Abstract
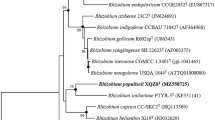
Strain NHI-8T was isolated from a forest soil sample, collected in South Korea, by using a modified culture method. Comparative analysis of its nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that strain NHI-8T belongs to the genus Mesorhizobium and to be closely related to Mesorhizobium chacoense PR5T (97.32 %). The levels of DNA–DNA relatedness between strain NHI-8T and reference type strains of the genus Mesorhizobium were 32.28–53.65 %. SDS-PAGE of total soluble proteins and the sequences of the housekeeping genes recA, glnII, and atpD were also used to support the clade grouping in rhizobia. The new strain contained summed feature 8 (57.0 %), cyclo-C19:0ω8c (17.3 %), and C18:0 (11.0 %) as the major fatty acids, as in genus Mesorhizobium. The strain contained cardiolipin, phosphatidylglycerol, ornithine-containing lipid, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidyl-N-dimethylethanolamine, and phosphatidylcholine. Morphological and physiological analyses were performed to compare the characteristics of our strain with those of the reference type strains. Based on the results, strain NHI-8T was determined to represent a novel member of the genus Mesorhizobium, and the name Mesorhizobium soli is proposed. The type strain is NHI-8T (=KEMB 9005-153T = KACC 17916T = JCM 19897T).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bethlenfalvay GJ, Abu-Shakra SS, Phillips DA (1978) Interdependence of nitrogen nutrition and photosynthesis in Pisum sativum L. II. Host plant response to nitrogen fixation by Rhizobium strains. Plant Physiol 62:131–133
Chen WX, Li GS, Qi YL, Wang ET, Yuan HL, Li JL (1991) Rhizobium huakuii sp. nov. isolated from the root nodules of Astragalus sinicus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:275–280
Chen W, Wang E, Wang S, Li Y, Chen X, Li Y (1995) Characteristics of Rhizobium tianshanense sp. nov., a moderately and slowly growing root nodule bacterium isolated from an arid saline environment in Xinjiang, People’s Republic of China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:153–159
Choma A, Komaniecka I (2002) Analysis of phospholipids and ornithine-containing lipids from Mesorhizobium spp. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:326–331
Doetsch RN (1981) Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: Gerdhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GB (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 21–33
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Wilson BA, Olsen GJ (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2461–2470
Gao JL, Turner SL, Kan FL, Wang ET, Tan ZY, Qiu YH, Gu J, Terefework Z, Young JP, Lindström K, Chen WX (2004a) Mesorhizobium septentrionale sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium temperatum sp. nov., isolated from Astragalus adsurgens growing in the northern regions of China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2003–2012
Gao JL, Weissenmayer B, Taylor AM, Thomas-Oates J, López-Lara IM, Geiger O (2004b) Identification of a gene required for the formation of lyso-ornithine lipid, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ornithine-containing lipids. Mol Microbiol 53:1757–1770
Gaunt MW, Turner SL, Rigottier-Gois L, Lloyd-Macgilp SA, Young JP (2001) Phylogenies of atpD and recA support the small subunit rRNA-based classification of rhizobia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2037–2048
Goldfine H (1984) Bacterial membranes and lipid packing theory. J Lipid Res 25:1501–1507
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Han TX, Han LL, Wu LJ, Chen WF, Sui XH, Gu JG, Wang ET, Chen WX (2008) Mesorhizobium gobiense sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium tarimense sp. nov., isolated from wild legumes growing in desert soils of Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2610–2618
Howieson JG, O’Hara GW, Carr SJ (2000) Changing roles for legumes in Mediterranean agriculture: developments from an Australian perspective. Field Crops Res 65:107–122
Jacin H, Mishkin AR (1965) Separation of carbohydrates on borate impregnated silica gel G plates. J Chromatogr 18:170–173
Jarvis BDW, Pankhurst CE, Patel JJ (1982) Rhizobium loti, a new species of legume root nodule bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:378–380
Jarvis BDW, Sivakumaran S, Tighe SW, Gillis M (1996) Identification of Agrobacterium and Rhizobium species based on cellular fatty acid composition. Plant Soil 184:143–158
Jarvis BDW, Van Berkum P, Chen WX, Nour SM, Fernandez MP, Cleyet-Marel JC, Gillis M (1997) Transfer of Rhizobium loti, Rhizobium huakuii, Rhizobium ciceri, Rhizobium mediterraneum, and Rhizobium tianshanense to Mesorhizobium gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:895–898
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laranjo M, Alexandre A, Oliveira S (2014) Legume growth-promoting rhizobia: an overview on the Mesorhizobium genus. Microbiol Res 169:2–17
Lohrke SM, Orf JH, Sadowsky MJ (1996) Inheritance of host-controlled restriction of nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain USDA 110. Crop Sci 36:1271–1277
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Nandasena KG, O’Hara GW, Tiwari RP, Willems A, Howieson JG (2009) Mesorhizobium australicum sp. nov. and Mesorhizobium opportunistum sp. nov., isolated from Biserrula pelecinus L. in Australia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2140–2147
Noel KD, Brill WJ (1980) Diversity and dynamics of indigenous Rhizobium japonicum populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:931–938
Nour SM, Cleyet-Marel JC, Normand P, Fernandez MP (1995) Genomic heterogeneity of strains nodulating chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.) and description of Rhizobium mediterraneum sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:640–648
Patel K, Easty DJ, Dunn MJ (1988) Detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels using an ultrasensitive silver staining technique. In: Walker JM (ed) New protein techniques, methods in molecular biology, vol 3. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 159–168
Pham HTV, Kim J (2014) Bacillus thaonhiensis sp. nov., a new species, was isolated from the forest soil of Kyonggi University by using a modified culture method. Curr Microbiol 68:88–95
Ramírez-Bahena MH, Hernández M, Peix A, Velázquez E, León-Barrios M (2012) Mesorhizobial strains nodulating Anagyris latifolia and Lotus berthelotii in Tamadaya ravine (Tenerife, Canary Islands) are two symbiovars of the same species, Mesorhizobium tamadayense sp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:334–341
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI, Inc, Newark, DE
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Sullivan JT, Patrick HN, Lowther WL, Scott DB, Ronson CW (1995) Nodulating strains of Rhizobium loti arise through chromosomal symbiotic gene transfer in the environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8985–8989
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA 5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Terpolilli JJ, Hood GA, Poole PS (2012) What determines the efficiency of N2-fixing Rhizobium-legume symbioses? In: Poole RK (ed) Advances in microbial physiology, vol 60. Academic Press, London, pp 325–389
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tighe SW, Lajudie PD, Dipietro K, Lindstrom K, Nick G, Jarvis BDW (2000) Analysis of cellular fatty acids and phenotypic relationships of Agrobacterium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium species using the Sherlock microbial identification systems. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:787–801
Velázquez E, Igual JM, Willems A, Fernández MP, Muñoz E, Mateos PF, Abril A, Toro N, Normand P, Cervantes E, Gillis M, Martínez-Molina E (2001) Mesorhizobium chacoense sp. nov., a novel species that nodulates Prosopis alba in the Chaco Arido region (Argentina). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1011–1021
Vidal C, Chantreuil C, Berge O, Mauré L, Escarré J, Béna G, Brunel B, Cleyet-Marel JC (2009) Mesorhizobium metallidurans sp. nov., a metal-resistant symbiont of Anthyllis vulneraria growing on metallicolous soil in Languedoc, France. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:850–855
Vinuesa P, Rademaker JLW, Bruijn FJ, Werner D (1998) Genotypic characterization of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating endemic woody legumes of the Canary Islands by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA (16S rDNA) and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacers, repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR genomic finger printing and partial 16S rDNA sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2096–2104
Vinuesa P, Silva C, Werner D, Romero EM (2005) Population genetics and phylogenetic inference in bacterial molecular systematics: the roles of migration and recombination in Bradyrhizobium species cohesion and delineation. Mol Phylogenet Evol 34:29–54
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Truper HG (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Weir BS, Turner SJ, Silvester WB, Park DC, Young JM (2004) Unexpectedly diverse Mesorhizobium strains and Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulate native legume genera of New Zealand, while introduced legume weeds are nodulated by Bradyrhizobium species. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5980–5987
Zhang JJ, Liu TY, Chen WF, Wang ET, Sui XH, Zhang XX, Li Y, Li Y, Chen WX (2012) Mesorhizobium muleiense sp. nov., nodulating with Cicer arietinum L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2737–2742
Zhou PF, Chen WM, Wei GH (2010) Mesorhizobium robiniae sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Robinia pseudoacacia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2552–2556
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Bio-industry Technology Development Program (312027-3), Minstry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, and by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2011-0010144).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA, recA, atpD, and glnII genes are KC484966, KM188061, KM188059, and KM188060, respectively.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.M., Pham, V.H.T. & Kim, J. Mesorhizobium soli sp. nov., a novel species isolated from the rhizosphere of Robinia pseudoacacia L. in South Korea by using a modified culture method. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 301–310 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0481-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0481-8