Abstract
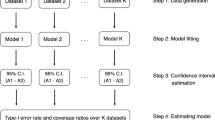
Breast lesions are the most common threat to the health of women. The accumulation of historical examination reports for diagnosing breast lesions in clinical practice provides the necessary foundations for analyzing the diagnostic preferences of radiologists and the mutual influence between radiologists in a hospital. This mutual influence is important for indicating the development of an ultrasonic department in which radiologists work. To conduct a data-driven analysis of the influence between the two radiologists, the influence of the diagnostic preferences of one radiologist on the other was qualitatively defined using regression models. Following the qualitative definition, the process of analyzing the influence between two radiologists was designed, in which ten machine learning regression algorithms were included to make a reliable analysis. A statistical comparison method was developed using each machine learning regression algorithm to generate the indicator pair. The indicator pairs generated by ten machine learning regression algorithms were integrated using absolute majority voting to derive the overall indicator pair, from which the influence between two radiologists was determined, namely the unclear influence, clear influence, or significant influence. Experiments were conducted based on historical examination reports collected from two hospitals in Hefei, Anhui, China. The experimental results indicate that the trend in the influence between two radiologists in one hospital is different from that in the other hospital, which is associated with the management pattern, innovation incentive, and reward pattern of the two hospitals. A general conclusion on managerial insights was drawn to generalize the findings of this study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsen, M. E., Ayvaci, M. U. S., & Raghunathan, S. (2019). When algorithmic predictions use human-generated data: A bias-aware classification algorithm for breast cancer diagnosis. Information Systems Research, 30(1), 97–116.
Alshabibi, A. S., Mo’ayyad, E. S., Tapia, K. A., Heard, R., & Brennan, P. C. (2021). Impact of hours awake and hours slept at night on radiologists’ mammogram interpretations. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 18(5), 730–738.
Athanasiou, A., Tardivon, A., Ollivier, L., Thibault, F., El Khoury, C., & Neuenschwander, S. (2009). How to optimize breast ultrasound. European Journal of Radiology, 69(1), 6–13.
Baradaran Rezaei, H., Amjadian, A., Sebt, M. V., Askari, R., & Gharaei, A. (2022). An ensemble method of the machine learning to prognosticate the gastric cancer. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04964-1
Berg, W. A., Bandos, A. I., Mendelson, E. B., Lehrer, D., Jong, R. A., & Pisano, E. D. (2016). Ultrasound as the primary screening test for breast cancer: analysis from ACRIN 6666. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 108(4), djv367.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., & Stone, C. J. (1984). Classification and regression trees. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. International Group, 432, 151–166.
Brem, R. F., Lenihan, M. J., Lieberman, J., & Torrente, J. (2015). Screening breast ultrasound: Past, present, and future. American Journal of Roentgenology, 204(2), 234–240.
Calisto, F. M., Ferreura, A., Nascimento, J. C., & Gonçalves, D. (2017). Towards touch-based medical image diagnosis annotation. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Conference on Interactive Surfaces and Spaces (pp. 390–395).
Calisto, F. M., Nunes, N., & Nascimento, J. C. (2020). BreastScreening: on the use of multi-modality in medical imaging diagnosis. In Proceedings of the international conference on advanced visual interfaces (pp. 1–5).
Calisto, F. M., Santiago, C., Nunes, N., & Nascimento, J. C. (2021). Introduction of human-centric AI assistant to aid radiologists for multimodal breast image classification. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 150, 102607.
Calisto, F. M., Santiago, C., Nunes, N., & Nascimento, J. C. (2022). BreastScreening-AI: Evaluating medical intelligent agents for human-AI interactions. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 127, 102285.
Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (pp. 785–794).
De Bock, K. W., Coussement, K., & Lessmann, S. (2020). Cost-sensitive business failure prediction when misclassification costs are uncertain: A heterogeneous ensemble selection approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 285(2), 612–630.
De Rosa, F., Migliatico, I., Vigliar, E., Salatiello, M., Pisapia, P., Iaccarino, A., Russo, D., Insabato, L., Accurso, A., Arpino, G., Palombini, L., Troncone, G., & Bellevicine, C. (2020). The continuing role of breast fine-needle aspiration biopsy after the introduction of the IAC Yokohama system for reporting breast fine needle aspiration biopsy cytopathology. Diagnostic Cytopathology, 48(12), 1244–1253.
Ditzler, G., Roveri, M., Alippi, C., & Polikar, R. (2015). Learning in nonstationary environments: A survey. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 10(4), 12–25.
Draper, N. R., & Smith, H. (1998). Applied regression analysis (Vol. 326). John Wiley & Sons.
Feng, H., Cao, J., Wang, H., Xie, Y., Yang, D., Feng, J., & Chen, B. (2020). A knowledge-driven feature learning and integration method for breast cancer diagnosis on multi-sequence MRI. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 69, 40–48.
Franklin, J. (2005). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference and prediction. The Mathematical Intelligencer, 27(2), 83–85.
Friedman, J. H. (2002). Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 38(4), 367–378.
Fu, C., Liu, W., & Chang, W. (2020). Data-driven multiple criteria decision making for diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Annals of Operations Research, 293(2), 833–862.
Ghoushchi, S. J., Ranjbarzadeh, R., Najafabadi, S. A., Osgooei, E., & Tirkolaee, E. B. (2021). An extended approach to the diagnosis of tumor location in breast cancer using deep learning. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03613-y
Giess, C. S., Wang, A., Ip, I. K., Lacson, R., Pourjabbar, S., & Khorasani, R. (2019). Patient, radiologist, and examination characteristics affecting screening mammography recall rates in a large academic practice. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 16(4), 411–418.
Guo, M., Liao, X., Liu, J., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Consumer preference analysis: A data-driven multiple criteria approach integrating online information. Omega, 96, 102074.
Haque, M. N., Tazubm, T., Khan, M. M., Faisal, S., Ibraheem, S. M., Algethami, H., & Almalki, F. A. (2022). Predicting characteristics associated with breast cancer survival using multiple machine learning approaches. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022, 1249692.
Hoerl, A. E., & Kennard, R. W. (1970). Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics, 12(1), 55–67.
Hooley, R. J., Andrejeva, L., & Scoutt, L. M. (2011). Breast cancer screening and problem solving using mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Quarterly, 27(1), 23–47.
Huang, Q., Hu, B., & Zhang, F. (2019). Evolutionary optimized fuzzy reasoning with mined diagnostic patterns for classification of breast tumors in ultrasound. Information Sciences, 502, 525–536.
Huber, P. J. (1973). Robust regression: Asymptotics, conjectures and Monte Carlo. The Annals of Statistics, 1(5), 799–821.
Kava, H., Spanaki, K., Papadopoulos, T., Despoudi, S., Rodriguez-Espindola, O., & Fakhimi, M. (2021). Data analytics diffusion in the UK renewable energy sector: An innovation perspective. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04263-1
Khan, S. A. R., Godil, D. I., Jabbour, C. J. C., Shujaat, S., Razzaq, A., & Yu, Z. (2021). Green data analytics, blockchain technology for sustainable development, and sustainable supply chain practices: Evidence from small and medium enterprises. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04275-x
Kulinskaya, E., Morgenthaler, S., & Staudte, R. G. (2011). Significance testing: An overview. In M. Lovric (Ed.), International encyclopedia of statistical science (Vol. Part 19, pp. 1318–1321). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Lee, J. Y., Lee, K. S., Seo, B. K., Cho, K. R., Woo, O. H., Song, S. E., Kim, E. K., Lee, H. Y., Kim, J. S., & Cha, J. (2022). Radiomic machine learning for predicting prognostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes of breast cancer using tumor heterogeneity and angiogenesis properties on MRI. European Radiology, 32, 650–660.
Lindley, D. V., & Smith, A. F. (1972). Bayes estimates for the linear model. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (methodological), 34(1), 1–18.
Liu, L. (2018). Research on logistic regression algorithm of breast cancer diagnose data by machine learning. In 2018 International Conference on Robots & Intelligent System (ICRIS) (pp. 157–160).
Liu, A., Lu, J., Liu, F., & Zhang, G. (2018). Accumulating regional density dissimilarity for concept drift detection in data streams. Pattern Recognition, 76, 256–272.
Liu, T., Huang, J., Liao, T., Pu, R., Liu, S., & Peng, Y. (2022). A hybrid deep learning model for predicting molecular subtypes of human breast cancer using multimodal data. IRBM, 43(1), 62–74.
Llamazares, B. (2004). Simple and absolute special majorities generated by OWA operators. European Journal of Operational Research, 158(3), 707–720.
Maldonado, S., Bravo, C., López, J., & Pérez, J. (2017). Integrated framework for profit-based feature selection and SVM classification in credit scoring. Decision Support Systems, 104, 113–121.
Mangasarian, O. L., & Musicant, D. R. (2000). Robust linear and support vector regression. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 22(9), 950–955.
Mishra, S., & Singh, S. P. (2020). A stochastic disaster-resilient and sustainable reverse logistics model in big data environment. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03573-0
Mohanty, F., Rup, S., Dash, B., Majhi, B., & Swamy, M. N. S. (2020). An improved scheme for digital mammogram classification using weighted chaotic salp swarm algorithm-based kernel extreme learning machine. Applied Soft Computing, 91, 106266.
Orel, S. G., Kay, N., Reynolds, C., & Sullivan, D. C. (1999). BI-RADS categorization as a predictor of malignancy. Radiology, 211(3), 845–850.
Peng, J., Zhu, X., Wang, Y., An, L., & Shen, D. (2019). Structured sparsity regularized multiple kernel learning for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Pattern Recognition, 88, 370–382.
Perry, N., Broeders, M., de Wolf, C., Törnberg, S., Holland, R., & von Karsa, L. (2008). European guidelines for quality assurance in breast cancer screening and diagnosis. -summary document. Oncology in Clinical Practice, 4(2), 74–86.
Pi, Y., Chen, Y., Deng, D., Qi, X., Li, J., Lv, Q., & Yi, Z. (2020). Automated diagnosis of multi-plane breast ultrasonography images using deep neural networks. Neurocomputing, 403, 371–382.
Ranjbarzadeh, R., Sarshar, N. T., Ghoushchi, S. J., Esfahani, M. S., Parhizkar, M., Pourasad, Y., Anari, S., & Bendechache, M. (2022). MRFE-CNN: Multi-route feature extraction model for breast tumor segmentation in Mammograms using a convolutional neural network. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04755-8
Rao, A. A., Feneis, J., Lalonde, C., & Ojeda-Fournier, H. (2016). A pictorial review of changes in the BI-RADS fifth edition. Radiographics, 36(3), 623–639.
Raza, S., Goldkamp, A. L., Chikarmane, S. A., & Birdwell, R. L. (2010). US of breast masses categorized as BI-RADS 3, 4, and 5: Pictorial review of factors influencing clinical management. Radiographics, 30(5), 1199–1213.
Sedgwick, E. (2011). The breast ultrasound lexicon: Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS). Seminars in Roentgenology, 46(4), 245–251.
Sehgal, C. M., Weinstein, S. P., Arger, P. H., & Conant, E. F. (2006). A review of breast ultrasound. Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia, 11(2), 113–123.
Shinagare, A. B., Lacson, R., Boland, G. W., Wang, A., Silverman, S. G., Mayo-Smith, W. W., & Khorasani, R. (2019). Radiologist preferences, agreement, and variability in phrases used to convey diagnostic certainty in radiology reports. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 16(4), 458–464.
Stavros, A. T., Thickman, D., Rapp, C. L., Dennis, M. A., Parker, S. H., & Sisney, G. A. (1995). Solid breast nodules: Use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology, 196(1), 123–134.
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(3), 209–249.
Tang, J., Rangayyan, R. M., Xu, J., El Naqa, I., & Yang, Y. (2009). Computer-aided detection and diagnosis of breast cancer with mammography: Recent advances. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 13(2), 236–251.
Torres, A. M., Maaren, M. C., Hendriks, M. P., Siesling, S., & Geleijnse, G. (2021). Explainable machine learning can outperform Cox regression predictions and provide insights in breast cancer survival. Scientific Reports, 11, 6968.
Tourassi, G., Voisin, S., Paquit, V., & Krupinski, E. (2013). Investigating the link between radiologists’ gaze, diagnostic decision, and image content. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 20(6), 1067–1075.
Turnbull, C., Ahmed, S., Morrison, J., Pernet, D., Renwick, A., Maranian, M., et al. (2010). Genome-wide association study identifies five new breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature Genetics, 42(6), 504–507.
Vapnick, V. N. (1998). Statistical learning theory (pp. 401–441). Wiley.
Vijayarajeswari, R., Parthasarathy, P., Vivekanandan, S., & Basha, A. A. (2019). Classification of mammogram for early detection of breast cancer using SVM classifier and Hough transform. Measurement, 146, 800–805.
Wang, Z., Wang, R., Gao, J., Gao, Z., & Liang, Y. (2020). Fault recognition using an ensemble classifier based on Dempster-Shafer theory. Pattern Recognition, 99, 107079.
Warner, E., Plewes, D. B., Hill, K. A., Causer, P. A., Zubovits, J. T., Jong, R. A., et al. (2004). Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, mammography, and clinical breast examination. JAMA, 292(11), 1317–1325.
Xu, S., & Pan, Z. (2020). A novel ensemble of random forest for assisting diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease on small handwritten dynamics dataset. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 144, 104283.
Zhang, X., & Mahadevan, S. (2019). Ensemble machine learning models for aviation incident risk prediction. Decision Support Systems, 116, 48–63.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 72171066, 72101074, and 72188101) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. JZ2021HGTA0139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, C., Wang, D. & Chang, W. Data-driven analysis of influence between radiologists for diagnosis of breast lesions. Ann Oper Res 328, 419–449 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-05086-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-05086-4