Abstract
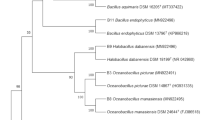
A Gram-negative, white, non-motile, rod shaped bacterial strain BN-19T was isolated from a root nodule of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) in Pakistan. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence revealed that strain BN-19T formed a subclade in the genus Rhizobium together with Rhizobium alkalisoli CCBAU 01393T, Rhizobium vignae CCBAU 05176T, Rhizobium huautlense SO2T and Rhizobium tarimense PL-41T with sequence similarities of 97.5, 97.3, 97.2 and 97.1 % respectively. Sequence analysis of housekeeping genes atpD, glnII and recA (with sequence similarities of ≤92 %) confirmed the unique position of BN-19T in the genus Rhizobium. DNA–DNA relatedness between the strain BN-19T and R. alkalisoli CCBAU 01393T, R. vignae CCBAU 05176T, R. huautlense SO2T and R. tarimense PL-41T were 20.6, 22.5, 15.9 and 20.5 % respectively, further confirming that BN-19T represents a novel species in the genus Rhizobium. The DNA G + C content was 60.1 mol%. The dominant fatty acids of strain BN-19T were C19:0 cyclo ω8c, summed feature 2 (C14:0 3OH and/or C16:1 iso I) and summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c). Some phenotypic features also differentiate the strain BN-19T from the related species. On the basis of these results, strain BN-19T is considered to represent a novel species in the genus Rhizobium, for which the name Rhizobium pakistanensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is BN-19T (=LMG 27895T = CCBAU 101086T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1996) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Cambridge University Press, London, p 232
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
deLajudie P, Willems A, Nick G, Moreira F, Molouba F, Hoste B, Torck U, Neyra M, Collins MD et al (1998) Characterization of tropical tree rhizobia and descriptionof Mesorhizobium plurifarium sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:369–382
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Frank B (1889) Ueber die Pilzsymbiose der Leguminosen. BerDtsch Bot Ges 7:332–346 (in German)
Gao J, Sun J, Li Y, Wang E, Chen W (1994) Numerical taxonomy and DNA relatedness of tropical rhizobia isolated from Hainan Province, China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:151–158
García-Fraile P, Rivas R, Willems A, Peix A, Martens M, Martínez-Molina E, Mateos PF, Velázquez E (2007) Rhizobium cellulosilyticum sp. nov., isolated from sawdust of Populus alba. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:844–848
Gaunt MW, Turner SL, Rigottier-Gois L, Lloyd-Macgilp SA, Young JPW (2001) Phylogenies of atpD and recA support the small subunit rRNA-based classification of rhizobia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2037–2048
Gu T, Sun LN, Zhang J, Sui XH, Li SP (2014) Rhizobium flavum sp. nov., a triazophos-degrading bacterium isolated from soil under the long-term application of triazophos. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2017–2022
Latif R, Ali S, Hayat R (2008) Nitrogen fixation and yield of peanut affected by inorganic fertilizers, variety and inoculums interaction in rainfed areas of Punjab. Soil and Environ 27:77–83
Lee KB, Liu CT, Anzai Y, Kim H, Aono T, Oyaizu H (2005) The hierarchical system of the ‘Alphaproteobacteria’: description of Hyphomonadaceae fam. nov., Xanthobacteraceae fam. nov. and Erythrobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:907–1919
Logan NA, Berge O, Bishop AH, Busse HJ, De Vos P, Fritze D, Heyndrickx M, Kämpfer P, Rabinovitch L, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Seldin L, Ventosa A (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2114–2121
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Martens M, Dawyndt P, Coopman R, Gillis M, De Vos P, Willems A (2008) Advantages of multilocus sequence analysis for taxonomic studies: a case study using 10 housekeeping genes in the genus Ensifer (including former Sinorhizobium). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:200–214
Mnasri B, Liu TY, Saidi S, Chen WF, Chen WX, Zhang XX, Mhamdi R (2014) Rhizobium azibense sp. nov., a nitrogen fixing bacterium isolated from root-nodules of Phaseolus vulgaris. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1501–1506
Moulin L, Béna G, Boivin-Masson C, Stépkowski T (2004) Phylogenetic analyses of symbiotic nodulation genes support vertical and lateral gene co-transfer within the Bradyrhizobium genus. Mol Phylogenet Evol 30:720–732
Parag B, Sasikala Ch, Ramana ChV (2014) Molecular and culture dependent characterization of endolithic bacteria in two beach sand samples and description of Rhizobium endolithicum sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:1235–1244
Quan ZX, Bae HS, Baek JH, Chen WF, Im WT, Lee ST (2005) Rhizobium daejeonense sp. nov. isolated from a cyanide treatment bioreactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:543–2549
Saidi S, Ramírez-Bahena MH, Santillana N, Zúñiga D, Álvarez-Martínez E, Peix A, Mhamdi R, Velázquez E (2014) Rhizobium laguerreae sp. nov. nodulates Vicia faba on several continents. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:242–247
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tan ZY, Xu XD, Wang ET, Gao JL, Martinez-Romero E, Chen WX (1997) Phylogenetic and genetic relationships of Mesorhizobium tianshanense and related rhizobia. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:874–879
Terefework Z, Kaijalainen S, Lindström K (2001) AFLP fingerprinting as a tool to study the genetic diversity of Rhizobium galegae isolated from Galega orientalis and Galega officinalis. J Biotechnol 91:169–180
Tindall BJ, Rosselló-Móra R, Busse HJ, Ludwig W, Kämpfer P (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:249–266
Turner SL, Young JPW (2000) The glutamine synthetases of rhizobia: phylogenetics and evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol 17:309–319
Vincent JM (1970) The cultivation, isolation and maintenance of rhizobia. In: Vincent JM (ed) A manual for the practical study of the root-nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp 1–13
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky M, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE et al (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Yao LJ, Shen YY, Zhan JP, Xu W, Cui GL, Wei GH (2012) Rhizobium taibaishanense sp. nov., isolated from a root nodule of Kummerowia striata. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:335–341
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Yi HS, Oh TK, Ryu CM (2010) Rhizobium soli sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1387–1393
Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martínez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2001) A revision of Rhizobium Frank 1889, with an emended description of the genus, and the inclusion of all species of Agrobacterium Conn 1942 and Allorhizobiumundicola de Lajudie et al. 1998 as new combinations: Rhizobium radiobacter, R. rhizogenes, R. rubi, R. undicola and R. vitis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 51:89–103
Zhang GX, Ren SZ, Xu MY, Zeng GQ, Luo HD, Chen JL, Tan ZY, Sun GP (2011) Rhizobium borbori sp. nov., aniline-degrading bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:816–822
Zhang XX, Tang X, Sheirdil RA, Sun L, Ma XT (2014) Rhizobium rhizoryzae sp. nov., isolated from rice roots. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1373–1377
Acknowledgments
This research was supported/financed by Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan under HEC Indigenous PhD Fellowship and International Research Support Initiative Programs (IRSIP) at Rhizobia Research Center, State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology, College of Biological Sciences, China Agriculture University, Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ sequence accession numbers of strain BN-19T (=LMG 27895T = CCBAU 101086T) for the partial 16S rRNA, atpD, glnII and recA gene are AB854065, AB856324, AB856325 and AB855792, respectively.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalid, R., Zhang, Y.J., Ali, S. et al. Rhizobium pakistanensis sp. nov., isolated from groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) nodules grown in rainfed Pothwar, Pakistan. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 281–290 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0326-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0326-x