Abstract
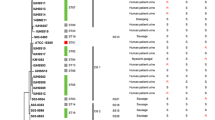
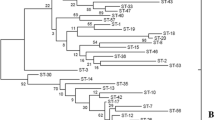
Staphylococcus equorum, the predominant bacterial species detected in Saeu-jeotgal, a Korean high-salt fermented seafood, is a candidate starter bacterium for Saeu-jeotgal fermentation. A multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme was developed to evaluate the genetic diversity and background of S. equorum strains isolated from Saeu-jeotgal. A total of 135 strains, including 117 isolates from Saeu-jeotgal, and others from Myeolchi-jeotgal, sausage, cheese and horse skin, were subjected to MLST, and the internal fragments of seven housekeeping genes, aroE, dnaJ, glpF, gmk, hsp60, mutS, and pta, were compared. This MLST scheme produced 45 sequence types (STs) and the eBURST algorithm clustered the STs into nine clonal groups and seven singletons. Clonal group 1, the major group, consisted of 30 isolates from cheese, Saeu-jeotgal and sausages, which were classified into 12 STs. The predominant ST, ST26, comprised 25 isolates and presented as a singleton. Most of the isolates from Myeolchi-jeotgal and sausages clustered on two different branches of a phylogenetic tree generated with a cluster analysis using the maximum likelihood algorithm. This MLST scheme established the genetic backgrounds of S. equorum strains isolated from different types of food. Among the housekeeping genes used for MLST, gmk had the fewest allele types and fairly low sequence identities (74.0–90.0 %) within the Staphylococcus species. Therefore, sequence analyses of the gmk gene and 16S rRNA gene can be used for the accurate and rapid identification of S. equorum.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berdague JL, Monteil P, Montel MC, Talon R (1993) Effects of starter cultures on the formation of flavour compounds in dry sausage. Meat Sci 35(3):275–287
Blaiotta G, Pennacchia C, Villani F, Ricciardi A, Tofalo R, Parente E (2004) Diversity and dynamics of communities of coagulase-negative staphylococci in traditional fermented sausages. J Appl Microbiol 97(2):271–284
Cheng VW, Zhang G, Oyedotun KS, Ridgway D, Ellison MJ, Weiner JH (2013) Complete genome of the solvent-tolerant Staphylococcus warneri strain SG1. Genome Announc 1(2):e0003813
Cocolin L, Manzano M, Cantoni C, Comi G (2001) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of the 16S rRNA gene V1 region to monitor dynamic changes in the bacterial population during fermentation of Italian sausages. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(11):5113–5121
Coppola S, Mauriello G, Aponte M, Moschetti G, Villani F (2000) Microbial succession during ripening of Naples-type salami, a southern Italian fermented sausage. Meat Sci 56(4):321–329
Corbiere Morot-Bizot S, Leroy S, Talon R (2006) Staphylococcal community of a small unit manufacturing traditional dry fermented sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 108(2):210–217
Cordero MR, Zumalacarregui JM (2000) Characterization of micrococcaceae isolated from salt used for Spanish dry-cured ham. Lett Appl Microbiol 31(4):303–306
Coton E, Desmonts MH, Leroy S, Coton M, Jamet E, Christieans S, Donnio PY, Lebert I, Talon R (2010) Biodiversity of coagulase-negative staphylococci in Frensh cheeses, dry fermented sausages, processing environments and clinical samples. Int J Food Microbiol 137:221–229
Even S, Leroy S, Charlier C, Zakour NB, Chacornac JP, Lebert I, Jamet E, Desmonts MH, Coton E, Pochet S, Donnio PY, Gautier M, Talon R, Le Loir Y (2010) Low occurrence of safety hazards in coagulase negative staphylococci isolated from fermented foodstuffs. Int J Food Microbiol 139(1–2):87–95
Garcia-Varona M, Santos EM, Jaime I, Rovira J (2000) Characterisation of Micrococcaceae isolated from different varieties of chorizo. Int J Food Microbiol 54(3):189–195
Giammarinaro P, Leroy S, Chacornac JP, Delmas J, Talon R (2005) Development of a new oligonucleotide array to identify staphylococcal strains at species level. J Clin Microbiol 43(8):3673–3680
Gill SR, Fouts DE, Archer GL, Mongodin EF, Deboy RT, Ravel J, Paulsen IT, Kolonay JF, Brinkac L, Beanan M, Dodson RJ, Daugherty SC, Madupu R, Angiuoli SV, Durkin AS, Haft DH, Vamathevan J, Khouri H, Utterback T, Lee C, Dimitrov G, Jiang L, Qin H, Weidman J, Tran K, Kang K, Hance IR, Nelson KE, Fraser CM (2005) Insights on evolution of virulence and resistance from the complete genome analysis of an early methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain and a biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain. J Bacteriol 187(7):2426–2438
Guan L, Cho KH, Lee JH (2011) Analysis of the cultivable bacterial community in jeotgal, a Korean salted and fermented seafood, and identification of its dominant bacteria. Food Microbiol 28(1):101–113
Hammes WP, Hertel C (1998) New developments in meat starter cultures. Meat Sci 49S1:S125–138
Irlinger F, Loux V, Bento P, Gibrat JF, Straub C, Bonnarme P, Landaud S, Monnet C (2012) Genome sequence of Staphylococcus equorum subsp. equorum Mu2, isolated from a French smear-ripened cheese. J Bacteriol 194(18):5141–5142
Itoh Y, Kawamura Y, Kasai H, Shah MM, Nhung PH, Yamada M, Sun X, Koyana T, Hayashi M, Ohkusu K, Ezaki T (2006) dnaJ and gyrB gene sequence relationship among species and strains of genus Streptococcus. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(5):368–374
Jeong DW, Kim HR, Han S, Jeon CO, Lee JH (2013) A proposal to unify two subspecies of Staphylococcus equorum: Staphylococcus equorum subsp. equorum and Staphylococcus equorum subsp. linens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:1049–1062
Jolley KA, Chan MS, Maiden MC (2004) mlstdbNet-distributed multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) databases. BMC Bioinformatics 5:86
Kuroda M, Ohta T, Uchiyama I, Baba T, Yuzawa H, Kobayashi I, Cui L, Oguchi A, Aoki K, Nagai Y, Lian J, Ito T, Kanamori M, Matsumaru H, Maruyama A, Murakami H, Hosoyama A, Mizutani-Ui Y, Takahashi NK, Sawano T, Inoue R, Kaito C, Sekimizu K, Hirakawa H, Kuhara S, Goto S, Yabuzaki J, Kanehisa M, Yamashita A, Oshima K, Furuya K, Yoshino C, Shiba T, Hattori M, Ogasawara N, Hayashi H, Hiramatsu K (2001) Whole genome sequencing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 357(9264):1225–1240
Kuroda M, Yamashita A, Hirakawa H, Kumano M, Morikawa K, Higashide M, Maruyama A, Inose Y, Matoba K, Toh H, Kuhara S, Hattori M, Ohta T (2005) Whole genome sequence of Staphylococcus saprophyticus reveals the pathogenesis of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(37):13272–13277
Kwok AY, Chow AW (2003) Phylogenetic study of Staphylococcus and Macrococcus species based on partial hsp60 gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(Pt 1):87–92
Landeta G, Reveron I, Carrascosa AV, de las Rivas B, Munoz R (2011) Use of recA gene sequence analysis for the identification of Staphylococcus equorum strains predominant on dry-cured hams. Food Microbiol 28(6):1205–1210
Leroy S, Lebert I, Chacornac JP, Chavant P, Bernardi T, Talon R (2009) Genetic diversity and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus equorum isolated from naturally fermented sausages and their manufacturing environment. Int J Food Microbiol 134(1–2):46–51
Leroy S, Giammarinaro P, Chacornac JP, Lebert I, Talon R (2010) Biodiversity of indigenous staphylococci of naturally fermented dry sausages and manufacturing environments of small-scale processing units. Food Microbiol 27(2):294–301
Maiden MC (2006) Multilocus sequence typing of bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:561–588
Martineau F, Picard FJ, Ke D, Paradis S, Roy PH, Ouellette M, Bergeron MG (2001) Development of a PCR assay for identification of staphylococci at genus and species levels. J Clin Microbiol 39(7):2541–2547
Mauriello G, Casaburi A, Blaiotta G, Villani F (2004) Isolation and technological properties of coagulase negative staphylococci from fermented sausages of Southern Italy. Meat Sci 67(1):149–158
Nam Y-D, Chung W-H, Seo M-J, Lim S-I (2012a) Draft genome sequence of Stpahylococcus vitulinus F1028, a strain isolated from a black of fermented soybean. J Batcteriol 194(21):5961
Nam Y-D, Chung W-H, Seo M-J, Lim S-I, Yi S-H (2012b) Genome sequence of Stpahylococcus lentus F1142, a strain isolated from Korean soybean paste. J Batcteriol. 194(21):5987
Papamanoli E, Tzanetakis N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Kotzekidou P (2003) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Greek dry-fermented sausage in respect of their technological and probiotic properties. Meat Sci 65(2):859–867
Place RB, Hiestand D, Gallmann HR, Teuber M (2003) Staphylococcus equorum subsp. linens, subsp. nov., a starter culture component for surface ripened semi-hard cheeses. Syst Appl Microbiol 26(1):30–37
Poyart C, Quesne G, Boumaila C, Trieu-Cuout P (2001) Rapid and accurate species-level identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci by using the sodA gene as a target. J Clin Microbiol 39(12):4296–4301
Rosenstein R, Nerz C, Biswas L, Resch A, Raddatz G, Schuster SC, Gotz F (2009) Genome analysis of the meat starter culture bacterium Staphylococcus carnosus TM300. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(3):811–822
Schleifer KH, Kippler-Balz R, Devriese LA (1984) Staphylococcus arlettae sp. nov., S. equorum sp. nov. and S. kloosii sp. nov.: three new coagulase-negative, novobiocin-resistant species from animals. Syst Appl Microbiol 5:501–509
Shah MM, Iihara H, Noda M, Song SX, Nhung PH, Ohkusu K, Kawamura Y, Ezaki T (2007) dnaJ gene sequence-based assay for species identification and phylogenetic grouping in the genus Staphylococcus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(Pt 1):25–30
Sondergaard AK, Stahnke LH (2002) Growth and aroma production by Staphylococcus xylosus, S. carnosus and S. equorum—a comparative study in model systems. Int J Food Microbiol 75(1–2):99–109
Stahnke LH (1994) Aroma components from dried sausages fermented with Staphylococcus xylosus. Meat Sci 38(1):39–53
Staley C, Harwood VJ (2010) The use of genetic typing methods to discriminate among strains of Vibrio cholerae, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus. J AOAC Int 93(5):1553–1569
Takeuchi F, Watanabe S, Baba T, Yuzawa H, Ito T, Morimoto Y, Kuroda M, Cui L, Takahashi M, Ankai A, Baba S, Fukui S, Lee JC, Hiramatsu K (2005) Whole-genome sequencing of Staphylococcus haemolyticus uncovers the extreme plasticity of its genome and the evolution of human-colonizing staphylococcal species. J Bacteriol 187(21):7292–7308
Tamura K, Peterson D, Petrson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEFA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thomas JC, Vargas MR, Miragaia M, Peacock SJ, Archer GL, Enright MC (2007) Improved multilocus sequence typing scheme for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol 45(2):616–619
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alihnment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Toyoda H, Kohara M, Kataoka Y, Suganuma T, Omata T, Imura N, Nomoto A (1984) Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol 174(4):561–585
Wang XM, Noble L, Kreiswirth BN, Eisner W, McClements W, Jansen KU, Anderson AS (2003) Evaluation of a multilocus sequence typing system for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Med Microbiol 52(Pt 11):989–998
Wisplinghoff H, Rosato AE, Enright MC, Noto M, Craig W, Archer GL (2003) Related clones containing SCCmec type IV predominate among clinically significant Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(11):3574–3579
Acknowledgments
The eleven S. equorum strains from sausages used herein were kindly provided by Dr. Sabine Leroy from the Institut National De La Recherche Agronomique in France. S. equorum Mu2 from cheese was kindly provided by Dr. Francoise Irlinger at the same research center. This research was supported by the R&D Convergence Center Support Program, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Republic of Korea, and supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2012R1A1A2039955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, DW., Kim, HR. & Lee, JH. Genetic diversity of Staphylococcus equorum isolates from Saeu-jeotgal evaluated by multilocus sequence typing. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106, 795–808 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0249-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0249-6