Abstract
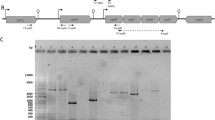
In this study consensus oligonucleotides PN5/PN3 were designed by aligning the aminopeptidase N genes (pepN) of various actinobacteria and applied to the isolation of the pepN genes of dairy propionibacteria (PAB) and closely related species associated with food. This allowed sequencing of a pepN gene region from Propionibacterium jensenii LMG 16541. The sequence of this gene was completed by inverse PCR. Consensus primer pairs NU1/D1 and NU2/D1 were derived from the alignment of the new sequence with its homologues in Propionibacterium acnes and other actinobacteria; these were used to start sequencing of the pepN genes of Propionibacterium freudenreichii, Propionibacterium thoenii, Propionibacterium microaerophilum, Propionibacterium acidipropionici, Propioni bacterium cyclohexanicum and Propionibacterium microaerophilum. Reverse transcription coupled with PN5/PN3 and NU1/D1 PCR tests indicated that the pepN genes of P. jensenii and P. freudenreichii are expressed during growth in skim milk and acid whey
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleve G, Rizzotti L, Dellaglio F, Torriani S (2003) Development of reverse transcription (RT-PCR) and Real-Time RT-PCR assays for rapid detection and quantification of viable yeasts and molds contaminating yogurts and pasteurized food products. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4116–4122
Britz TJ, Riedel KH (1994) Propionibacterium species diversity in Leerdammer cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 22:257–267
Brüggemann H, Henne A, Hoster F, Liesegang H, Wiezer A, Strittmatter A, Hujer S, Dürre P, Gottschalk G (2004) The complete genome sequence of Propionibacterium acnes, a commensal of human skin. Science 305:671–673
Butler MJ, Aphale JS, DiZonno MA, Krygsman P, Walczyk E, Malek LT (1994a) Intracellular aminopeptidases in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Ind Microbiol 13:24–29
Butler MJ, Aphale JS, Binnie C, DiZonno MA, Krygsman P, Soltes GA, Walczyk E, Malek LT (1994b) The aminopeptidase N-encoding pepN gene of Streptomyces lividans 66. Gene 141:115–119
Chandu D, Nandi D (2003) PepN is the major aminopeptidase in Escherichia coli: insights on substrate specificity and role during sodium-salicylate-induced stress. Microbiology 149:3437–3447
Chavagnat F, Casey MG, Meyer J (1999) Purification, characterization, gene cloning, sequencing, and overexpression of aminopeptidase N from Streptococcus thermophilus A. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3001–3007
Drake MA, Small CL, Spence KD, Swanson BG (1996) Rapid detection and identification of Lactobacillus spp. in dairy products by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Food Prot 59:1031–1036
Fernandez-Espla MD, Fox PF (1998) Effect of adding P. freudenreichii subsp. shermanii NCDO 853 or Lactobacillus casei ssp. casei IFPL 731 on proteolysis and flavor development of Cheddar cheese. J Agric Food Chem 46:1228–1234
Foglino M, Lazdunski A (1987) Deletion analysis of the promoter region of the Escherichia coli pepN gene, a gene subject in vivo to multiple global controls. Mol Gen Genetics 210:523–527
Gagnaire V, Thierry A, Léonil J (2001a) Propionibacteria and facultatively heterofermentative lactobacilli weakly contribute to secondary proteolysis of Emmental cheese. Lait 81:339–353
Gagnaire V, Mollé D, Herrouin M, Léonil J (2001b) Peptides identified during Emmental cheese ripening: origin and proteolytic systems involved. J Agric Food Chem 49:4402–4413
Gagnaire V, Piot M, Camier B, Vissers JPC, Jan G, Léonil J (2004) Survey of bacterial proteins released in cheese: a proteomic approach. Int J Food Microbiol 94:185–201
Guédon E, Renault P, Ehrlich SD, Delorme C (2001) Transcriptional pattern of genes coding for the proteolytic system of Lactococcus lactis and evidence for coordinated regulation of key enzymes by peptide supply. J Bacteriol 183:3614–3622
Jan G, Leverrier P, Pichereau V, Boyaval P (2001) Changes in protein synthesis and morphology during acid adaptation of Propionibacterium freudenreichii. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2029–2036
Leenhouts K, Bolhuis A, Boot J, Deutz I, Toonen M, Venema G, Kok J, Ledeboer A (1998) Cloning, expression and chromosomal stabilization of the Propionibacterium shermanii proline iminopeptidase gene (pip) for food-grade application in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4736–4742
Midwinter RG, Pritchard GG (1994) Aminopeptidase N from Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus NCDO 573: purification and properties. J Appl Bacteriol 77:288–295
Neviani E, Rossi F, Fornasari ME, Dellaglio F, Torriani S (2002) Aminopeptidase activities of Propionibacterium freudenreichii dairy isolates. Ann Microbiol 52:275–282
Ochman H, Gerber AS, Hartl DL (1988) Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics 120:621–623
Rawlings ND, Tolle DP, Barrett AJ (2004) MEROPS: the peptidase database. Nucleic Acids Res 32(Database):D160–D164
Rossi F, Torriani S, Dellaglio F (1998) Identification and clustering of dairy propionibacteria by RAPD-PCR and CGE-REA methods. J Appl Microbiol 85:956–964
Thierry A, Maillard MB, Bonnarme P, Roussel E (2005) The addition of Propionibacterium freudenreichii to Raclette cheese induces biochemical changes and enhances flavor development. J Agric Food Chem 53:4157–4165
Valence F, Richoux R, Thierry A, Palva A, Lortal S (1998) Autolysis of Lactobacillus helveticus and Propionibacterium freudenreichii in Swiss cheeses: first evidence by using species-specific lysis markers. J Dairy Res 65:609–620
Van Alen-Boerritger IJ, Baankreis R, de Vos WM (1991) Characterization and overexpression of the Lactococcus lactis pepN gene and localization of its product,␣aminopeptidase N. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2555–2561
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, F., Busetto, M. & Torriani, S. Isolation of aminopeptidase N genes of food associated propionibacteria and observation of their transcription in skim milk and acid whey. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 91, 87–96 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9098-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9098-2