting. Braz J Biol 75:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.07513
Hinarejos E, Castellano M, Rodrigo I, Bellés JM, Conejero V, López-Gresa MP, Lisón P (2016) Bacillus subtilis IAB/BS03 as a potential biological control agente. Eur J Plant Pathol 146:597–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0945-3
Hoffmann JF, Barbieri RL, Rombaldi CV, Chaves FC (2014) Butia spp. (Arecaceae): an overview. Sci Hortic 179:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.08.011
Idris EE, Iglesias DJ, Talon M, Borriss R (2007) Tryptophan-Dependent Production of Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) affects level of plant growth promotion by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0619
Karnwal A, Dohroo A (2018) Effect of maize root exudates on indole-3-acetic acid production by rice endophytic bacteria under influence of L-tryptophan. F1000Res 7:112. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.13644.1
Karthik M, Pushpakanth P, Krishnamoorthy R, Senthilkumar M (2017) Endophytic bacteria associated with banana cultivars and their inoculation effect on plant growth. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 92:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2017.1310600
Kavamura VN, Santos SN, Silva JL, Parma MM, Ávila LA, Visconti A, Zucchi TD, Taketani RG, Andreote FD, Melo IS (2013) Screening of Brazilian cacti rhizobacteria for plant growth promotion under drought. Microbiol Res 168:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.12.002
Kepler RM, Maul JE, Rehner SA (2017) Managing the plant microbiome for biocontrol fungi: examples from Hypocreales. Curr Opin Microbiol 37:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2017.03.006
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahmad E (2014) Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and physiological functions of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. In: Khan M, Zaidi A, Musarrat J (eds) Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. Springer, Cham, pp 31–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08216-5_2
Khan AL, Halo BA, Elyassi A, Ali S, Al-Hosni K, Hussain J, Al-Harrasi A, Lee I (2016) Indole acetic acid and ACC deaminase from endophytic bacteria improves the growth of Solanum lycopersicum. Electron J Biotechnol 21:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.02.001
Kochar M, Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2011) Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens Psd and plant growth regulation by hormone overexpression. Res Microbiol 162:426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2011.03.006
Kraft NJB, Cornwell WK, Webb CO, Ackerly DD (2007) Trait evolution, community assembly, and the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities. Am Nat 170:271–283
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kvakić M, Pellerin S, Ciais P, Achat DL, Augusto L, Denoroy P, Gerber JS, Goll D, Mollier A, Mueller ND, Wang X, Ringeval B (2018) Quantifying the limitation to world cereal production due to soil phosphorus status. Global Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GB005754
Laranjo M, Alexandre A, Oliveira S (2014) Legume growth-promoting rhizobia: an overview on the Mesorhizobium genus? Microbiol Res 169:2–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.012
Ligoxigakis EK, Markakis EA, Papaioannou IA, Typas MA (2013) First report of palm rot of Phoenix spp. caused by Neodeightonia phoenicum in Greece. Plant Dis 97:286. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-08-12-0727-PDN
Lin Y, Du D, Si C, Zhao Q, Li Z, Li P (2014) Potential biocontrol Bacillus sp. strains isolated by an improved method from vinegar waste compost exhibit antibiosis against fungal pathogens and promote growth of cucumbers. Biol Control 71:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.12.010
Liu X, Jiang X, Zhao W, Cao Y, Guo T, He X, Ni H, Tang X (2018) Colonization of phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp. strain P34-L in the wheat rhizosphere and its effects on wheat growth and the expression of phosphate transporter gene TaPT4 in wheat. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/294736
Lorenzi H, Kahn F, Noblick LR, Ferreira E (2010) Flora Brasileira: Arecaceae (Palmeiras) Nova Odessa, SP: Instituto Plantarum
Lozano GL, Holt J, Ravel J, Rasko DA, Thomas MG, Handelsman J (2016) Draft genome sequence of biocontrol agent Bacillus cereus UW85. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00910-16
ludueña ML, Anzuay MS, Angelini JS, Mcintosh M, Becker A, Rupp O, Goesmann A, Blom J, Fabra A, Taurian T (2018) Strain Serratia sp: a potential biofertilizer for peanut and maize and a model bacterium to study phosphate solubilization mechanisms. Appl Soil Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.12.024
Mahmoud FM, Krimi Z, Maciá-Vicente JG, Errahmani MB, Lopez-Llorca LV (2017) Endophytic fungi associated with roots of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) in coastal dunes. Rev Iberoam Micol 34:116–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riam.2016
Marks BB, Megías M, Ollero FJ, Nogueira MA, Araujo RS, Hungria M (2015) Maize growth promotion by inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense and metabolites of Rhizobium tropici enriched on lipo-chitooligosaccharides (LCOs). AMB Express 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-015-0154-z
Marra LM, Soares CRFS, Oliveira SM, Ferreira PAA, Soares BL, Carvalho RF, Lima JM, Moreira FMS (2012) Biological nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilization by bacteria isolated from tropical soils. Plant Soil 357:289–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1157-z
Martins RC, Filgueiras TSF, Albuquerque UP (2014) Use and diversity of palm (Arecaceae) resources in central western Brazil. Sci World J 2014:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/942043
Martiny AC, Treseder K, Pusch G (2013) Phylogenetic conservatism of functional traits in microorganisms. ISME J 7:83083–83088. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012
Martiny JBH, Jones SE, Lennon JT, Martiny AC (2015) Microbiomes in light of traits: a phylogenetic perspective. Science 350:aac9323-1–aac9323-8. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9323
Mew TW, Rosales AM (1986) Bacterization of rice plants for control of sheath blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 76:1260–1264
Meyer SE, Briscoe L, Martínez-Hidalgo P, Agapakis CM, De Los Santos PE, Seshadri R, Reeve W, Weinstock G, O’Hara G, Howieson JG, Hirsch AM (2016) Symbiotic Burkholderia species show diverse arrangements of nif/fix and nod genes and lack typical high-affinity cytochrome cbb3 oxidase genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 29:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-16-0091-R
Misha A, Singh SP, Mahfooz S, Singh SP, Bhattacharya A, Mishra N, Nautiyal CS (2018) Endophyte-mediated modulation of defense-responsive genes and systemic resistance in Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal under Alternaria alternate stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02845-17
Missong A, Bol R, Willbold S, Siemens J, Klumpp E (2016) Phosphorus forms in forest soil colloids as revealed by liquid-state 31P-NMR. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 179:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201500119
Murphy BR, Doohan FM, Hodkinson TR (2018) From concept to commerce: developing a successful fungal endophyte inoculant for agricultural crops. J Fungi 4:24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4010024
Osorio Vega NW (2007) A review on beneficial effects of rhizosphere bacteria on Soil nutrient availability and plant nutrient uptake. Rev Fac Nac Agron Medellin 60:3621–3643
Palaniyandi SA, Yang SH, Damodhara K, Suh J (2013) Genetic and functional characterization of culturable plant-beneficial actinobacteria associated with yam rhizosphere. J Basic Microbiol 53:985–995. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201200531
Pedraza RO, Motok J, SalazaR SM, Ragout AL, Mentel MI, Tortora ML, Guerrero-Molina MF, Winik BC, Díaz-Ricci JC (2010) Growth-promotion of strawberry plants inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0169-1
Pereira GVM, Magalhães KT, Lorenzetii ER, Souza TP, Schwan RF (2012) A multiphasic approach for the identification of endophytic bacterial in strawberry fruit and their potential for plant growth promotion. Microb Ecol 63:405–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9919-3
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SC, Bakker PA (2014) Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:347–375. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102340
Rocha R, Luz DE, Engels C, Pileggi SAV, Jaccoud Filho DS, Matiello RR, Pileggi M (2009) Selection of endophytic fungi from comfrey (Symphytum officinale L.) for in vitro biological control of the Phytopathogen sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.). Braz J Microbiol 40:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822009000100011
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Mark PVD, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Russo ML, Pelizza SA, Cabello MN, Stenglein SA, Scorsetti AC (2015) Endophytic colonisation of tobacco, corn, wheat and soybeans by the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota, Hypocreales). Biocontrol Sci Technol 25:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2014.982511
Santoyo G, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Orozco-Mosqueda MC, Glick BR (2016) Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol Res 183:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen DG, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, Mcwilliam H, Remmert M, Soding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Soares MA, Li H-Y, Kowalski KP, Bergen M, Torres MS, White JF (2016) Functional role of bacteria from invasive Phragmites australis in promotion of host growth. Microb Ecol 72:407–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0793-x
Souchie EL, Abboud ACS, Caproni AL (2007) Solubilização de fosfato in vitro por microrganismos rizosféricos de guandu. Biosci J 23:53–60
Souza LS, De Souza SA, Oliveira M, Ferraz TM, Figueiredo FAMMA, Da Silva ND, Rangel PL, Panisset CRS, Olivares FL, Campostrini E, De Souza Filho GA (2016) Endophytic colonization of Arabidopsis thaliana by Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus and its effect on plant growth promotion, plant physiology, and activation of plant defense. Plant Soil 399:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2672-5
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J (2011) Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 17:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001438
Srinivasan R, Alagawadi AR, Yandigeri MS, Meena KK, Saxena AK (2012) Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms from salt-affected soils of India and their effect on growth of sorghum plants [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Ann Microbiol 62:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0233-6
Surono, Narisawa K (2018) The inhibitory role of dark septate endophytic fungus Phialocephala fortinii against Fusarium disease on the Asparagus officinalis growth in organic source conditions. Biol Control 121:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2018.02.017
Sylvester-Bradley R, Asakawa N, Latorraca S, Magalhães FMM, Oliveira LA, Pereira RM (1982) Levantamento quantitativo de micro-organismos solubilizadores de fosfatos na rizosfera de gramíneas e leguminosas forrageiras na Amazônia. Acta Amaz 12:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-43921982121015
Turner BL, Condron LM, Richardson SJ, Peltzer DA, Allison VJ (2007) Soil organic phosphorus transformations during pedogenesis. Ecosystems 10:1166–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.11.012
Udvardi M, Poole PS (2013) Transport and metabolism in legume-rhizobia symbioses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:781–805. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120235
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Nikolaeva I (2006) Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: potentials and future trends. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0380-z
Vassilev N, Eichler-Löbermann B, Vassileva M (2012) Stress-tolerant P-solubilizing microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:851–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4224-8
Verma JP, Yadav J, Tiwari KN, Lavakush Singh V (2010) Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on crop production. Int J Agric Res 5:954–983. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijar.2010.954.983
Vestergren JE, Vincent AG, Persson P, Jansson M, Ilstedt U, Giesler R, Schleucher J, Grobner G (2013) Novel approaches for identifying phosphorus species in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems with 31P NMR. Biophys J 104:501A–502A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.2768
Vitorino LV, Silva FG, Soares MA, Souchie EL, Costa AC, Lima WC (2012) Solubilization of calcium and iron phosphate and in vitro production of indoleacetic acid by endophytic isolates of Hyptis marrubioides Epling (Lamiaceae). Int Res J Biotechnol 3:47–54
Waqas M, Khan AL, Shahzad R, Ullah I, Khan AR, Lee I (2015) Mutualistic fungal endophytes produce phytohormones and organic acids that promote japonica rice plant growth under prolonged heat stress. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 16:1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500081
Zhang F, Ge H, Zhang F, Guo N, Wang Y, Chen L, Ji X, Li C (2016) Biocontrol potential of Trichoderma harzianum isolate T-aloe against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem 100:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.12.017
Zhao K, Penttinen P, Zhang X, Ao X, Liu M, Yu X, Chen Q (2014) Maize rhizosphere in Sichuan, China, hosts plant growth promoting Burkholderia cepacia with phosphate solubilizing and antifungal abilities. Microbiol Res 169:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.07.003
Zouari I, Jlaiel L, Tounsi S, Trigui M (2016) Biocontrol activity of the endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 1 strain 2 CEIZ-11 against Pythium aphanidermatum and purification of its bioactive 3 compounds. Biol Control 100:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.05.012
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Goiano Federal Institute—Rio Verde Campus (Instituto Federal Goiano campus Rio Verde) for assisting in the obtaining of plant material, making possible the search in the field of the analyzed specie; the Research Foundation of the State of Goiás (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Goiás- FAPEG) for the for the financial assistance that has occurred through the public announcement 012/2012; the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—CNPq) and Brazilian Federal Agency for the Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior- CAPES) for the doctorate scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors. The formal consent is not required in this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, C.F., Vitorino, L.C., Soares, M.A. et al. Multifunctional potential of endophytic and rhizospheric microbial isolates associated with Butia purpurascens roots for promoting plant growth. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 111, 2157–2174 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1108-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1108-7