Abstract
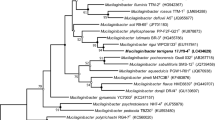
A Gram-negative, aerobic, non-flagellated, non-gliding, rod-shaped bacterial strain, designated WR-R1YT, was isolated from soil at a field of reeds in South Korea. Strain WR-R1YT grew optimally at 30 °C, at pH 7.0–7.5 and in the absence of NaCl. Neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain WR-R1YT fell within the clade comprising Mucilaginibacter species, coherently clustering with the type strain of Mucilaginibacter composti, with which it exhibited the highest 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity value of 97.6 %. Sequence similarities to the type strains of the other Mucilaginibacter species and the other species used in the phylogenetic analysis were 93.1–96.9 % and <91.1 %, respectively. Strain WR-R1YT contained MK-7 as the predominant menaquinone and iso-C15:0, summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω6c and/or C16:1 ω7c), C16:0 and iso-C17:0 3-OH as the major fatty acids. The major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine and one unidentified aminophospholipid. The DNA G+C content of strain WR-R1YT was 43.1 mol% and its mean DNA–DNA relatedness value with M. composti KACC 14956T was 17 %. The differential phenotypic properties, together with the phylogenetic and genetic distinctiveness, revealed that strain WR-R1YT is separate from other Mucilaginibacter species. On the basis of the data presented, strain WR-R1YT represents a novel species of the genus Mucilaginibacter, for which the name Mucilaginibacter calamicampi sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is WR-R1YT (= KCTC 32214T = CCUG 63418T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
An DS, Yin CR, Lee ST, Cho CH (2009) Mucilaginibacter daejeonensis sp. nov., isolated from dried rice straw. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1122–1125
Baik KS, Park SC, Kim EM, Lim CH, Seong CN (2010) Mucilaginibacter rigui sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater, and emended description of the genus Mucilaginibacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:134–139
Barrow GI, Feltham RKA (1993) Cowan and steel’s manual for the identification of medical bacteria, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070
Bowman JP (2000) Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1861–1868
Cui CH, Choi TE, Yu H, Jin F, Lee ST, Kim SC, Im WT (2011a) Mucilaginibacter composti sp. nov., with ginsenoside converting activity, isolated from compost. J Microbiol 49:393–398
Cui CH, Choi TE, Yu H, Jin F, Lee ST, Kim SC, Im WT (2011b) Mucilaginibacter composti sp. nov. in list of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published, validation list no. 142. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2563–2565
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Han SI, Lee HJ, Lee HR, Kim KK, Whang KS (2012) Mucilaginibacter polysacchareus sp. nov., an exopolysaccharide-producing bacterial species isolated from the rhizoplane of the herb Angelica sinensis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:632–637
Jeon Y, Lee SS, Chung BS, Kim JM, Bae JW, Park SK, Jeon CO (2009) Mucilaginibacter oryzae sp. nov., isolated from soil of a rice paddy. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1451–1454
Jiang F, Dai J, Wang Y, Xue X, Xu M, Guo Y, Li W, Fang C, Peng F (2012) Mucilaginibacter soli sp. nov., isolated from Arctic tundra soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1630–1635
Joung Y, Joh K (2011) Mucilaginibacter myungsuensis sp. nov., isolated from a mesotrophic artificial lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1506–1510
Kang SJ, Jung YT, Oh KH, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2011) Mucilaginibacter boryungensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1549–1553
Kang CH, Jung YT, Yoon JH (2013) Mucilaginibacter sabulilitoris sp. nov., isolated from marine sand in a firth. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.045989-0
Kim BC, Lee KH, Kim MN, Lee J, Shin KS (2010) Mucilaginibacter dorajii sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of Platycodon grandiflorum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 309:130–135
Kim BC, Lee KH, Kim MN, Lee J, Shin KS (2011) Mucilaginibacter dorajii sp. nov. in list of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published, validation list no. 133. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1–3
Kim BC, Poo H, Lee KH, Kim MN, Kwon OY, Shin KS (2012a) Mucilaginibacter angelicae sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of Angelica polymorpha Maxim. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:55–60
Kim JH, Kang SJ, Jung YT, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2012b) Mucilaginibacter lutimaris sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:515–519
Komagata K, Suzuki KI (1987) Lipid and cell wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Lányí B (1987) Classical and rapid identification methods for medically important bacteria. Methods Microbiol 19:1–67
Luo X, Zhang L, Dai J, Liu M, Zhang K, An H, Fang C (2009) Mucilaginibacter ximonensis sp. nov., isolated from Tibetan soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1447–1450
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Lee JS, Senthilkumar M, Lee KC, Sundaram S (2010) Mucilaginibacter gossypii sp. nov. and Mucilaginibacter gossypiicola sp. nov., plant-growth-promoting bacteria isolated from cotton rhizosphere soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2451–2457
Männistö MK, Tiirola M, McConnell J, Häggblom MM (2010) Mucilaginibacter frigoritolerans sp. nov., Mucilaginibacter lappiensis sp. nov. and Mucilaginibacter mallensis sp. nov., isolated from soil and lichen samples. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2849–2856
Minnikin DE, Patel PV, Alshamaony L, Goodfellow M (1977) Polar lipid composition in the classification of Nocardia and related bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 27:104–117
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Schaal AM, Parlett AJH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Pankratov TA, Tindall BJ, Liesack W, Dedysh SN (2007) Mucilaginibacter paludis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Mucilaginibacter gracilis sp. nov., pectin-, xylan- and laminarin-degrading members of the family Sphingobacteriaceae from acidic Sphagnum peat bog. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2349–2354
Reichenbach H (1992) The order Cytophagales. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The Prokaryotes, vol 4, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 3631–3675
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids., MIDI technical note 101Microbial ID, Inc, Newark
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamaoka J, Komagata K (1984) Determination of DNA base composition by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol Lett 25:125–128
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Urai M, Aizawa T, Nakagawa Y, Nakajima M, Sunairi M (2008) Mucilaginibacter kameinonensis sp., nov., isolated from garden soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2046–2050
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Yoon JH, Kim H, Kim SB, Kim HJ, Kim WY, Lee ST, Goodfellow M, Park YH (1996) Identification of Saccharomonospora strains by the use of genomic DNA fragments and rRNA gene probes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:502–505
Yoon JH, Lee ST, Park YH (1998) Inter- and intraspecific phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardioides and related taxa based on 16S rDNA sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:187–194
Yoon JH, Kang KH, Park YH (2003) Psychrobacter jeotgali sp. nov., isolated from jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:449–454
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Lee SY (2012a) Salinimonas lutimais sp. nov., a polysaccharide-degrading bacterium isolated from a tidal flat. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:803–810
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Park S, Oh TK (2012b) Mucilaginibacter litoreus sp. nov., isolated from marine sand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2822–2827
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for Collection of Domestic Biological Resources from the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) and the Program for Collection, Management and Utilization of Biological Resources and BK 21 program from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) of the Republic of Korea. We are very grateful to the KACC for kindly providing the type strains of Mucilaginibacter species.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain WR-R1YT is KC537738.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, JH., Park, S. & Jung, YT. Mucilaginibacter calamicampi sp. nov., a member of the family Sphingobacteriaceae isolated from soil at a field of reeds. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 37–45 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9922-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9922-4