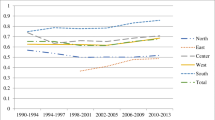
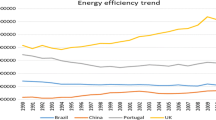
Abstract
In this paper, we review the energy efficiency in China, and the following topics are discussed. (i) Some useful empirical analyses applied on the energy efficiency based on some expanded models, (ii) the relationship among environment, energy and economic growth, (iii) some important environmental efficiency evaluation indexes, and (iv) some latest researches on the emission system. Finally, some policy recommendations are made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carbone, J., Helm, C., & Rutherford, T. (2009). The case for international emission trade in the absence of cooperative climate policy. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 58(3), 266–280.
Cheng, B. (1997). Energy consumption and economic growth in Brazil, Mexico and Venezuela: a time series analysis. Applied Economics Letters, 4(11), 671–674.
Chou, C., Chen, C., & Liu, H. (2000). Economic-statistical design of X charts for non-normal data by considering quality loss. Journal of Applied Statistics, 27(8), 939–951.
Ellerman, A., Buchner, B., & Carraro, C. (2007). Allocation in the European emissions trading scheme: rights, rents and fairness. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Esty, D., Levy, M., Srebotnjak, T., et al. (2005). Environmental sustainability index: benchmarking national environmental stewardship. Resource document, Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy. http://www.yale.edu/esi/.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., Lovell, C., et al. (1989). Multilateral productivity comparisons when some outputs are undesirable: a nonparametric approach. Review of Economics and Statistics, 71, 90–98.
Hu, J., & Wang, S. (2006). Total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy Policy, 34, 3206–3217.
Li, F., Dong, S., Li, X., et al. (2011). Energy consumption-economic growth relationship and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy, 39(2), 568–574.
Liu, W., Meng, W., Li, X., et al. (2010). DEA models with undesirable outputs. Annals of Operations Research, 173(1), 177–194.
Malueg, D., & Yates, A. (2009). Strategic behavior, private information, and decentralization in the European union emissions trading system. Environmental & Resource Economics, 43(3), 413–432.
Mohtadi, H. (1995). Public spending, political structure and growth: evidence for the Middle East and North Africa from an international perspective. Working papers 9506, Economic Research Forum.
Oh, W., & Lee, K. (2004). Causal relationship between energy consumption and GDP revisited: the case of Korea. Energy Economics, 26(1), 51–59.
Oueslati, W. (2002). Environmental policy in an endogenous growth model with human capital and endogenous labor supply. Economic Modelling, 19, 487–507.
Roberts, I. (1959). Control chart tests based on geometric moving averages. Technometrics, 1, 239–250.
Shephard, R. (1970). Theory of cost and production functions. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Shi, G., Bi, J., & Wang, J. (2010). Chinese regional industrial energy efficiency evaluation based on a DEA model of fixing non-energy inputs. Energy Policy, 38(10), 6172–6179.
Woerdman, E. (2000). Organizing emissions trading: the barrier of domestic permit allocation. Energy Policy, 8, 613–623.
Yuana, J. H., Kang, J. G., Zhao, C. H., & Hu, Z. G. (2008). Energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from China at both aggregated and disaggregated levels. Energy Economics, 30(6), 3077–3094.
Zaim, O. (2004). Measuring environmental performance of state manufacturing through changes in pollution intensities: a DEA framework. Ecological Economics, 48, 37–47.
Zha, D., Zhou, D., & Ding, N. (2009). The contribution degree of sub-sectors to structure effect and intensity effects on industry energy intensity. in China from 1993 to 2003. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 13, 895–902.
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by National Natural Science Funds of China for Innovative Research Groups (No. 70821001), National Natural Science Funds of China (Nos. 70901069, 71222106), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20133402110028) and Soft Science Research Fund of Shaanxi Province (No. 11020503021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Song, M. & Yang, L. Advances in energy and environmental issues in China: theory, models, and applications. Ann Oper Res 228, 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1528-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1528-3