Abstract
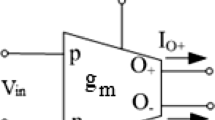
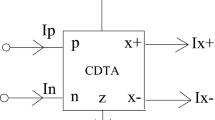
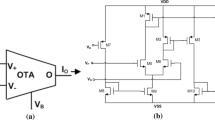
In this paper a robust design of a dual mode grounded memristor using single output operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) and differential voltage current conveyor (DVCC) has been reported. The reported memristor emulator design features a 50 mV operating voltage and a 1 MHz operating frequency, making it most appropriate for low-power and high-frequency applications. The presented memristor emulator design employs Cadence Virtuoso 0.18 µm CMOS technology, our reported emulator is validated by both theoretical and simulation results. By adjusting the DVCC's input voltage, the emulator can be set to work in both incremental and decremental mode. The proposed memristor has demonstrated improved performance in terms of band-width and tunability after sensitivity study of various parameters variability such as process variation, capacitor, and frequency variation, etc.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L. O. (1971). Memristor—The missing circuit element. IEEE Transaction on Circuit Theory, 18(5), 507–519.
Strukov, D. B., Stewart, G. S., & Williams, R. S. (2008). The missing memristor found. Nature Letters, 453, 80–83.
Wang, X., & Chen, Y. (2010). Spintronic memristor device and application. In Proceedings of design, automation and text in Europe conference and exhibition (pp. 667–674).
Valov, I., & Kozicki, M. (2017). Organic memristors come of age. Nature Materials, 16, 1170–1172.
Chanthbouala, A., Garcia, V., Cherifi, R. O., Bouzehouane, K., Fusil, S., Moya, X., Xavier, S., Yamada, H., Deranlot, C., Mathur, N. D., Bibes, M., Barthelemy, A., & Grollier, J. (2012). A ferroelectric memristor. Nature Materials, 11, 86–864.
Elwakil, A. S., Fouda, M. E., & Radwan, A. G. (2013). a simple model of double loop hysteresis behavior in memristive elements. IEEE Transaction on Circuits System II, 60(8), 487–491.
Pershin, Y. V., & Di Ventra, M. (2012). Neuromorphic, digital and quantum computation with memory circuit elements. Proceedings of the IEEE, 100(6), 2071–2080.
Sung, H., Chang, T., Ebong, I., Bhadviya, B. B., Mazumder, P., & Lu, W. (2010). Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Letters, 10(4), 1297–1301.
Shin, S., Kim, K., & Kang, S. M. (2010). Memristor applications for programmable analog ICs. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 10(2), 266–274.
Wang, F. Z., et al. (2013). Adaptive neuromorphic architecture (ANA). Neural Networks, 45, 111–116.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2018). Design and experimental evolution of memristor with only one VDTA and one capacitor. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 99, 1–9.
Hussein, A., & Fouda, M. E. (2013). A simple MOS realization of current controlled memristor emulator. In IEEE 2013 25th international conference on microelectronics (ICM) (pp. 1–4).
Pal, I., Kumar, V., Aishwarya, N., Nayak, A., & Islam, A. (2019). A VDTA-based robust electronically tunable memristor emulator circuit. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 1–13.
Babacan, Y., Yesil, A., & Kacar, F. (2017). Memristor emulator with tunable characteristic and its experimental results. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 81, 99–104.
Ibrayev, T., Fedorova, I., Maan, A. K., & James, A. P. (2014). Memristive operational amplifiers. Procedia Computer Science, 41, 114–119.
Cheng, K. T. T., & Strukov, D. B. (2012). 3D CMOS-memristor hybrid circuits: Devices, integration, architecture, and applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM international symposium on international symposium on physical design (pp. 33–40).
Cong, J., & Xiao, B. (2011). A novel FPGA architecture with memristor-based reconfiguration. In 2011 IEEE/ACM international symposium on nanoscale architectures (pp. 1–8).
Ranjan, R. K., Sharma, P. K., Sagar, N., Kumari, R. B., & Khateb, F. (2019). Memristor emulator circuit using multiple-output OTA and Its experimental results. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 28(10), 1950166.
Yesil, A. (2019). Floating memristor employing single MO-OTA with hard-switching behaviour. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 28(02), 1950026.
Lee, S. Y., Wang, C. P., & Chu, Y. S. (2018). Low-voltage OTA–C filter with an area-and power-efficient OTA for biosignal sensor applications. IEEE transactions on biomedical circuits and systems, 13(1), 56–67.
Cini, U., & Toker, A. (2017). DVCC-based very low-offset current-mode instrumentation amplifier. International Journal of Electronics, 104(8), 1346–1357.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2020). An electronically controllable, fully floating memristor based on active elements: DO-OTA and DVCC. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 153315.
Mishra, S. K., Gupta, M., & Upadhyay, D. K. (2020). Active realization of fractional order Butterworth lowpass filter using DVCC. Journal of King Saud University-Engineering Sciences, 32(2), 158–165.
Yesil, A., Babacan, Y., & Kacar, F. (2019). “Electronically tunable memristor based on VDCC. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 107, 282–290.
Davis, W. R., Wilson, J., Mick, S., Xu, J., Hua, H., Mineo, C., Sule, A. M., & Steer, M. (2005). Demystifying 3D ICs: the pros and cons of going vertical. In IEEE design & test of computers (Vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 498–510). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MDT.2005.136.
Dongaonkar, S., Mudanai, S. P., & Giles, M. D. (2018). From process corners to statistical circuit design methodology: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 66(1), 19–27.
Cao, P., Bao, W., & Guo, J. (2020). An accurate and efficient timing prediction framework for wide supply voltage design based on learning method. Electronics, 9(4), 580.
Kumar, R., & Kursun, V. (2006). Impact of temperature fluctuations on circuit characteristics in 180nm and 65nm CMOS technologies. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 1–5).
Rasekh, A., & Bakhtiar, M. S. (2017). Design of low-power low-area tunable active RC filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 65(1), 6–10.
Compassi-Severo, L., & Van Noije, W. (2019). A 0.4-V 10.9-µ W/pole third order complex BPF for low energy RF receivers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 66(6), 2017–2026.
Lee, S. Y., Wang, C. P., & Chu, Y. S. (2018). Low-voltage OTA-C filter with an area-and power-efficient OTA for biosignal sensor applications. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 13(1), 56–67.
Ranjan, R. K., Sagar, S., Roushan, S., Kumari, B., Rani, N., & Khateb, F. (2019). High-frequency floating memristor emulator and its experimental results. IET Circuits, Devices and Systems, 13(3), 292–302.
Xie, X., Zou, L., Wen, S., Zeng, Z., & Huang, T. (2019). A flux-controlled logarithmic memristor model and emulator. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 38(4), 1452–1465.
Sánchez-López, C., & Aguila-Cuapio, L. E. (2017). A 860 kHz grounded memristor emulator circuit. AEU-International Journal of Electronic and Communications, 73, 23–33.
Ayten, U. E., Minaei, S., & Sağbaş, M. (2017). Memristor emulator circuits using single CBTA. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 82, 109–118.
Yadav, N., Rai, S. K., & Pandey, R. (2020). New grounded and floating memristor emulators using OTA and CDBA. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications .
Petrović, P. B. (2018). Floating incremental/decremental flux-controlled memristor emulator circuit based on single VDTA. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 96(3), 417–433.
Ranjan, R. K., Raj, N., Bhuwal, N., & Khateb, F. (2017). Single DVCCTA based high frequency incremental/decremental memristor emulator and its application. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 82, 177–190.
Yu, D., Zheng, C., Iu, H. H. C., Fernando, T., & Chua, L. O. (2017). A new circuit for emulating memristors using inductive coupling. IEEE Access, 5, 1284–1295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, A., Singh, S. & Kumar, P. Dual mode, high frequency and power efficient grounded memristor based on OTA and DVCC. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 110, 81–89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01949-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01949-1