Abstract
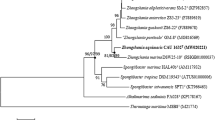
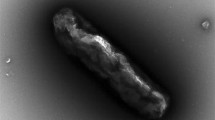
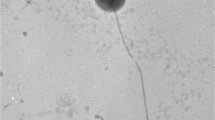
A marine bacterium, NMD7T, was isolated from seawater of the East China Sea. The cells were found to be aerobic, Gram-stain negative, non-motile rods. Growth of strain NMD7T could be observed in the medium without Na+. Flexirubin-type pigments were observed to be produced. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain NMD7T is an authentic member of the Cytophaga–Flavobacterium–Bacteroides phylum, forming a monophyletic clade as retrieved in neighbor-joining, maximum-likelihood and maximum-parsimony phylogenetic trees, and is closely related to Formosa spongicola A2T (96.0 %). The predominant respiratory quinone was determined to be MK-6. Major cellular fatty acids were identified as iso-C15:0, iso-C15:1 G and iso-C17:0 3-OH. The main polar lipids were found to consist of phosphatidylethanolamine, one aminophospholipid, three aminolipids and five unidentified lipids. Based on phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic characteristics, it is proposed that strain NMD7T be classified as representing a new genus, Feifantangia gen. nov. and a new species, Feifantangia zhejiangensis sp. nov. The type strain is NMD7T (=KCTC 42445T =MCCC 1K00458T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B, Flavobacteri ST (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070
Bowman JP, Nichols DS (2005) Novel members of the family Flavobacteriaceae from Antarctic maritime habitats including Subsaximicrobium wynnwilliamsii gen. nov., sp. nov., Subsaximicrobium saxinquilinus sp. nov., Subsaxibacter broadyi gen. nov., sp. nov., Lacinutrix copepodicola gen. nov., sp. nov., and novel species of the genera Bizionia, Gelidibacter and Gillisia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1471–1486
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Determinative manual for routine bacteriology. Scientific Press (English translation), Beijing
Fang MX, Zhang WW, Zhang YZ, Tan HQ, Zhang XQ, Wu M, Zhu XF (2012) Brassicibacter mesophilus gen. nov., sp nov., a strictly anaerobic bacterium isolated from food industry wastewater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:3018–3023
Garrity GM, Holt JG (2001) The road map to the Manual. In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 119–166
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Ivanova EP et al (2004) Formosa algae gen. nov., sp nov., a novel member of the family Flavobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:705–711
Kim OS et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide-sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kirchman DL (2002) The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:91–100
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Kuykendall LD, Roy MA, Oneill JJ, Devine TE (1988) Fatty-acids, antibiotic-resistance, and deoxyribonucleic-acid homology groups of Bradyrhizobium Japonicum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:358–361
Kwon KK, Lee HS, Jung HB, Kang JH, Kim SJ (2006) Yeosuana aromativorans gen. nov., sp nov., a mesophilic marine bacterium belonging to the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from estuarine sediment of the South Sea, Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:727–732
Mac Faddin JF (1981) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria. Public Health 95:244
Marmur J (1963) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. Method Enzymol 6:726–738
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic-acid by high-performance liquid-chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, Odonnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Nedashkovskaya OI, Kim SB, Lysenko AM, Frolova GM, Mikhailov VV, Bae KS (2005) Bizionia paragorgiae gen. nov., sp nov., a novel member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from the soft coral Paragorgia arborea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:375–378
Nichols CM, Bowman JP, Guezennec J (2005) Olleya marilimosa gen. nov., sp nov., an exopolysaccharide-producing marine bacterium from the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from the Southern Ocean. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1557–1561
Nokhal TH, Schlegel HG (1983) Taxonomic study of Paracoccus Denitrificans. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:26–37
Park S, Lee JS, Lee KC, Yoon JH (2013) Formosa undariae sp. nov., isolated from a reservoir containing the brown algae Undaria pinnatifida. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4130–4135
Reichenbach H (1989) Order I. Cytophagales Leadbetter 1974, 99AL. In: Staley JT, Bryant MP, Pfennig N, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2011–2013
Simon M, Glockner FO, Amann R (1999) Different community structure and temperature optima of heterotrophic picoplankton in various regions of the Southern Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 18:275–284
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Yoon BJ, Oh DC (2011) Formosa spongicola sp. nov., isolated from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon flavia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:330–333
Yoon JH, Lee SY, Oh TK (2013) Gaetbulibacter lutimaris sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:995–1000
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and technology project of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2014F30024) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Scicence Foundation of China (No. LY13D060006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, G., Chen, ZG., Jiang, RJ. et al. Feifantangia zhejiangensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from seawater of the East China Sea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 1441–1447 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0598-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0598-9