Abstract
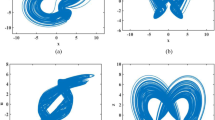
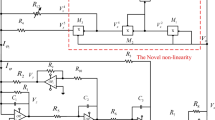
In the present contribution, we design a novel chaotic circuit with a symmetrical nonlinear component by replacing the single semiconductor diode in the original circuit by [Namajunas & Tamasevicius, 1995] with a pair of diodes connected in antiparallel. By exploiting the Shockley diode equation and adopting a judicious choice of state variables, we derive a smooth (i.e. with hyperbolic nonlinearities) mathematical model to investigate both the regular and chaotic dynamics of the novel RC oscillator. In addition to the familiar period-doubling bifurcations already observed in previous versions of the same oscillator, the novel oscillator exhibits more interesting dynamical properties including for instance, symmetry breaking bifurcation, merging crisis and coexisting multiple attractors as well. Interestingly, one of the most gratifying (and rare) features of the new circuit is the occurrence of both bubbles and reverse bubbles of bifurcation for some suitable parameter ranges. An excellent agreement is observed between theoretical and experimental results. The model is digitalized for digital image encryption. First the Hahn orthogonal moments of each pixel of the plain image is computed, and then Knuth permutation algorithm is combined to chaotic sequences to scramble the resulting image in the transform domain. Finally, the permuted image will be diffused using the pseudo random chaotic sequences. Security analysis indicates good performances of the model to encrypt and decrypt digital images.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L. (1993). A universal circuit for studying and generating chaos-part II: Stange attractors. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 40(10), 182–186.
Chen, M., Li, M., Yu, Q., Bao, B., Xu, Q., & Wang, J. (2015). Dynamics of self-excited attractors and hidden attractors in generalized memristor-based Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dynamics, 81(1), 215–226.
Tsafack, N., & Kengne, J. (2019). Complex dynamics of the chua’s circuit system with adjustable symmetry and nonlinearity: multistability and simple circuit realization. World Journal of Applied Physics, 4(2), 24–34.
Duffing, G. (1918). Erzwungene Schwingungen bei veränderlicher Eigenfrequenz und ihre technische Bedeutung (No. 41–42). Vieweg.
B. Van der Pol. "LXXXVIII. On “relaxation-oscillations”," The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, vol. 2, no. 11, pp. 978–992.
Sprott, J. C. (2000). Simple chaotic systems and circuits. American Journal of Physics, 68(8), 758–763.
Nestor, T., De Dieu, N. J., Jacques, K., Yves, E. J., Iliyasu, A. M., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2019). A multidimensional hyperjerk oscillator: Dynamics analysis, analogue and embedded systems implementation, and its application as a cryptosystem. Sensors, 20(1), 83.
Maggio, G. M., Di Bernardo, M., & Kennedy, M. P. (2000). Nonsmooth bifurcations in a piecewise-linear model of the Colpitts oscillator. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 47(8), 1160–1177.
GM Maggio, O De Feo, and MP Kennedy Nonlinear analysis of the Colpitts oscillator and applications to design. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications 46(9): 1118–1130.
Tchitnga, R., Fotsin, H. B., Nana, B., Fotso, P. H. L., & Woafo, P. (2012). Hartley’s oscillator: the simplest chaotic two-component circuit. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 45(3), 306–313.
Cuomo, K. M., Oppenheim, A. V., & Strogatz, S. H. (1993). Synchronization of Lorenz-based chaotic circuits with applications to communications. IEEE Transactions on circuits and systems II: Analog and digital signal processing, 40(10), 626–633.
Swathy, P., Sabarathinam, S., Suresh, K., & Thamilmaran, K. (2014). Chaos synchronization and transmission of information in coupled SC-CNN-based canonical Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dynamics, 78(2), 1033–1047.
Volos, C. K., Kyprianidis, I. M., & Stouboulos, I. N. (2013). Image encryption process based on chaotic synchronization phenomena. Signal Processing, 93(5), 1328–1340.
Tsafack, N., Kengne, J., Abd-El-Atty, B., Iliyasu, A. M., Hirota, K., Abd, A. A., & EL-Latif,. (2020). Design and implementation of a simple dynamical 4-D chaotic circuit with applications in image encryption. Information Sciences, 515, 191–217.
Djimasra, F., Nkapkop, J. D. D., Tsafack, N., et al. (2021). Robust cryptosystem using a new hyperchaotic oscillator with stricking dynamic properties. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(16), 1–17.
R Modeste Nguimdo, R Tchitnga, and P Woafo (2013) Dynamics of coupled simplest chaotic two-component electronic circuits and its potential application to random bit generation. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 23(4): 43122.
Fortuna, L., Frasca, M., & Rizzo, A. (2003). Chaotic pulse position modulation to improve the efficiency of sonar sensors. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 52(6), 1809–1814.
Tamang, J., Nkapkop, J. D. D., Ijaz, M. F., et al. (2021). Dynamical properties of ion-acoustic waves in space plasma and its application to image encryption. IEEE Access, 9, 18762–18782.
Njitacke, Z. T., Isaac, S. D., Nestor, T., & Kengne, J. (2021). Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3D Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Computing and Applications, 33(12), 1–20.
Tsafack, N., Sankar, S., Abd-El-Atty, B., et al. (2020). A new chaotic map with dynamic analysis and encryption application in internet of health things. IEEE Access, 8, 137731–137744.
Belazi, A., Abd El-Latif, A. A., & Belghith, S. (2016). A novel image encryption scheme based on substitution-permutation network and chaos. Signal Processing, 128, 155–170.
Abd-El-Atty, B., Iliyasu, A. M., Alanezi, A., & Abd El-latif, A. A. (2021). Optical image encryption based on quantum walks. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 138, 106403.
Alhadawi, H. S., Majid, M. A., Lambić, D., & Ahmad, M. (2020). A novel method of S-box design based on discrete chaotic maps and cuckoo search algorithm. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(5), 7333–7350.
Razaq, A., Ahmad, M., Yousaf, M. A., & Masood, S. (2021). A novel finite rings based algebraic scheme of evolving secure S-boxes for images encryption. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(11), 1–25.
Ravichandran, D., Murthy, B., Balasubramanian, V., Fathima, S., & Amirtharajan, R. (2021). An efficient medical image encryption using hybrid DNA computing and chaos in transform domain. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 59(3), 589–605.
Namajunas, A., & Tamasevicius, A. (1996). Simple RC chaotic oscillator. Electronics letters, 32(11), 945–946.
Kengne, J. (2015). Coexistence of chaos with hyperchaos period-3 doubling bifurcation and transient chaos in the hyperchaotic oscillator with gyrators. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 25(4), 1550052.
Namajunas, A., & Tamasevicius, A. (1995). Modified Wien-bridge oscillator for chaos. Electronics letters, 31(5), 335–336.
Morgul, O. (1995). Inductorless realisation of Chua oscillator. Electronics letters, 31(17), 1403–1404.
Sprott, J. C. (2011). A new chaotic jerk circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 58(4), 240–243.
Banerjee, T. (2011). Single amplifier biquad based inductor-free Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dynamics, 68(4), 565–573.
Hanias, M., Giannaris, G., Spyridakis, A., & Rigas, A. (2006). Time series analysis in chaotic diode resonator circuit. Chaos Solitons & Fractals, 27(2), 569–573.
DW Sukow, ME Bleich, DJ Gauthier, and JE Socolar (1997) Controlling chaos in a fast diode resonator using extended time-delay autosynchronization: Experimental observations and theoretical analysis. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 7(4): 560–576.
Strogatz, S. H. (2018). Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: With applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering. CRC Press.
Wolf, A., Swift, J. B., Swinney, H. L., & Vastano, J. A. (1985). Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 16(3), 285–317.
Kengne, J., Chedjou, J., Kom, M., Kyamakya, K., & Tamba, V. K. (2014). Regular oscillations chaos and multistability in a system of two coupled van der Pol oscillators: numerical and experimental studies. Nonlinear Dynamics, 76(2), 1119–1132.
Murali, K., & Lakshmanan, M. (1992). Effect of sinusoidal excitation on the Chua’s circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Part I: Regular Papers, 39(4), 264–270.
A. Rukhin, J. Soto, J. Nechvatal, et al. "A statistical test suite for random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications,” NIST Special Publication 800–22 (revised May 15)
J. Zhou, H. Shu, H. Zhu, C. Toumoulin, and L. Luo, "Image analysis by discrete orthogonal Hahn moments," In: International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition 524–531: Springer: 2005.
Chai, X., Wu, H., Gan, Z., Han, D., Zhang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2021). An efficient approach for encrypting double color images into a visually meaningful cipher image using 2D compressive sensing. Information Sciences, 556, 305–340.
Ye, G., Pan, C., Dong, Y., Jiao, K., & Huang, X. (2021). A novel multi-image visually meaningful encryption algorithm based on compressive sensing and Schur decomposition. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32(2), e4071.
Ma, K., Teng, L., Wang, X., & Meng, J. (2021). Color image encryption scheme based on the combination of the fisher-yates scrambling algorithm and chaos theory. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(16), 1–21.
Wu, X., Wang, K., Wang, X., Kan, H., & Kurths, J. (2018). Color image DNA encryption using NCA map-based CML and one-time keys. Signal Processing, 148, 272–287.
Kaur, M., Singh, D., Sun, K., & Rawat, U. (2020). Color image encryption using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm with local chaotic search based 5D chaotic map. Future Generation Computer Systems, 107, 333–350.
Abuturab, M. R. (2020). A superposition based multiple-image encryption using fresnel-domain high dimension chaotic phase encoding. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 129, 106038.
Abd, A. A., & EL-Latif, B Abd-El-Atty, and SE Venegas-Andraca,. (2020). Controlled alternate quantum walk-based pseudo-random number generator and its application to quantum color image encryption. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 547, 123869.
Chai, X., Fu, X., Gan, Z., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., & Chen, Y. (2018). An efficient chaos-based image compression and encryption scheme using block compressive sensing and elementary cellular automata. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(9), 4961–4988.
Chai, X., Bi, J., Gan, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2020). Color image compression and encryption scheme based on compressive sensing and double random encryption strategy. Signal Processing, 176, 107684.
Gan, Z., Chai, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2020). An effective image compression–encryption scheme based on compressive sensing (CS) and game of life (GOL). Neural Computing and Applications, 32(17), 14113–14141.
Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Han, S., Wei, X., & Wan, X. (2021). Multiple-image encryption based on light-field imaging and gravity model. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 141, 106565.
Zou, C., Zhang, Q., Wei, X., & Liu, C. (2020). Image encryption based on improved Lorenz system. IEEE Access, 8, 75728–75740.
Funding
This work is partially funded by Centre for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology, India vide funding number CIT/CNS/2021/RD/022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramadoss, J., Kengne, J., Telem, A.N.K. et al. Chaos in a novel Wien bridge-based RC chaotic oscillator: dynamic analysis with application to image encryption. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 112, 495–516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-022-02061-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-022-02061-8