Abstract
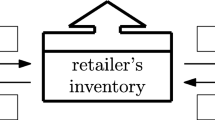
With the prevalence of network technologies, the world is shrinking and it is observed that the decision policies of the players of the supply chain go hand in hand. Thus the optimal replenishment decisions of retailers cannot be taken in isolation and need to be integrated with that of the supplier. This research work establishes a supplier-retailer supply chain in which demand for the products is displayed stock dependent. Nowadays, trade credit is also seen as prime source of short term financing, thus the retailer takes the benefit of permissible delay in payments from the supplier. The objective of the proposed model is to obtain the optimal decisions of the supply chain under three different policies- centralized, Supplier-led Stackelberg policy and Nash equilibrium solution. In this study, the influence of trade credit offered by the supplier, replenishment decisions and integration among the players of supply chain through different centralized and decentralized policies is analyzed for deteriorating items where retailer faces displayed stock dependent demand with two storage facilities. The model is best suitable for the emerging retail markets or supermarkets with limited shelf space displaying consumable items such as grocery, consumer goods, etc. The results have been validated with the help of a numerical example. Sensitivity analysis has also been performed to study the effect of various parameters on the optimal solution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad, P. L., & Jaggi, C. K. (2003). A joint approach for setting unit price and the length of the credit period for a seller when end demand is price sensitive. International Journal of Production Economics, 83(2), 115–122.
Aggarwal, S. P., & Jaggi, C. K. (1995). Ordering policies of deteriorating items under permissible delay in payments. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 46, 658–662.
Chen, L. H., & Kang, F. S. (2010). Integrated inventory models considering the two-level trade credit policy and a price-negotiation scheme. European Journal of Operational Research, 205(1), 47–58.
Chern, M. S., Pan, Q., Teng, J. T., Chan, Y. L., & Chen, S. C. (2013). Stackelberg solution in a vendor–buyer supply chain model with permissible delay in payments. International Journal of Production Economics, 144(1), 397–404.
Chung, K. J., & Huang, T. S. (2007). The optimal retailer’s ordering policies for deteriorating items with limited storage capacity under trade credit financing. International Journal of Production Economics, 106(1), 127–145.
Ghare, P. M., & Schrader, G. F. (1963). A model for exponentially decaying inventories. Journal of Industrial Engineering, 14, 238–243.
Ghiami, Y., Williams, T., & Wu, Y. (2013). A two-echelon inventory model for a deteriorating item with stock-dependent demand, partial backlogging and capacity constraints. European Journal of Operational Research, 231(3), 587–597.
Goyal, S. K. (1977). An integrated inventory model for a single supplier-single customer problem. The International Journal of Production Research, 15(1), 107–111.
Goyal, S. K. (1985). Economic order quantity under conditions of permissible delay in payments. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 36(4), 335–338.
Gupta, R., & Vrat, P. (1986). Inventory model for stock-dependent consumption rate. Opsearch, 23(1), 19–24.
Hsieh, T. P., Dye, C. Y., & Ouyang, L. Y. (2008). Determining optimal lot size for a two-warehouse system with deterioration and shortages using net present value. European Journal of Operational Research, 191(1), 182–192.
Jaggi, C. K., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., Tiwari, S., & Shafi, A. A. (2017a). Two-warehouse inventory model for deteriorating items with imperfect quality under the conditions of permissible delay in payments. Scientia Iranica. Transaction E Industrial Engineering, 24(1), 390.
Jaggi, C. K., Tiwari, S., & Goel, S. K. (2017b). Credit financing in economic ordering policies for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with price dependent demand and two storage facilities. Annals of Operations Research, 248(1–2), 253–280.
Levin, R. I. (1972). Production operations management: Contemporary policy for managing operating systems. McGraw-Hill Companies.
Liao, J. J., Chung, K. J., & Huang, K. N. (2013). A deterministic inventory model for deteriorating items with two warehouses and trade credit in a supply chain system. International Journal of Production Economics, 146(2), 557–565.
Liao, J. J., Huang, K. N., & Chung, K. J. (2012). Lot-sizing decisions for deteriorating items with two warehouses under an order-size-dependent trade credit. International Journal of Production Economics, 137(1), 102–115.
Maiti, T., & Giri, B. C. (2015). A closed loop supply chain under retail price and product quality dependent demand. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 37, 624–637.
Mandal, B. A., & Phaujdar, S. (1989). An inventory model for deteriorating items and stock-dependent consumption rate. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 40(5), 483–488.
Min, J., Zhou, Y. W., Liu, G. Q., & Wang, S. D. (2012). An EPQ model for deteriorating items with inventory-level-dependent demand and permissible delay in payments. International Journal of Systems Science, 43(6), 1039–1053.
Mishra, U., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., Tiwari, S., Shaikh, A. A., & Treviño-Garza, G. (2017). An inventory model under price and stock dependent demand for controllable deterioration rate with shortages and preservation technology investment. Annals of Operations Research, 254(1–2), 165–190.
Niu, B., & Xie, J. (2008). A note on “Two-warehouse inventory model with deterioration under FIFO dispatch policy”. European Journal of Operational Research, 190(2), 571–577.
Ouyang, L. Y., Ho, C. H., Su, C. H., & Yang, C. T. (2015). An integrated inventory model with capacity constraint and order-size dependent trade credit. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 84, 133–143.
Padmanabhan, G., & Vrat, P. (1995). EOQ models for perishable items under stock dependent selling rate. European Journal of Operational Research, 86(2), 281–292.
Ray, J., & Chaudhuri, K. S. (1997). An EOQ model with stock-dependent demand, shortage, inflation and time discounting. International Journal of Production Economics, 53(2), 171–180.
Shah, N. H., & Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E. (2015). Retailer’s decision for ordering and credit policies for deteriorating items when a supplier offers order-linked credit period or cash discount. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 259, 569–578.
Teng, J. T., Chang, C. T., & Chern, M. S. (2012). Vendor–buyer inventory models with trade credit financing under both non-cooperative and integrated environments. International Journal of Systems Science, 43(11), 2050–2061.
Teng, J. T., & Goyal, S. K. (2007). Optimal ordering policies for a retailer in a supply chain with up-stream and down-stream trade credits. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 58(9), 1252–1255.
Teng, J. T., Yang, H. L., & Chern, M. S. (2013). An inventory model for increasing demand under two levels of trade credit linked to order quantity. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(14), 7624–7632.
Tiwari, S., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., Khanna, A., & Jaggi, C. K. (2016). Impact of trade credit and inflation on retailer’s ordering policies for non-instantaneous deteriorating items in a two-warehouse environment. International Journal of Production Economics, 176, 154–169.
Tiwari, S., Jaggi, C. K., Bhunia, A. K., Shaikh, A. A., & Goh, M. (2017). Two-warehouse inventory model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with stock-dependent demand and inflation using particle swarm optimization. Annals of Operations Research, 254(1–2), 401–423.
Wu, J., Al-khateeb, F. B., Teng, J. T., & Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E. (2016). Inventory models for deteriorating items with maximum lifetime under downstream partial trade credits to credit-risk customers by discounted cash-flow analysis. International Journal of Production Economics, 171(Part 1), 105–115.
Wu, J., Ouyang, L. Y., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., & Goyal, S. K. (2014). Optimal credit period and lot size for deteriorating items with expiration dates under two-level trade credit financing. European Journal of Operational Research, 237(3), 898–908.
Yue, D., & You, F. (2014). Game-theoretic modeling and optimization of multi-echelon supply chain design and operation under Stackelberg game and market equilibrium. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 71, 347–361.
Zhong, Y. G., & Zhou, Y. W. (2013). Improving the supply chain’s performance through trade credit under inventory-dependent demand and limited storage capacity. International Journal of Production Economics, 143(2), 364–370.
Zhou, Y. W., & Yang, S. L. (2005). A two-warehouse inventory model for items with stock-level-dependent demand rate. International Journal of Production Economics, 95(2), 215–228.
Zhou, Y. W., Zhong, Y., & Li, J. (2012). An uncooperative order model for items with trade credit, inventory-dependent demand and limited displayed-shelf space. European Journal of Operational Research, 223(1), 76–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaggi, C.K., Gupta, M., Kausar, A. et al. Inventory and credit decisions for deteriorating items with displayed stock dependent demand in two-echelon supply chain using Stackelberg and Nash equilibrium solution. Ann Oper Res 274, 309–329 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2925-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2925-9