Abstract
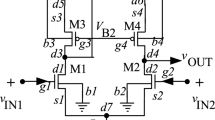
A tunable low-pass Gm-C filter with 1 GHz cutoff frequency is presented. The core of this filter is a high frequency low voltage operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) in which CMOS inverters are used. For enhancing the linearity of the filter, a novel common mode feedforward circuit is merged with a common mode feedback circuit. Moreover, in this paper, a new tuning circuit is presented for tuning transconductance in order to compensate effects of elements mismatch and temperature variations on OTA. Accordingly, the cutoff frequency is compensated by the bulk voltage tuning, while this circuit is less complex and consumes low power. The circuit is designed and simulated using TSMC 90 nm CMOS technology and a 1 V power supply. The results of simulation show that the DC differential gain, − 3 dB cutoff frequency and the unity-gain frequency of OTA are 37.7 dB, 325 MHz and 25 GHz, respectively. After applying two-tone input voltages 0.2 Vp-p, the IM3 value of the filter at 1 GHz is − 36 dB. The filter consumes 8 mW of power and occupies an area of 0.113 mm × 0.144 mm.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suadet, A., & Kasemsuwan, V. (2013). A CMOS inverter-based class-AB pseudo-differential amplifier with current-mode common-mode feedback (CMFB). Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 24(2), 387–398.
Algueta Miguel, J. M., de la Cruz Blas, C. A., & Lopez-Martin, A. J. (2010). CMOS triode transconductor based on quasi-floating-gate transistors. Electronics Letters, 46(17), 1190–1191.
Rezaei, F., & Azhari, S. J. (2011). Ultra low voltage, high performance operational transconductance amplifier and its application in a tunable Gm-C filter. Microelectronics Journal, 42, 827–836.
Ismail, A., & Mostafa, I. (2016). A process-tolerant, low-voltage, inverter-based OTA for continuous-time ∑–∆ ADC. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 24(9), 2911–2917.
Fahmideh Akbarian, S. M., Lotfi, R., & Maymandi-Nejad, M. (2013). Low-voltage low-power Gm-C filters: A modified configuration for improving performance. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 74(1), 297–302.
Lo, T. Y., & Hung, C. C. (2011). A 1 GHz equiripple low-pass filter with a high-speed automatic tuning scheme. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 19(2), 175–181.
Dosho, S., Morie, T., & Fujiyama, H. (2002). A 200 MHz seventh-order equiripple continuous-time filter by design of nonlinearity suppression in 0.25 µm CMOS process. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(5), 559–565.
Soares, C. F. T., Moraes, G. S., & Petraglia, A. (2014). A low-transconductance OTA with improved linearity suitable inverters operating from 1-V power supply for low-frequency Gm-C filters. Microelectronics Journal, 45, 1499–1507.
Sun, C.-Y., & Lee, S.-Y. (2018). A fifth-order butterworth OTA-C LPF with multiple-output differential-input OTA for ECG applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 65(4), 421–425.
Sharan, T., Chetri, P., & Bhadauria, V. (2018). Ultra-low-power bulk-driven fully differential subthreshold OTAs with partial positive feedback for Gm-C filters. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 94(3), 427–447.
Yang, S.-H., Kim, K.-H., Kim, Y.-H., You, Y., & Cho, K.-R. (2005). A novel CMOS operational transconductance amplifier based on a mobility compensation technique. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 52(1), 37–42.
Zheng, Y., & Saavedra, C. E. (2008). Feedforward-regulated cascode OTA for gigahertz applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 55(11), 3373–3382.
Rezaei, F., & Azhari, S. J. (2015). A new controllable adaptive biasing linearization technique for a CMOS OTA and its application to tunable Gm-C filter design. Microelectronics Journal, 46, 810–818.
Yodtean, A., & Thanachayanont, A. (2013). Sub 1-V highly-linear low-power class-AB bulk-driven tunable CMOS transconductor. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 75(3), 383–397.
Elamien, M. B., & Mahmoud, S. A. (2018). On the design of highly linear CMOS digitally programmable operational transconductance amplifiers for low and high-frequency applications. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 97(2), 225–241.
Geiger, R. L., & Sinencio, E. S. (1985). Active filter design using operational transconductance amplifiers: A tutorial. IEEE Circuits and Devices Magazine, 1, 20–32.
Jusung, K., & Silva-Martinez, J. (2013). Low-power, low-cost CMOS direct-conversion receiver front-end for multi standard applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(9), 2090–2103.
Nauta, B. (1992). A CMOS transconductance-C filter technique for very high frequencies. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 27(2), 142–153.
Tanimoto, H., Yazawa, K., & Haraguchi, M. (2014). A fully-differential OTA based on CMOS cascode inverters operating from 1-V power supply. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 78(1), 23–31.
Zhou, M., & Wang, K. (2018). 0.18 mW/pole inverter-based Gm-C bandpass filter with automatic frequency tuning. Electronics Letters, 54(15), 943–945.
Barthelemy, H., Meillere, S., Gaubert, J., Dehaese, N., & Bourdel, S. (2008). OTA based on CMOS inverters and application in the design of the tunable bandpass filter. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 57(3), 169–178.
Hwang, Y. S., Shen, J. H., Chen, J. J., & Fan, M. R. (2014). A THD-reduction high-efficiency audio amplifier using inverter-based OTAs with filter-output feedback. Microelectronics Journal, 45, 102–109.
Christen, T. (2012). A 15 bit 140 μW scalable-bandwidth inverter-based audio∑–∆ modulator with > 78 dB PSRR. In Proceedings of ESSCIRC (pp. 209–212).
Luo, H., Han, Y., Cheung, R. C. C., Liu, X., & Cao, T. (2013). A 0.8-V 230-μW 98-dB DR inverter-based ∑–∆ modulator for audio applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(10), 2430–2441.
Essawy, A., & Ismail, A. (2014). A low voltage inverter-based continuous-time sigma delta analog-to-digital converter in 65 nm CMOS technology. In: Proceedings of IEEE Faible Tension Faible Consommation (FTFC) (pp. 1–4).
Alaybeyoglu, E., & Kuntman, H. (2018). A new implementation of the reconfigurable analog baseband low pass filter with cell-based variable transconductance amplifier. Springer, Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 97(1), 87–96.
Silva-Martínez, J., Adut, J., Rocha-Perez, J. M., Robinson, M., & Rokhsaz, S. (2003). A 60 mW, 200 MHz continuous-time seventh-order linear phase filter with on-chip automatic tuning system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(2), 216–225.
Pandey, P., Silva-Martinez, J., & Liu, X. (2006). A CMOS 140-mW fourth-order continuous-time low-pass filter stabilized with a class AB common-mode feedback operating at 550 MHz. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 53(4), 811–820.
Lechevallier, J., Struiksma, R., Sherry, H., Catheli, A., Klumperink, E., & Nauta, B. (2015). A forward-body-bias tuned 450 MHz Gm-C 3rd-order low-pass filter in 28 nm UTBB FD-SOI with > 1 dBVp IIP3 over a 0.7-to-1 V Supply. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers.
Sarrafinazhad, A., Kara, I., & Baskaya, F. (2015). Design of a digitally tunable 5th order Gm-C filter using linearized OTA in 90 nm CMOS technology. In IEEE International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems (ISSCS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdolmaleki, M., Dousti, M. & Tavakoli, M.B. Design and simulation of tunable low-pass Gm-C filter with 1 GHz cutoff frequency based on CMOS inventers for high speed telecommunication applications. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 100, 279–286 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01484-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01484-0