Abstract
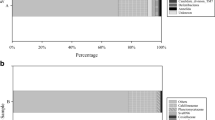
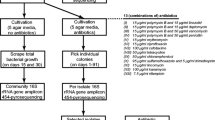
Sponges offer an excellent model to investigate invertebrate–microorganism interactions. Furthermore, bacteria associated with marine sponges represent a rich source of bioactive metabolites. The aim of this study was to characterize the bacteria inhabiting a genus of sponges, Oscarella, and their potentiality for antimicrobial production. Bacterial isolates were recovered from different Oscarella specimens, among which 337 were phylogenetically identified. The culturable community was dominated by Proteobacteria and Firmicutes, and Vibrio was the most frequently isolated genus, followed by Shewanella. When tested for antimicrobial production, bacteria of the 12 genera isolated were capable of producing antimicrobial substances. The majority of strains were involved in antagonistic interactions and inhibitory activities were also observed against bacteria of medical importance. It was more pronounced in some isolated genera (Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Photobacterium, Shewanella and Vibrio). These findings suggest that chemical antagonism could play a significant role in shaping bacterial communities within Oscarella, a genus classified as low-microbial abundance sponge. Moreover, the identified strains may contribute to the search for new sources of antimicrobial substances, an important strategy for developing therapies to treat infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. This study was the first to investigate the diversity and antagonistic activity of bacteria isolated from Oscarella spp. It highlights the biotechnological potential of sponge-associated bacteria.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boury-Esnault N, Lavrov DV, Ruiz CA, Pérez T (2013) The integrative taxonomic approach applied to Porifera: a case study of the Homoscleromorpha. Integr Comp Biol 53:416–427
Domingos C, Lage A, Muricy G (2016) Overview of the biodiversity and distribution of the class Homoscleromorpha in the Tropical Western Atlantic. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 96:379–389
Ereskovsky AV, Borchiellini C, Gazave E, Ivanisevic J, Lapébie P, Perez T, Renard E, Vacelet J (2009) The Homoscleromorph sponge Oscarella lobularis, a promising sponge model in evolutionary and developmental biology. BioEssays 31:89–97
Esteves AIS, Amer N, Nguyen M, Thomas T (2016) Sample processing impacts the viability and cultivability of the sponge microbiome. Front Microbiol 7:499. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00499
Flemer B, Kennedy J, Margassery LM, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F, Dobson AD (2011) Diversity and antimicrobial activities of microbes from two Irish marine sponges, Suberitescarnosus and Leucosolenia sp. J Appl Microbiol 112:289–301
Friedrich AB, Fischer I, Proksch P, Hacker H, Hentschel U (2001) Temporal variation of the microbial community associated with the Mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:105–113
Fuhrman JA, Cram JA, Needham DM (2015) Marine microbial community dynamics and their ecological interpretation. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:133–146
Gazave E, Lapébie P, Ereskovsky AV, Vacelet J, Renard E, Cardenas P, Borchiellini C (2012) No longer Demospongiae: Homoscleromorpha formal nomination as a fourth class of Porifera. Hydrobiologia 687:3–10
Gerçe B, Schwartz T, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2011) Differences between bacterial communities associated with the surface or tissue of Mediterranean sponge species. Microb Ecol 61:769–782
Gilbert JA, Steele JA, Caporaso JG, Steinbrück L, Reeder J, Temperton B, Huse S, McHardy AC, Knight R, Joint I, Somerfield P, Fuhrman JA, Field D (2012) Defining seasonal marine microbial community dynamics. ISME J 6:298–308
Giles E, Kamke J, Moitinho-Silva L, Taylor M, Hentschel U, Ravasi T, Schmitt S (2012) Bacterial community profiles in low microbial abundance sponges. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83:232–241
Gloeckner V, Hentschel U, Ereskovsky AV, Schmitt S (2013) Unique and stable microbial communities in Oscarella lobularis and other Mediterranean Oscarella species (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha). Mar Biol 160:781–791
Gloeckner V, Wehrl M, Moitinho-Silva L, Gernert C, Schupp P, Pawlik JR, Lindquist NL, Erpenbeck D, Wörheide G, Hentschel U (2014) The HMA-LMA dichotomy revisited: an electron microscopical survey of 56 sponge species. Biol Bull 227:78–88
Graça AP, Viana F, Bondoso J, Correia MI, Gomes L, Humanes M, Reis A, Xavier JR, Gaspar H, Lage OM (2015) The antimicrobial activity of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from the marine sponge Erylus deficiens (Astrophorida, Geodiidae). Front Microbiol 7:e389. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00389
Hardoim CC, Costa R, Araújo F, Hadju E, Peixoto RS, Lins U, Rosado AS, Elsas JDV (2009) Microbial diversity in the marine sponge Aplysina fulva in Brazilian coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3331–3343
Hardoim CC, Cardinale M, Cúcio AC, Esteves AI, Berg G, Xavier JR, Cox CJ, Costa R (2014) Effects of sample handling and cultivation bias on the specificity of bacterial communities in keratose marine sponges. Front Microbiol 18:611. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00611
Hentschel U, Hopke J, Horn M, Friedrich AB, Wagner M, Hacker J, Moore BS (2002) Molecular evidence for a uniform microbial community in sponges from different oceans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4431–4440
Hentschel U, Fieseler L, Wehrl M, Gernert C, Steinert M, Hacker J, Horn M (2003) Microbial diversity of marine sponges. In: Müller WEG (ed) Marine molecular biotechnology—sponges (Porifera). Springer, Berlin, pp 59–88
Hentschel U, Usher KM, Taylor MW (2006) Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:167–177
Hibbing ME, Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Peterson SB (2010) Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:15–25
Ivanišević J, Thomas OP, Lejeusne C, Chevaldonné P, Pérez T (2011) Metabolic fingerprinting as an indicator of biodiversity: towards understanding inter-specific relationships among Homoscleromorpha sponges. Metabolomics 7:289–304
Kamke J, Taylor MW, Schmitt S (2010) Activity profiles for marine sponge-associated bacteria obtained by 16S rRNA versus 16S rRNA gene comparisons. ISME J 4:498–508
Kanagasabhapathy M, Sasaki H, Nagata S (2008) Phylogenetic identification of epibiotic bacteria possessing antimicrobial activities isolated from red algal species of Japan. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2315–2321
Laport MS, Santos-Gandelman JF, Muricy G, Giambiade-deMarval M, George I (2016) Antagonistic interactions among bacteria isolated from either the same or from different sponges native to the Brazilian coast. J Mar Sci Res Dev 6:185. doi:10.4172/2155-9910.1000185
Marinho PR, Moreira AP, Pellegrino FL, Muricy G, Bastos MC, Santos KR, Giambiagi-deMarval M, Laport MS (2009) Marine Pseudomonas putida: a potential source of antimicrobial substances against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. MIOC 104:678–682
Martín-Rodríguez AJ, González-Orive A, Hernández-Creus A, Morales A, Dorta-Guerra R, Norte M, Martín VS, Fernández JJ (2014) On the influence of the culture conditions in bacterial antifouling bioassays and biofilm properties: Shewanella algae, a case study. BMC Microbiol 14:102. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-14-102
Montalvo NF, Davis J, Vicente J, Pittiglio R, Ravel J, Hill RT (2014) Integration of culture-based and molecular analysis of a complex sponge-associated bacterial community. PLoS ONE 9:e90517
Muricy G (2016) Porifera in Catálogo Taxonômico da Fauna do Brasil. PNUD. http://fauna.jbrj.gov.br/fauna/faunadobrasil/6
Olson JB, Gao X (2013) Characterizing the bacterial associates of three Caribbean sponges along a gradient from shallow to mesophotic depths. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85:74–84
Pérez T, Ivanisevic J, Dubois M, Pedel L, Thomas OP, Tokina D, Ereskovsky AV (2011) Oscarella balibaloi, a new sponge species (Homoscleromorpha: Plakinidae) from the Western Mediterranean Sea: cytological description, reproductive cycle and ecology. Mar Ecol 32:174–187
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35:7188–7196
Ribes M, Coma R, Gili J-M (1999) Seasonal variation of particulate organic carbon, dissolved organic carbon and the contribution of microbial communities to the live particulate organic carbon in a shallow near-bottom ecosystem at the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. J Plankton Res 21:1077–1100
Rua CP, Trindade-Silva AE, Appolinario LR, Venas TM, Garcia GD, Carvalho LS, Lima A, Kruger R, Pereira RC, Berlinck RG, Valle RA, Thompson CC, Thompson F (2014) Diversity and antimicrobial potential of culturable heterotrophic bacteria associated with the endemic marine sponge Arenosclera brasiliensis. Peer J 2:e419. doi:10.7717/peerj.419
Santavy DL, Willenz Ph, Colwell RR (1990) Phenotypic study of bacteria associated with the Caribbean sclerosponge, Ceratoporella nicholsoni. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1750–1762
Santos OCS, Pontes PVML, Santos JFM, Muricy G, Giambiagi-deMarval M, Laport MS (2010) Isolation, characterization and phylogeny of sponge-associated bacteria with antimicrobial activities from Brazil. Res Microbiol 161:604–612
Santos-Gandelman JF, Santos OC, Pontes PV, Andrade CL, Korenblum E, Muricy G, Giambiagi-deMarval M, Laport MS (2013) Characterization of cultivable bacteria from Brazilian sponges. Mar Biotechnol 15:668–676
Santos-Gandelman JF, Giambiagi-deMarval M, Oelemann WMR, Laport MS (2014) Biotechnological potential of sponge-associated bacteria. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 15:143–155
Schmitt S, Tsai P, Bell J, Fromont J, Ilan M, Lindquist N, Perez T, Rodrigo A, Schupp PJ, Vacelet J, Webster N, Hentschel U, Taylor MW (2012) Assessing the complex sponge microbiota: core, variable and species-specific bacterial communities in marine sponges. ISME J 6:564–576
Shade A, Handelsman J (2012) Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environ Microbiol 14:4–12
Sipkema D, Schippers K, Maalcke WJ, Yang Y, Salim S, Blanch HW (2011) Multiple approaches to enhance the cultivability of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Haliclona (Gellius) sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2130–2140
Taylor MW, Radax R, Steger D, Wagner M (2007) Sponge associated microorganisms: evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol Mol Biol R 71:295–347
Thomas T, Moitinho-Silva L, Lurgi M, Björk JR, Easson C, Astudillo-García C, Olson JB, Erwin PM, López-Legentil S, Luter H, Chaves-Fonnegra A, Costa R, Schupp PJ, Steindler L, Erpenbeck D, Gilbert J, Knight R, Ackermann G, Victor-Lopez J, Taylor MW, Thacker RW, Montoya JM, Hentschel U, Webster NS (2016) Diversity, structure and convergent evolution of the global sponge microbiome. Nat Commun 16:11870. doi:10.1038/ncomms11870
Turque AS, Cardoso AM, Silveira CB, Vieira RP, Freitas FAD, Albano RM, Gonzalez AM, Paranhos R, Muricy G, Martins OB (2008) Bacterial communities of the marine sponges Hymeniacidon heliophila and Polymastia janeirensis and their environment in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mar Biol 155:135–146
Vacelet J (1975) Étude en microscopie électronique de l’association entre bactéries et spongiaires du genre Verongia (Dictyoceratida). J Microsc Biol Cell 23:271–288
Vacelet J, Donadey C (1977) Electron microscope study of the association between some sponges and bacteria. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 30:301–314
van Soest RWM, Boury-Esnault N, Hooper JNA, Rützler K, de Voogd NJ, Alvarez de Glasby B, Hajdu E, Pisera AB, Manconi R, Schoenberg C, Janussen D, Tabachnick KR, Klautau M, Picton B, Kelly M, Vacelet J, Dohrmann M, Díaz M-C, Cárdenas P (2016) World Porifera database. http://www.marinespecies.org/porifera Accessed 3 August 2016
Webster NS, Hill RT (2001) The culturable microbial community of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is dominated by an alpha-Proteobacterium. Mar Biol 138:843–851
Webster NS, Taylor MW (2012) Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: love and other relationships. Environ Microbiol 14:335–346
Webster NS, Luter HM, Soo RM, Botté ES, Simister RL, Abdo D, Whalan S (2013) Same, same but different: symbiotic bacterial associations in GBR sponges. Front Microbiol 3:e444. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2012.00444
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wilkinson CR, Nowak M, Austin B, Colwell RR (1981) Specificity of bacterial symbionts in Mediterranean and Great Barrier Reef sponges. Microb Ecol 7:13–21
Wilkinson CR, Garrone R, Vacelet J (1984) Marine sponges discriminate between food bacteria and bacterial symbionts: electron microscope radioautography and in situ evidence. Proc R Soc Lond B 220:519–528
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CAPES, CNPq and FAPERJ to M.S. Laport, and to G. Muricy, and by a “Crédit de Recherches” Grant from FRS-FNRS to I. George. We are also grateful to Science Without Borders, a CNPq Program for the post doctorate scholarship to M.S. Laport; and to Prof. Philippe Dubois and Prof. Chantal de Ridder for accepting her in the “Laboratoire de Biologie Marine”, at “Université Libre de Bruxelles”, Belgium. Ph.W. received a travel Grant from the “Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique” (FNRS) to conduct field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest is declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laport, M.S., Bauwens, M., de Oliveira Nunes, S. et al. Culturable bacterial communities associated to Brazilian Oscarella species (Porifera: Homoscleromorpha) and their antagonistic interactions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 489–499 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0818-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0818-y