Abstract
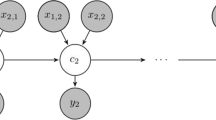
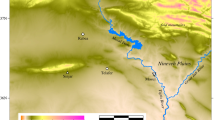
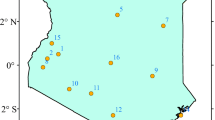
A reservoir in south east Queensland can supply irrigators, industry or domestic users. Stochastic inflow is modelled by a hidden state Markov chain, with three hidden states corresponding to prevailing climatic conditions. A stochastic dynamic program that relies on estimation of the hidden state is implemented. The optimal decisions are compared with those obtained if the hidden state Markov chain model is replaced with a model that relies on the Southern Oscillation Index to define prevailing climatic conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akintuğ, B., & Rasmussen, P. F. (2005). A Markov switching model for annual hydrologic time series. Water Resources Research, 41(9), W09424.
Baum, L. E., et al. (1970). A maximization technique occurring in the statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of Markov chains. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 41(1), 164–171.
Bayraktar, E., & Ludkovski, M. (2010). Inventory management with partially observed nonstationary demand. Annals of Operations Research, 176, 7–39.
Borkar, V. S. (1991). A remark on control of partially observed Markov chains. Annals of Operations Research, 29, 429–438.
Brown, B. W. (1965). On the iterative method of dynamic programming on a finite space discrete time Markov process. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 36(4), 1279–1285.
Cao, X.-R., & Guo, X. (2007). Partially observed Markov decision processes with reward information: basic ideas and models. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 52, 677.
David, I., et al. (1999). A simple suboptimal algorithm for system maintenance under partial observability. Annals of Operations Research, 25–40.
Edirisinghe, N. C. P., et al. (2000). Capacity planning model for a multipurpose water reservoir with target-priority operation. Annals of Operations Research, 100, 273–303.
Fisher, A. J., et al. (2010). Managing river flows in arid regions with matrix analytic methods. Journal of Hydrology, 382, 128–137.
Himmelmann, L. (2010). HMM—Hidden Markov models. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/HMM/index.html.
Lovejoy, W. S. (1991). A survey of algorithmic methods for partially observed Markov decision processes. Annals of Operations Research, 28, 47–66.
R Development Core Team (2011). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov-models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77, 257–286.
Webby, R. B., et al. (2009). Modelling water blending-sensitivity of optimal policies. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 14(6), 749–757.
Whiting, J. P., et al. (2003). Modelling persistence in annual Australian point rainfall. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 7(2), 197–211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ALIO-INFORMS Joint International 2010, Buenos Aires.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisher, A., Green, D. & Metcalfe, A. Modelling of hydrological persistence for hidden state Markov decision processes. Ann Oper Res 199, 215–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-0992-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-0992-2