Abstract
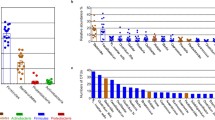
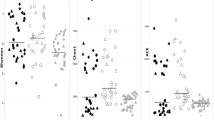
The combination of a Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem with ad hoc molecular techniques (i.e. pyrosequencing, denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative PCR) allowed an evaluation of the extent to which two plant polysaccharide supplements could modify a complex gut microbial community. The presence of Aloe vera gel powder and algae extract in product B as compared to the standard blend (product A) improved its fermentation along the entire simulated colon. The potential extended effect of product B in the simulated distal colon, as compared to product A, was confirmed by: (i) the separate clustering of the samples before and after the treatment in the phylogenetic-based dendrogram and OTU-based PCoA plot only for product B; (ii) a higher richness estimator (+33 vs. −36 % of product A); and (iii) a higher dynamic parameter (21 vs. 13 %). These data show that the combination of well designed in vitro simulators with barcoded pyrosequencing is a powerful tool for characterizing changes occurring in the gut microbiota following a treatment. However, for the quantification of low-abundance species—of interest because of their relationship to potential positive health effects (i.e. bifidobacteria or lactobacilli)—conventional molecular ecological approaches, such as PCR–DGGE and qPCR, still remain a very useful complementary tool.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi A, Fraser W, Tarelli E, Bland M, Axford J (2011a) An open-label dosing study to evaluate the safety and effects of a dietary plant derived polysaccharide supplement on the N-glycosylation status of serum glycoproteins in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr 65:648–656
Alavi A, Goodfellow L, Fraser O, Tarelli E, Bland M, Axford J (2011b) A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study to explore the efficacy of a dietary plant-derived polysaccharide supplement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 50:1111–11119
Andersson AF, Lindberg M, Jakobsson H, Bäckhed F, Nyrén P, Engstrand L (2008) Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS One 3:e2836
Best T, Kemps E, Bryan J (2010) Saccharide effects on cognition and well-being in middle-aged adults: a randomized controlled trial. Dev Neuropsychol 35:66–80
Boon N, Top EM, Verstraete W, Siciliano SD (2003) Bioaugmentation as a tool to protect the structure and function of an activated sludge microbial community against a 3-chloroaniline shock load. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1511–1520
Collado MC, Isolauri E, Laitinen K, Salminen S (2008) Distinct composition of gut microbiota during pregnancy in overweight and normal-weight women. Am J Clin Nutr 88:894–899
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14691–14696
De Santis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R, Andersen GL (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W394–W399
Degnan BA, Macfarlane GT (1995) Arabinogalactan utilization in continuous cultures of Bifidobacterium longum: effect of co-culture with Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Anaerobe 1:103–112
Dodd D, Moon YH, Swaminathan K, Mackie RI, Cann IK (2010) Transcriptomic analyses of xylan degradation by Prevotella bryantii and insights into energy acquisition by xylanolytic bacteroidetes. J Biol Chem 285:30261–30273
Duncan SH, Lobley GE, Holtrop G, Ince J, Johnstone AM, Louis P, Flint HJ (2008) Human colonic microbiota associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int J Obes 32:1720–1724
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Evans J, Sheneman L, Foster J (2006) Relaxed neighbor joining: a fast distance-based phylogenetic tree construction method. J Mol Evol 62:785–792
Gibson GR, Probert HM, Loo JV, Rastall RA, Roberfroid MB (2004) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr Res Rev 17:259–275
Gihring TM, Green SJ, Schadt CW (2012) Massively parallel rRNA gene sequencing exacerbates the potential for biased community diversity comparisons due to variable library sizes. Environ Microbiol 14:285–290
Grootaert C, Van den Abbeele P, Marzorati M, Broekaert WF, Courtin CM, Delcour JA, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T (2009) Comparison of prebiotic effects of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides and inulin in a simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:231–242
Guo X, Xia X, Tang R, Zhou J, Zhao Hand Wang K (2008) Development of a real-time PCR method for Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in faeces and its application to quantify intestinal population of obese and lean pigs. Lett Appl Microbiol 47:367–373
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12:1889–1898
Karlsson FH, Ussery DW, Nielsen J, Nookaew I (2011) A closer look at bacteroides: phylogenetic relationship and genomic implications of a life in the human gut. Microb Ecol 61:473–485
Koetzner L, Grover G, Boulet J, Jacoby H (2010) Plant-derived polysaccharide dietary supplements inhibits dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 55:1278–1285
Ley RE (2010) Obesity and the human microbiome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 26:5–11
Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11070–11075
Liu Z, Lozupone C, Hamady M, Bushman FD, Knight R (2007) Short pyrosequencing reads suffice for accurate microbial community analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 35:e120
Lorenz MO (1905) Methods of measuring concentration of wealth. J Am Stat Assoc 9:209–219
Manning TS, Gibson GR (2004) Microbial-gut interactions in health and disease: prebiotics. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 18:287–298
Marzorati M, Wittebolle L, Boon N, Daffonchio D, Verstraete W (2008) How to get more out of molecular fingerprints: practical tools for microbial ecology. Environ Microb 10:1571–1581
Marzorati M, Possemiers S, Verstraete W (2009) The use of the SHIME-related technology platform to assess the efficacy of pre- and probiotics. Agro Food Ind Hi-Tech 20:S50–S53
Marzorati M, Verhelst A, Luta G, Sinnott R, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T, Possemiers S (2010) In vitro modulation of the human gastrointestinal microbial community by plant-derived polysaccharide-rich dietary supplements. Int J Food Microbiol 139:168–176
Molly K, Vande Woestyne M, De Smet B, Verstraete W (1994) Validation of the simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (SHIME) reactor using microorganism-associated activities. Microb Ecol Health Dis 7:191–200
Pogribna M, Freeman JP, Paine D, Boudreau MD (2008) Effect of Aloe vera whole leaf extract on short chain fatty acids production by Bacteroides fragilis, Bifidobacterium infantis and Eubacterium limosum. Lett Appl Microbiol 46:575–580
Possemiers S, Grootaert C, Vermeiren J, Gross G, Marzorati M, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T (2009) The intestinal environment in health and disease—recent insights on the potential of intestinal bacteria to influence human health. Curr Pharm Des 15:2051–2065
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35:7188–7196
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T et al (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65
Rajilić-Stojanović M, Maathuis A, Heilig HG, Venema K, de Vos WM, Smidt H (2010) Evaluating the microbial diversity of an in vitro model of the human large intestine by phylogenetic microarray analysis. Microbiology 156:3270–3281
Ramberg JE, Nelson ED, Jacoby HI, Li Q, Koetzner L, Zhang B, Boulet J, Sinnot RA (2010) Plant plysaccharide supplements reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in colonic tissue of mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Int J Probiotics Prebiotics 5:229–236
Read S, Marzorati M, Guimarães BCM, Boon N (2011) Microbial resource management: successful parameters and new concepts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:861–871
Salyers AA, Vercellotti JR, West SE, Wilkins TD (1977) Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:319–322
Sanchez JI, Marzorati M, Grootaert C, Baran M, Van Craeyveld V et al (2009) Arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides (AXOS) affect the protein/carbohydrate fermentation balance and microbial population dynamics of the simulator of human intestinal microbial ecosystem. Microb Biotechnol 2:101–113
Schloss PD (2009) A high-throughput DNA sequence aligner for microbial ecology studies. PLoS One 4:e8230
Schloss PD (2010) The effects of alignment quality, distance calculation method, sequence filtering, and region on the analysis of 16S rRNA gene-based studies. PLoS Comput Biol 6:e1000844
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schäfer K, Beijer S, Bos NA, Donus C, Hardt PD (2010) Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity 18:190–195
Sheneman L, Evans J, Foster JA (2006) Clearcut: a fast implementation of relaxed neighbor joining. Bioinformatics 22:2823–2824
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444:1027–1031
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE et al (2009) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457:480–484
Van de Wiele T, Boon N, Possemiers S, Jacobs H, Verstraete W (2007) Inulin-type fructans of longer degree of polymerization exert more pronounced in vitro prebiotic effects. J Appl Microbiol 102:452–460
Van den Abbeele P, Grootaert C, Marzorati M, Possemiers S et al (2010) Microbial community development in a dynamic gut model is reproducible, colon region specific, and selective for Bacteroidetes and Clostridium cluster IX. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5237–5246
Van Laere KMJ, Hartemink R, Bosveld M, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ (2000) Fermentation of plant cell wall derived polysaccharides and their corresponding oligosaccharides by intestinal bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 48:1644–1652
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2009) Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2365–2370
Acknowledgments
Tom Van de Wiele, Sam Possemiers and Massimo Marzorati are Postdoctoral Fellows of the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marzorati, M., Maignien, L., Verhelst, A. et al. Barcoded pyrosequencing analysis of the microbial community in a simulator of the human gastrointestinal tract showed a colon region-specific microbiota modulation for two plant-derived polysaccharide blends. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 409–420 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9821-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9821-0