Abstract
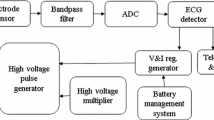
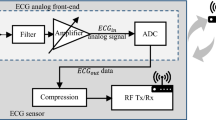
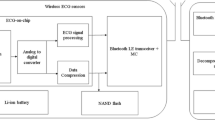
This paper describes a novel sinusoidal signal generator for thoracic bioimpedance measurement system and signals decomposition filter, based on an analog wavelet filter approach. The proposed system can be adjusted in amplitude, frequency, and phase for differents sinusoidal injection currents, presenting a harmonic distortion rate lower than \(1.4\, \%\) and a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of \(\mathrm {36.67\,dB}\). Applying the proposed sinusoidal generator to a bioimpedance measurement system (TEB), the obtained recovery accuracy was \(\mathrm {0.11\,\mathrm \Omega _{rms}}\). Also, an analog wavelet filter approach was implemented on a new design of a TEB decomposing system, in order to extract its cardiac and respiratory components. From a system validation of the TEB decomposer, it was able to recover efficiently the cardiac and respiratory signals with a root mean square error (RMSE) below \(\mathrm {92.73\,m\mathrm \Omega _{rms}}\), even under dynamic variations of its parameters over time. Finally, previous works indicate that the proposed analog wavelet filter system can be implemented using a ultra low-power circuit design techniques, which allows its use in implantable systems such as pacemakers.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. (2018). World health statistics 2018: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO., 2018. [Online]. Available: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/272596
Rezaeiyan, Y., Zamani, M., Shoaei, O., & Serdijn, W. A. (2018). Mixed-signal IC with pulse width modulation wireless telemetry for implantable cardiac pacemakers in 0.18-\(\mu\)m CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 12(3), 589–600.
Zamani, M., Rezaeiyan, Y., Shoaei, O., & Serdijn, W. A. (2018). A 1.55 \(\mu\)W bio-impedance measurement system for implantable cardiac pacemakers in 0.18 \(\mu\)m CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 12(1), 211–221.
I. 60601-1, (2015). Medical electrical equipment—Part 1-11: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance. Standard, International, p. 109.
Hong, S. K., & Jee, D. W. (2019). A 0.052 mm2, <0.4% THD, Sinusoidal current generator for bio-Impedance measurement using a recursive digital oscillator and current-domain FIR Filter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 66(6), 894–898.
Yan, L., Bae, J., Lee, S., Roh, T., Song, K., & Yoo, H. J. (2011). A 3.9 mW 25-electrode reconfigured sensor for wearable cardiac monitoring system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(1), 353–364.
Nawito M., Richter., H., & Burghartz., J. N.,(2016). Compact wide-range sinusoidal signal generator for in vivo impedance spectroscopy. In 2015 Conference on Design of Circuits and Integrated Systems (DCIS), No. 978, (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Leal, G. T., & Haddad, S. A. P. (2020). The use of the analog wavelet filter to generate a sinusoidal signal and decompose chest bioimpedance in an implantable cardiac pacemaker. Conference on Symposium on Integrated Circuits and Systems Design, SBCCI, 2020, 1–6.
Krivoshei, A. (2006) A bio-impedance signal synthesiser (BISS) for testing of an adaptive filtering system. In 2006 International Biennial Baltic Electronics Conference, (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Long Yan, J., Pettine, S. Mitra., Kim, Sunyoung, Jee, Dong-Woo., Hyejung Kim, M., Osawa, Y., et al. (2013). A 13 \(\mu\)A Analog signal processing IC for accurate recognition of multiple intra-cardiac signals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 7(6), 785–795.
Krivoshei, A., Kukk, V., & Min, M. (2008). An adaptively tunable model of the cardiac signal for the bio-impedance signal decomposer (BISD). In 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Medical Measurements and Applications Proceedings, MeMeA, No. 1, (pp. 49–52). IEEE.
Yazicioglu, R. F., Kim, S., Torfs, T., Kim, H., & Hoof, C. V. (2011). A 30 \(\mu\)W Analog signal processor ASIC for portable biopotential signal monitoring. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(1), 209–223.
Wei, Chia-Ling., Wang, Yi-Wen., & Liu, Bin-Da. (2013). Wide-range filter-based sinusoidal wave synthesizer for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 8(3), 442–450.
Min, M., & Parve, T. (2007). Improvement of lock-in electrical bio-impedance analyzer for implantable medical devices. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 56(3), 968–974.
Biniyam, A., Tesema, A. G., Mohammed, A. A., Ramaiah, N. S., & Dilla, A. E. (2017). Design and implementation of heart beat monitoring using PIC microcontroller. In 2017 International Conference On Smart Technologies For Smart Nation (SmartTechCon), (pp. 784–787). IEEE.
Rodríguez-Molinero, A., Narvaiza, L., Ruiz, J., & Gálvez-Barrón, C. (2013). Normal respiratory rate and peripheral blood oxygen saturation in the elderly population. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 61(12), 2238–2240.
Belalcazar, A., Patterson, R. & Shult, R. (2007). Impedance monitoring for detecting pulmonary edema and thoracic congestion. p. 20. [Online]. Available: https://patents.google.com/patent/US7313434
Min, M., Parve, T., & Kink, A. (1999). Thoracic bioimpedance as a basis for pacing control. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 873, 155–166.
Kassanos, P., Constantinou, L., Triantis, I. F., & Demosthenous, A. (2013). A CMOS magnitude/phase measurement chip for impedance spectroscopy. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(6), 2229–2236.
Kassanos, P., & Yang, G. Z. (2018). A CMOS programmable phase shifter for compensating synchronous detection bioimpedance systems. In 2017 24th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Vol. 2018, (pp. 218–221). IEEE.
Krivoshei, A., Min, M., Annus, P., & Butsenko M. (2018). Decomposition of the EBI signal into components using two channel cross-compensating singular spectrum analysis. In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), No.18051943, (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Martens, O., Min, M., Member, S., Annus, P., Land, R., Krivoshei, A., Metshein, M., (2018). PLL-based extraction of the cardiac component from the bio-impedance signal. In 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Karel, J. M. H., Haddad, S. A. P., Hiseni, S., Westra, R. L., Serdijn, W. A., & Peeters, R. L. M. (2012). Implementing wavelets in continuous-time analog circuits with dynamic range optimization. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 59(2), 229–242.
Haddad, S. A. P., Karel, J. M. H., Peeters, R. L. M., Westra R. L., & Serdijn, W. A. (2005). Analog complex wavelet filters. In 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems No. 4, (pp. 3287–3290). IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Acknowledgment to the Federal Institute of Mineiro Triangle (IFTM) for supporting the development of this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leal, G.T., de Moura Rodrigues, G.M. & Haddad, S.A.P. A sinusoidal current generator and a TEB decomposer for measuring bioimpedance in a cardiac pacemaker, using an analog wavelet filter. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 108, 525–538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01896-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01896-x